
Catalog excerpts

White Paper | September 2014 Solid State Drive for Client Applications The laptop PC is evolving with thin and lightweight design, long battery life and high-performance processing capability. In particular, great efforts are being devoted to enhancing operability so as to realize a more responsive user experience on portable PCs from the human-interface viewpoint. In order to support from ultra-sleek clamshell laptop PCs to keyboard-detachable tablets, storage devices need to offer faster transfer rates, shorter access latency, a variety of small form factors, and greater efficiency (lower power consumption) as well as larger capacity. Solid State Drive (SSD) with NAND flash memory is the most suitable storage device for integration on such laptop PC platforms. SSD provides very fast access speed in writing and reading as well as low power consumption. SSD is also thin, compact and very robust against the shock and vibration to which portable PCs are likely to experience during operation. As the first company to develop NAND flash memory, Toshiba has been a leader in the SSD market with its high technologies. is as small as 30.0 mm x 50.95 mm and the thickness is 4.85 mm. A newly developed form factor in practical use is the M.2 type As it is for Hard disk drive (HDD), the Serial AT Attachment (SATA) with various sizes. There are Type 22110, 2280, 2260, 2242 and interface is also widely used in SSD for client applications such as 2230 in the M.2 type form factor for SSD (Figure 2). laptop PCs and other industry equipment. The SATA interface has the following features: Point-to-point connection, ATA command set, and 6 Gbit/s interface speed. For some high-performance PC models, SSD with PCIe (PCI Express) interface has started to be used. The PCIe interface currently uses ATA command set over AHCI (Advanced Host Controller Interface) protocol. NVM Express (NVMe) optimized for data access to SSD may be used as a popular protocol in the Form Factors There are several form factors in SSD. The 2.5-inch compatible with HDD is widely used. The size is 69.85 mm x 100.0 mm and the thickness is 9.5 mm and 7.0 mm. Figure 2: PCI Express M.2 Specification Besides, there is also the 1.8-inch form factor that is smaller than the 2.5-inch and compatible with HDD. The size is 54.0 mm x 78.5 mm and the thickness is 5.0 mm. Additionally, there is a smaller and lighter form factor for SSD SSD requires only electrical operation, and a read and write called the mSATATM (or mini-SATA) module (Figure 1) and its size operation to access data through NAND flash memory although HDD requires the mechanical operation to access data. Additionally, the multiple access to NAND flash memory is the most important feature, realizing, compared to HDD, very high speed in data transactions. The data transfer rate is more than 500 MB/s for recent client SSD with 19nm NAND flash memory. The random access speed is about 80,000 Input Output Per Second (IOPS) for 4 KiB data transactions. Turning to NAND write/read speed, Single Level Cell (SLC) storing 1 bit in a cell is the fastest NAND device, followed by Multi Level Cell (MLC) storing 2 bits in a cell. For client applications, MLC has been mostly used because MLC is more cost effective than SLC. Recently Triple Level Cell (TLC) storing 3 bits in a cell has been introduced in the client SSD market. Figure 1: mSATATM module Copyright © 2014 TOSHIBA CORPORATION, All Rights Reserved.
Open the catalog to page 1
White Paper | September 2014 Error Detection and Correction Technology Trusted Computing Group (TCG) Opal. Some models also provide Toshiba’s innovative “Wipe Technology”(2) function. Wipe The SSD controllers offer an error detection/correction function technology can automatically execute the Cryptographic Erase to improve data reliability. when SSD is connected to an unauthorized host. As the NAND flash memor y generation advances toward fine process, error detection and error correction code (ECC) technologies have become more important for SSD. 1) YAMAKAWA Teruji, et al., Implementation...
