
Catalog excerpts

MOTORS Technical Information RS Orbital Motors
Open the catalog to page 1
3 Contents Chapter 1 General Data ______________________________________________________________________ 4 Operating Recommendations ________________________________________________________________________ 5 Oil type ___________________________________________________________________________________________________ Fluid viscosity & Filtration ____________________________________________________________________________________ Installation & Start- Up ______________________________________________________________________________________ Motor protection...
Open the catalog to page 3
Chapter 1 General Data Topics: • • • • • • • Operating Recommendations Product testing Allowable Bearing & Shaft Loading Vehicle Drive Calculations Induced Side Load Hydraulic Equations Shaft nut information WHITE can accept no responsibility for possible errors in catalogues, brochures, and other printed material. WHITE reserves the right to alter its products without notice. This also applies to products already on order provided that such alterations can be made without subsequent changes being necessary in specifications already agreed. All trademarks in this material are the property...
Open the catalog to page 4
Operating Recommendations Oil type Hydraulic oils with anti-wear, anti-foam and demulsifiers are recommended for systems incorporating these motors. Straight oils can be used but may require VI (viscosity index) improvers depending on the operating temperature range of the system. Other water based and environmentally friendly oils may be used, but service life of the motor and other components in the system may be significantly shortened. Before using any type of fluid, consult the fluid requirements for all components in the system for compatibility. Testing under actual operating...
Open the catalog to page 5
Motor/Brake Precaution Caution! - The motors/brakes are intended to operate as static or parking brakes. System circuitry must be designed to bring the load to a stop before applying the brake. Caution! - Because it is possible for some large displacement motors to overpower the brake, it is critical that the maximum system pressure be limited for these applications. Failure to do so could cause serious injury or death. When choosing a motor/brake for an application, consult the performance chart for the series and displacement chosen for the application to verify that the maximum operating...
Open the catalog to page 6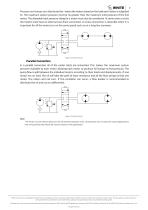
7 Pressure and torque are distributed be- tween the motors based on the load each motor is subjected to. The maximum system pressure must be no greater than the maximum inlet pressure of the first motor. The allowable back pressure rating for a motor must also be considered. In some series circuits the motors must have an external case drain connected. A series connection is desirable when it is important for all the motors to run the same speed such as on a long line conveyor. Figure 2 Series Circuit Parallel Connection In a parallel connection all of the motor inlets are connected. This...
Open the catalog to page 7
Product testing Performance testing is the critical measure of a motor’s ability to convert flow and pressure into speed and torque. All product testing is conducted using a state of the art test facility. This facility utilizes fully automated test equipment and custom designed software to provide accurate, reliable test data. Test routines are standardized, including test stand calibration and stabilization of fluid temperature and viscosity, to provide consistent data. The example below provides an explanation of the values pertaining to each heading on the performance chart. WHITE can...
Open the catalog to page 8
Allowable Bearing & Shaft Loading This catalog provides curves showing allowable radial loads at points along the longitudinal axis of the motor. They are dimensioned from the mounting flange. Two capacity curves for the shaft and bearings are shown. A vertical line through the centerline of the load drawn to intersect the x-axis intersects the curves at the load capacity of the shaft and of the bearing. In the example below the maximum radial load bearing rating is between the internal roller bearings illustrated with a solid line. The allowable shaft rating is shown with a dotted line....
Open the catalog to page 9
Vehicle Drive Calculations When selecting a wheel drive motor for a mobile vehicle, a number of factors concerning the vehicle must be taken into consideration to determine the required maximum motor RPM, the maximum torque required and the maximum load each motor must support. The following sections contain the necessary equations to determine this criteria. An example is provided to illustrate the process. equations to determine this criteria. An example is provided to illustrate the process Sample application (vehicle design criteria) Step One: Determine Rolling Resistance Rolling...
Open the catalog to page 10
11 Acceleration Force (FA) is the force necessary to accelerate from a stop to maximum speed in a desired time. FA = Step Seven: Determine Wheel Slip To verify that the vehicle will perform as designed in regard to tractive effort and acceleration, it is necessary to calculate wheel slip (TS) for the vehicle. In special cases, wheel slip may actually be desirable to prevent hydraulic system overheating and component breakage should the vehicle become stalled. Where: t = time to maximum speed (seconds) Example FA = Step Four: Determine Drawbar Pull Drawbar Pull (DP) is the additional force,...
Open the catalog to page 11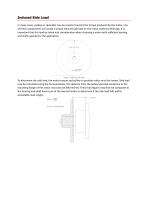
Induced Side Load In many cases, pulleys or sprockets may be used to transmit the torque produced by the motor. Use of these components will create a torque induced side load on the motor shaft and bearings. It is important that this load be taken into consideration when choosing a motor with sufficient bearing and shaft capacity for the application. Figure 5 Induced side load To determine the side load, the motor torque and pulley or sprocket radius must be known. Side load may be calculated using the formula below. The distance from the pulley/sprocket centerline to the mounting flange of...
Open the catalog to page 12All White Drive Products catalogs and technical brochures
-
HP 30
42 Pages
-
VIS 40, 45
65 Pages
-
OMSW
21 Pages
-
OMS
53 Pages
-
2012 Product Catalog
259 Pages
-
FD
6 Pages
-
SB
7 Pages
-
BK series 913
4 Pages
-
D9
14 Pages
-
DT
18 Pages
-
DR
23 Pages
-
RE
27 Pages
-
CE
21 Pages
-
WS
26 Pages
-
HB/HK
22 Pages
-
WG
22 Pages
-
WR
18 Pages
-
RS
15 Pages
-
WP
18 Pages
-
WD
14 Pages
-
WM
8 Pages
-
HB
20 Pages
Archived catalogs
-
Product Catalog
258 Pages
-
RS
16 Pages
-
WS
22 Pages
-
FD
6 Pages
-
BK series 910
4 Pages
-
DT
20 Pages
-
RG Series
32 Pages
-
White Hydraulics - Drive products
204 Pages
































