
Excertos do catálogo

Technical Explanation for Displacement Sensors and Measurement Sensors Introduction Sensors What Is a Displacement Sensor? A Displacement Sensor is a device that measures the distance between the sensor and an object by detecting the amount of displacement through a variety of elements and converting it into a distance. Depending on what element is used, there are several types of sensors, such as optical displacement sensors, linear proximity sensors, and ultrasonic displacement sensors. What Is a Measurement Sensor? A Measurement Sensor is a device that measures the dimensions of an object by converting changes in amount of light into electrical signals when the object interrupts a wide laser beam. Safety Components Features 1. A physical quantity of an object can be measured. A Displacement Sensor measures and detects changes (displacement) in a physical quantity. The Sensor can measure the height, width, and thickness of an object by determining the amount of displacement of that object. A Measurement Sensor measures the position and dimensions of an object. 2. Physical quantity output is also possible in addition to ON/OFF signal output. Analog output of physical quantities (current output or voltage output) can also be performed (excluding some models). Some models also support digital (serial) communications. Control Components Automation Systems Motion / Drives Energy Conservation Support / Environment Measure Equipment Power Supplies / In Addition Others Common
Abrir o catálogo na página 1
Technical Explanation for Displacement Sensors and Measurement Sensors Operating Principles and Classification Sensors Displacement Sensors 1. Optical Displacement Sensors Triangulation Measurement Method FAR Light source Light-receiving element Emitter lens Receiver lens Emitter axis Receiver axis Safety Components Light from the light source is condensed by the lens and directed onto the object. Light reflected from the object is condensed onto a onedimensional position sensing device (PSD)* by the receiving lens. If the position of the object (the distance to the measuring device)...
Abrir o catálogo na página 2
Technical Explanation for Displacement Sensors and Measurement Sensors • Regular Reflection Model and Diffuse Reflection Model Diffuse reflection A specular reflection is produced, such as from a mirror surfaced or glossy object. A beam is reflected in all directions from an object with a standard surface. Laser beam Incident light to the receiver Laser beam Incident light to the receiver Regular reflection • Line Beams and Spot Beams Line Beam Model This model measures the average displacement within a line beam. Depending on the measurement conditions, this model provides stable...
Abrir o catálogo na página 3
Technical Explanation for Displacement Sensors and Measurement Sensors Confocal Principle The height is detected based on the wavelength. Reflected light is not received because the reflected light is not focused at the light emission point. Even if the measurement object is inclined or contains different materials, the reflected light will be focused at the light emission point as long as the measurement object is at the focal point. spectroscope Receiver Light emission point = Focal point Light emission point Colors are separated along the height direction. Focal point Focal point Focal...
Abrir o catálogo na página 4
Technical Explanation for Displacement Sensors and Measurement Sensors Eddy currents Center of the core Displacement direction Core Center of the coil Automation Systems Detection coil Control Components As the distance between the metal object and the Sensor Head decreases, eddy currents increase and the oscillation amplitude of the oscillation circuit decreases. Conversely, as the distance between the metal object and the Sensor Head increases, eddy currents decrease and the oscillation amplitude of the oscillation circuit increases. The oscillation amplitude of the oscillation circuit...
Abrir o catálogo na página 5
Technical Explanation for Displacement Sensors and Measurement Sensors Measurement Sensors Product names / models Smart Sensor ZX-LT Light source Lens Parallel Beam Line Sensor ZX-GT Light source Lens • Determining outer diameters • Detecting edge positions (including transparent objects) • Determining pin pitch • Detecting bar positions *CCD: Charge Coupled Device Light source PD* Rotating Lens mirror *PD: Photo Diode Emitter • Determining outer diameters (including transparent objects) • Detecting edge positions (including transparent objects) • Determining pin pitch Automation Systems...
Abrir o catálogo na página 6
Technical Explanation for Displacement Sensors and Measurement Sensors Explanation of Terms Response Time This is the width, expressed in terms of the distance, of the fluctuation in the linear output when the measured object is still. The narrower the width of the fluctuation is, the better the resolution is. Linear output when the displacement and width of the object are changed to steps. In analog output, the time required for 10% to 90% change is expressed in terms of the “response time”. Linear output Response time “Full scale” indicates the full scope of the measurement range. For...
