 Website:
ZwickRoell GmbH & Co. KG
Website:
ZwickRoell GmbH & Co. KG
Grupo: ZwickRoell Group
Excertos do catálogo

FP 303 2.0509 Hardness Testing with Zwick Intelligent testing
Abrir o catálogo na página 1
3 The Zwick Roell Group – Over a Hundred Years of Materials Testing Experience Mechanical testing is the oldest branch of materials testing and one which has continued to gain in importance. As early as the 15th and 16th centuries, Leonardo da Vinci and Galileo Galilei were considering matters such as the bending load and elastic properties of materials. The first such testing machines appeared in France in the middle of the 18th century. The Swiss, later German company Amsler began materials testing in the mid-19th century, followed by Roell & Korthaus in 1920, while mechanical-testing...
Abrir o catálogo na página 3
4 Innovative Hardness Testing Zwick has been supplying stationary hardness testing devices for all standardized methods for many years, plus a wide range of portable hardness testers. Through our active involvement in national and international standards committees we are helping to shape modern, innovative hardness testing – for both today and tomorrow. Our hardness testing portfolio has been considerably expanded, especially during the last few years. The Zwick Roell Group probably has the most comprehensive selection of hardness testing machines and instruments available – for almost any...
Abrir o catálogo na página 4
5 Fig. 1: Overview of hardness testing methods Hardness Testing – Basic Principles, Methods and Standards Basic Principles Around 1900 Martens proposed the following definition: “Hardness is the resistance of a body to penetration by a second (harder) body.” This simple, graphic definition became accepted in technical circles and is still used today. Technical hardness is a mechanical characteristic used to describe a material or the state of a material. Hardness cannot be measured directly, but is derived from primary measured variables including: • Test load • Indentation depth •...
Abrir o catálogo na página 5
6 For metals, methods involving static force application are usually employed. An indentor (ball, cone or pyramid) made of steel, hard metal or diamond is pressed into a specimen supported on a firm base. The test load is applied perpendicularly, without shock, and with a defined initial application time and duration. With many test methods, the indentation is measured after removal of the load. The length measurement values (indentation depth, diagonals, diameter) are used to calculate the hardness value. Fig. 2: Zwick/ZHU0.2/Z2.5 universal hardness testing machine with HU measuring head,...
Abrir o catálogo na página 6
7 Hardness Testing Methods and Standards Rockwell Hardness Testing (A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, K, N, T) Measured quantity Rockwell hardness HR. Indentation depth h in mm Definition HR = N - h/S N ... numerical value (specified for each Rockwell method) h ... indentation depth difference in mm S ... scale value in mm. This value is the change in indentation in mm corresponding to one Rockwell unit. Explanation of test result display: e.g. 61,2 HRC Code letter for selected Rockwell method Code letters for Rockwell hardness Hardness value Advantages • Test requires little time as the hardness...
Abrir o catálogo na página 7
8 Knoop Hardness Testing Measured value Knoop hardness HK. Length of long diagonals from residual test indentation measured. Definition HK = 0.102 F/A = 1.451 F/d² F ... test load in N A ... projection area of test indentation in mm² d ... length of long diagonals in mm Brinell Hardness Testing Measured value Brinell hardness HB. Two diameters (at right angles) of the residual indentation in the specimen surface are measured. Definition HB = 0.102 F/A F ... test load in N A ... indentation surface in mm² D ... Ø of ball indentor in mm d ... arithmetical average of two measured indentation...
Abrir o catálogo na página 8
9 hp hr hmax h Fmax F a c b 1 2 3 hp hc hmax Instrumented Indentation Testing (Martens) Measured value Test load and associated (synchronous) indentation depth during loading and load removal are measured. Definition 1 indentor 2 surface of residual plastic indentation in specimen 3 surface of indentation at maximum indentation depth and test load a test load application b test load removal c tangent to curve b at Fmax This testing method is also referred to as an instrumented test to determine hardness and other materials parameters. The result of the test is the continuous...
Abrir o catálogo na página 9
10 Modified Brinell HBT Method Measured value Modified Brinell hardness HBT. Indentation depth difference h from test indentation under pre-load measured in mm. Definition HBT = hardness value, converted from indentation depth using a reference specimen. Explanation of test result display: e.g. 205 HBT 10/3000 calibration method for reference specimen code letters for test method hardness value Advantages • Only short time required for test, as hardness value can be read off / is displayed directly following the indentation • Capable of automation • No operator influence -hardness value...