Open the catalog to page 2All Toshiba Europe Storage Device Division catalogs and technical brochures
-
Canvio Advance
3 Pages
-
S300 Surveillance Hard Drive
3 Pages
-
eSSD-PX04SR
2 Pages
-
AL14SEBxxxN
2 Pages
-
eHDD-AL14SXB
2 Pages
-
eSSD-PX04SV
2 Pages
-
PX05SVB/PX05SVQ
3 Pages
-
TransferJet TM
2 Pages
-
Gate Drive Couplers
2 Pages
-
e • MMC TM
2 Pages
-
DTMOS
4 Pages
-
AL13SXB xx E x
2 Pages
-
Flash Memory
20 Pages
-
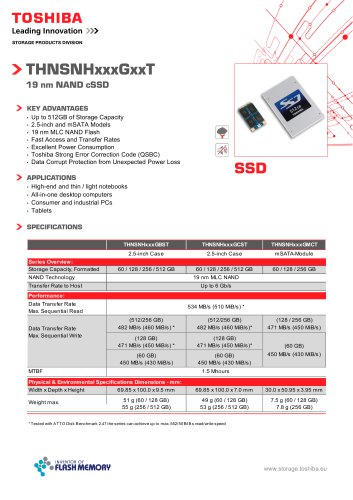
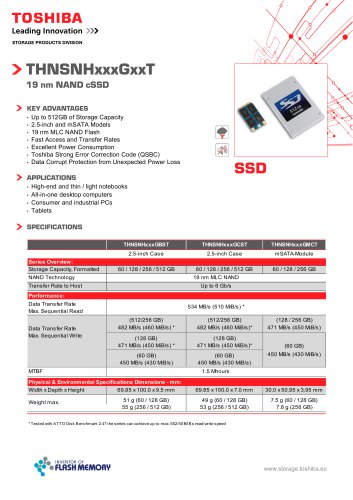
THNSNHxxxGMCT
1 Pages
-
THNSNHxxxGBST
1 Pages
-
MKxx76GSXZ
1 Pages
-
MKxx50GACY
1 Pages
-
MG04ACAxxxA
1 Pages
-
MG03SCAxxx
1 Pages
-
MBF2xxxRC
1 Pages
-
AL13SEBxxx
1 Pages
-
MKxx60GSC
1 Pages
-
MKxx36GAC
1 Pages
-
THNSNFxxxGBSS
2 Pages
-
MQ01ABCxxx
1 Pages
-
MKxx60GSCX
1 Pages
-
PX02SSFxxx
1 Pages
-
MG04SCAxxxA
1 Pages
-
THNSNFxxxGMCS
2 Pages
-
MG03ACAxxx
1 Pages
-
MQ01ABFxxxH
1 Pages
-
THNSNHxxxGCST
1 Pages
-
THNSNFxxxGCSS
2 Pages
-
THNSNJxxxPCS3
1 Pages
-
THNSNHxxxGxxT
1 Pages
-
DT01ACAxxx
1 Pages
-
THNSNFxxxGxxS
2 Pages
-
mk1665gsx
1 Pages
-
mk6465gsx
1 Pages
-
mk3265gsx
1 Pages
-
mk2565gsx
1 Pages
-
/mkxx59gsm
1 Pages
-
mkxx76gsx
1 Pages
-
mk3263gsx
1 Pages
-
mkxx61gsy
1 Pages
-
mk1252gsx
1 Pages
-
mk1251gsy
1 Pages
-
mk1249gsy
1 Pages
-
mk1246gsx
1 Pages
-
mk6037gsx
2 Pages
-
mk2035gss
1 Pages
-
MK8032-1032GSX
1 Pages
-
MK1032GAX
1 Pages
-
DT01ABAxxx
1 Pages
-
MQ01ABDxxx
1 Pages
-
mkxx75gsx
1 Pages
-
MKxx61GSY[N] 2.5-inch SATA HDD
1 Pages
-
MKxx61GSYB 2.5-inch SATA HDD
1 Pages
-
MK2565GSX 2.5-inch SATA HDD
1 Pages
-
MKxx33GSG 1.8-inch SATA HDD
1 Pages
Archived catalogs
-
Toshiba Industrial HDD Flyer
2 Pages























































![MKxx61GSY[N] 2.5-inch SATA HDD](https://img.directindustry.com/pdf/repository_di/40449/mkxx61gsy-n-25-inch-sata-hdd-177140_1mg.jpg)