Abrir o catálogo na página 7
Technical Explanation for Displacement Sensors and Measurement Sensors Further InformationHow to Interpret the Engineering Data Optical Displacement Sensors Diffuse-reflective Sensors and Regular-reflective Sensors Example: Characteristic of the ZX2-LD50 Linearity Characteristic for Different Materials Example: Characteristic of the ZX2-LD50V 0° Inclination - FAR side-- NEAR side-►! Measurement Displacement • This graph shows the amount of error in the measurement distance based on the material of the object. • The error values shown are based on the values at the measurement center...
Abrir o catálogo na página 8Todos os catálogos e folhetos técnicos OMRON
-
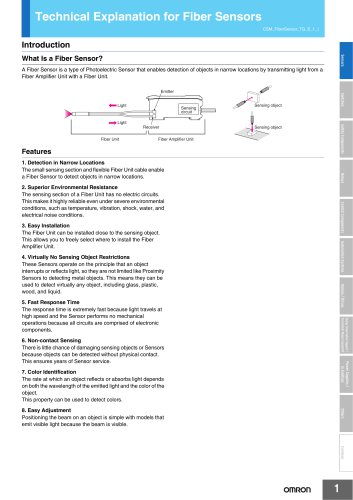
Technical Explanation for Fiber Sensors
14 Páginas
-
D4F
8 Páginas
-
D4GS-N
11 Páginas
-
E4E2
5 Páginas
-
Smart Laser Sensors E3NC-L/E3NC-S
16 Páginas
-
Fiber SensorBest Selection Catalog
104 Páginas
-
Fiber Unit E32-LT/LD
4 Páginas
-
G9SE Series
20 Páginas
-
NX-SL/SI/SO
20 Páginas
-
G9SP
28 Páginas
-
G9SX-SM
24 Páginas
-
G9SX-SM/LM
9 Páginas
-
G9SX/G9SX-GS
49 Páginas
-
G9SX-LM
28 Páginas
-
G9SB
10 Páginas
-
G9SA
16 Páginas
-
DST1 Series
5 Páginas
-
WS02-CFSC1-E
3 Páginas
-
G9SA-300-SC
9 Páginas
-
K8AK-AS
12 Páginas
-
K8AK-AW
16 Páginas
-
K8AK-VS
12 Páginas
-
K8AK-VW
12 Páginas
-
K8AK-PH
12 Páginas
-
K8DS-PH
12 Páginas
-
K8AK-PM
16 Páginas
-
K8DS-PM
12 Páginas
-
K8AK-PA
12 Páginas
-
K8DS-PA
12 Páginas
-
K8AK-PW
12 Páginas
-
K8DS-PU
12 Páginas
-
K8DS-PZ
12 Páginas
-
K8AK-TS/PT
12 Páginas
-
K8AK-LS
12 Páginas
-
K8AK-TH
12 Páginas
-
K2CM
16 Páginas
-
SE
15 Páginas
-
SAO
13 Páginas
-
APR-S
6 Páginas
-
XS5
25 Páginas
-
XS2
29 Páginas
-
F92A
4 Páginas
-
GLS
3 Páginas
-
TL-L
5 Páginas
-
V680 series
68 Páginas
-
V680S Series
68 Páginas
-
MY
35 Páginas
-
Safety Light Curtain F3SG-R Series
80 Páginas
-
E3NC-L/-S
16 Páginas
-
61F-GPN-BT / -BC
5 Páginas
-
NE1A-SCPU Series
8 Páginas
-
NE1A-SCPU0[]-EIP
8 Páginas
-
NE0A-SCPU01
6 Páginas
-
LY
14 Páginas
-
G2R-[]-S
11 Páginas
-
G7T
7 Páginas
-
G2A
9 Páginas
-
G2A-434
7 Páginas
-
G2AK
7 Páginas
-
MK-S
9 Páginas
-
MK-S(X)
12 Páginas
-
MM
17 Páginas
-
MMK
14 Páginas
-
G4Q
6 Páginas
-
G7Z
9 Páginas
-
G7J
10 Páginas
-
E4B
12 Páginas
-
E4A-3K
9 Páginas
-
E4C-UDA
5 Páginas
-
E6H-C
5 Páginas
-
E6F-C
5 Páginas
-
E6D-C
5 Páginas
-
E6B2-C
5 Páginas
-
E6A2-C
5 Páginas
-
NL