Abrir o catálogo na página 10
11 Rebound Hardness Test Measured values Rebound hardness. Impact velocity va and rebound velocity vr (or height) of impact body are measured. Definition Rebound hardness = c · vr / va c ... constant vr ... rebound velocity of impact body va ... impact velocity of impact body Explanation of test result display: e.g. 540 HL code letters for rebound hardness hardness value Advantages • Portable device, simple to operate • Automatic test sequence; very short test time • Testing in any position, e.g. overhead measurement possible using correction factors Disadvantages • Testing thinner...
Abrir o catálogo na página 11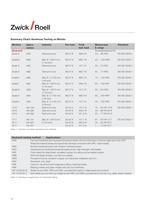
12 Summary Chart: Hardness Testing on Metals Table 1: Overview of metals standards and methods Method Rockwell Scale A Scale B Scale C Scale D Scale E Scale F Scale G Scale H Scale K 15 N 30 N 45 N 15 T 30 T 45 T Standard EN ISO 6508-1 EN ISO 6508-1 EN ISO 6508-1 EN ISO 6508-1 EN ISO 6508-1 EN ISO 6508-1 EN ISO 6508-1 EN ISO 6508-1 EN ISO 6508-1 EN ISO 6508-1 EN ISO 6508-1 Pre-load 98.07 N 98.07 N 98.07 N 98.07 N 98.07 N 98.07 N 98.07 N 98.07 N 98.07 N 29.42 N 29.42 N 29.42 N 29.42 N 29.42 N 29.42 N Abbreviation HRA HRB HRC HRD HRE HRF HRG HRH HRK HR 15N HR 30N HR 45N HR 15T HR 30T HR 45T...
Abrir o catálogo na página 12Todos os catálogos e folhetos técnicos ZwickRoell GmbH & Co. KG
-
Plastics & rubber
56 Páginas
-
Extrusion plastometers
12 Páginas
-
Image Brochure
20 Páginas
Catálogos arquivados
-
Zwick/ZHU250
3 Páginas
-
20 l/min. hydraulic power-pack
3 Páginas
-
Dynamic and fatigue testing systems
28 Páginas
-
HC range
2 Páginas
-
teachXpert Academia Package
2 Páginas
-
Vibrophores 20-30 kN
2 Páginas
-
Sheet forming 1000 kN
2 Páginas
-
Rebound resilience tester Zwick 5109
2 Páginas
-
Creep Testing Kappa SS
4 Páginas
-
Mflow Extrusion Plastometers
4 Páginas
-
HDT/Vicat Allround_cool
2 Páginas
-
Cflow Extrusion Plastometers
4 Páginas
-
Specimen Grinder
2 Páginas
-
Specimen blanking
3 Páginas
-
Static Materials Testing Machines
4 Páginas
-
DWT Pellini 550 and 1650
2 Páginas
-
HIT230F for tests on plastics
4 Páginas
-
Pendulum impact tester RKP450
2 Páginas
-
HIT pendulum impact testers
24 Páginas
-
Hardness Testing with Zwick
24 Páginas
-
Sheet forming 100/200 kN
2 Páginas
-
TorsionLine 20 up to 500 Nm
2 Páginas
-
TorsionLine 1000 bis 2000 Nm
2 Páginas
-
roboTest P Metal
2 Páginas
-
roboTest F_formstabil
2 Páginas
-
roboTest A
2 Páginas
-
Vibrophore HFP 5 and 10 kN
2 Páginas
-
Hydrostatic Testing Actuators
2 Páginas
-
ProLine
2 Páginas
-
PrecisionLine Automatic
2 Páginas
-
testXpert II
20 Páginas
-
Testing Machines and Systems for Metals
72 Páginas
-
Testing of plastics and rubber
68 Páginas
-
Testing machines for paper materials
40 Páginas
-
HIT Pendulum Impact Testers
24 Páginas






























