8 Páginas
-
VB
5 Páginas
-
SC
5 Páginas
-
D5F
5 Páginas
-
D5A
8 Páginas
-
E3S-GS3E4
3 Páginas
-
E3S-R
11 Páginas
-
E3S-A
21 Páginas
-
E3S-CL
9 Páginas
-
E3ZM-C
14 Páginas
-
E3T Data Sheet
26 Páginas
-
E3T Series
6 Páginas
-
G5 Series
59 Páginas
-
Sysmac Catalog
410 Páginas
-
VT-X700
6 Páginas
-
E5AC-T
8 Páginas
-
CP1
12 Páginas
-
CP1E
12 Páginas
-
MS4800
40 Páginas
-
VC-DL100
6 Páginas
-
FZ4 Series
42 Páginas
-
ZG2
16 Páginas
-
ZS Series
32 Páginas
-
ZW Series
24 Páginas
-
E9NC-T
2 Páginas
-
Vision System FH series
54 Páginas
-
CompoNet
28 Páginas
-
F3SJ Series Safety Light Curtain
108 Páginas
-
Code Reader/OCR
24 Páginas
-
Fiber Sensor Best Selection Catalog
100 Páginas
-
Portable Multi-logger ZR-RX70
12 Páginas
-
Air Particle Sensor ZN-PD-S
2 Páginas
-
Smart Fiber Amplifier Units E3NX-FA
8 Páginas
-
NT series
18 Páginas
-
Programmable Controller SYSMAC CVM1
16 Páginas
-
Round Water-resistant Connectors
31 Páginas
-
Modular Temperature Controller EJ1
24 Páginas
-
Safety Controller G9SP
28 Páginas
-
E3FA PHOTOELECTRIC SENSORS
24 Páginas
-
Switch Mode Power Supply S8VK-G
22 Páginas
-
Data Logger ZR-RX Series
12 Páginas
-
Programmable Terminals NS Series
57 Páginas
-
DeviceNet Safety System
30 Páginas
-
Switching Power Supplies
16 Páginas
-
Photomicro Sensors
7 Páginas
-
Displacement Sensors
4 Páginas
-
R87F / R87T AC Axial Fans
28 Páginas
-
G9SX-GS Safety Guard Switching Unit
28 Páginas
-
H8PS Cam Positioner
32 Páginas
-
OS32C Safety Laser Scanner
24 Páginas
-
FQ Vision Sensor
17 Páginas
-
UM, MC3 Safety Mat/Safety Mat Controller
19 Páginas
-
ZN-PD Air Particle Sensor
16 Páginas
-
ZUV-C20H / C30H Smart Curing System
14 Páginas
-
E5CC Digital Temperature Controller
38 Páginas
-
S8EX Switch Mode Power Supply
24 Páginas
-
CP1L CP series CP1L CPU Unit
36 Páginas
-
E2EF
8 Páginas
-
FQ2 Smart camera
24 Páginas
Catálogos arquivados
-
SAFETY APPLICATION HANDBOOK
55 Páginas
-
SMART REMOTE I/O
12 Páginas
-
Sensor Accessories
38 Páginas
-
REGULATION SOLUTIONS
24 Páginas
-
Vision Systems
20 Páginas


























































![NE1A-SCPU0[]-EIP](https://img.directindustry.com/pdf/repository_di/15954/ne1a-scpu0-eip-616667_1mg.jpg)


![G2R-[]-S](https://img.directindustry.com/pdf/repository_di/15954/g2r-s-616653_1mg.jpg)



























































































