Website:
TOPWAY LCD
Website:
TOPWAY LCD
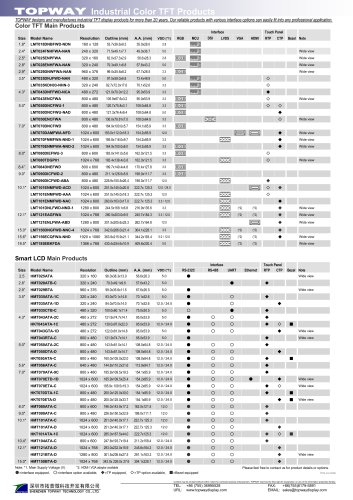
Catalog excerpts

SOLOMON SYSTECH SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA Advance Information 1215KB Embedded Display SRAM LCD Display Controller This document contains information on a new product. Specifications and information herein are subject to change without notice. http://www.solomon-systech.com SSD1963 Rev 1.1 P 1/93 Copyright © 2010 Solomon Systech Limited
Open the catalog to page 1
Appendix: IC Revision history of SSD1963 Specification Version 0.10 21-Nov-08 0.10 08-Dec-08 Change Items Changed status to Advance Information Update min/max rating of VDDD and VDDPLL in Table 11-1 Added tape and reel drawing of 128-pin LQFP package in Section 15.3 Revised Section 13.2 5. Added 12 bits for Table 7-1 Removed TTL interface Revised section 7.1.5 Change the title of section 7.2 Revised command description in section 8 Removed the command 0x0C and 0x3A Added figures in section 13.4 Revised figures in section 13.3 Revise Table 6-1 Update Table 7-1 Revised section 9.72 Solomon...
Open the catalog to page 2
Solomon Systech
Open the catalog to page 3
Solomon Systech
Open the catalog to page 4
Solomon Systech
Open the catalog to page 5
Solomon Systech
Open the catalog to page 6
Solomon Systec
Open the catalog to page 7
GENERAL DESCRIPTION SSD1963 is a display controller of 1215K byte frame buffer to support up to 864 x 480 x 24bit graphics content. It also equips parallel MCU interfaces in different bus width to receive graphics data and command from MCU. Its display interface supports common RAM-less LCD driver of color depth up to 24 bit-perpixel. Display feature − Built-in 1215K bytes frame buffer. Support up to 864 x 480 at 24bpp display − Support TFT 18/24-bit generic RGB interface panel − Support 8-bit serial RGB interface − Hardware rotation of 0, 90, 180, 270 degree − Hardware display mirroring −...
Open the catalog to page 8
BLOCK DIAGRAM Figure 4-1: SSD1963 Block Diagram Solomon Systech
Open the catalog to page 9
80 balls TFBGA Figure 5-1: Pinout Diagram –TFBGA (Topview) Solomon Systech Signal Name LDATA4 LDATA3 LDATA2 LDATA1 VSS VDDD R/W# (WR#) D[4] VDDPLL LDATA18 LDATA19 LDATA0 D[19] VSS VDDD E(RD#) D[3] CLK
Open the catalog to page 10
Figure 5-2 : Pinout Diagram – LQFP (Topview) Solomon Systech
Open the catalog to page 11
Signal Name VDDD VSS VSS VDDIO VSS VDDD D0 D1 D2 D3 D4 VDDIO VSS VDDD CLK VDDIO VSS VDDPLL VSSPLL VSS VDDD XTAL_IN VSS XTAL_OUT VDDD VSS VDDLCD LDATA23 LDATA22 LDATA21 LDATA20 VDDD Solomon Systech Signal Name VSS VDDLCD LDATA17 GPIO0 GPIO1 GPIO2 GPIO3 VDDD VSS VDDLCD LFRAME LLINE LSHIFT VDDD VSS VDDLCD LDEN TE PWM GAMAS0 GAMAS1 VDDLCD VSS VDDD VSS VDDLCD LDATA16 LDATA15 LDATA14 LDATA13 LDATA12 VDDD Signal Name VDDIO D17 D16 VDDIO VSS VDDD D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 VDDIO VSS VDDD D10 D9 D8 D7 D6 D5 VDDIO VSS VDDD R/W#(WR#) E(RD#) D/C# CS# VDDIO VSS VDDD RESET# CONF
Open the catalog to page 12
Key: I = Input O =Output IO = Bi-directional (input/output) P = Power pin Hi-Z = High impedance Table 6-1: MCU Interface Pin Mapping Pin Name Reference Type Voltage Level VDDIO VDDIO Description TTL clock input. This pin should be tied to VSS if TTL clock input is not used Crystal oscillator input. This pin should be tied to VSS if not used Crystal oscillator output. This pin should be floating if not used Chip select Data/Command select 6800 mode: E (enable signal) 8080 mode: RD# (read strobe signal) 6800 mode: R/W# 0: Write cycle 1: Read cycle 8080 mode: WR# (write strobe signal) Solomon...
Open the catalog to page 13
Table 6-2: LCD Interface Pin Mapping Pin Name LFRAME LLINE LSHIFT LDEN Reference Type Voltage Level O VDDLCD O VDDLCD O VDDLCD O VDDLCD VDDLCD VDDLCD Description Vertical sync (Frame pulse) Horizontal sync (Line pulse) Pixel clock (Pixel shift signal) Data valid These pins can be configured for display 36, 37, 38, 39 miscellaneous signals or as general purpose I/O. Default as input 52, 53 Gamma selection for panel 51 PWM output for backlight driver Table 6-3: Control Signal Pin Mapping Pin Name RESET# CONF Reference Type Voltage Level I VDDIO I Description Master synchronize reset MCU...
Open the catalog to page 14
Note (1) These pin mappings use signal names commonly used for each panel type, however signal names may differ between panel manufacturers. Solomon Systech
Open the catalog to page 15
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DESCRIPTIONS The MCU interface connects the MCU and SSD1963 graphics controller. The MCU interface can be configured as 6800 mode and 8080 mode by the CONF pin. By pulling the CONF pin to VSSIO, the MCU interface will be configured as 6800 mode interface. If the CONF pin is connected to VDDIO, the MCU interface will be configure in 8080 mode. The 6800 mode MCU interface consist of CS#, D/C#, E, R/W#, D[23:0], and TE signals (Please refer to Table 6-1 for pin multiplexed with 8080 mode). This interface supports both fixed E and clock E scheme to define a read/write cycle. If...
Open the catalog to page 16
Table 7-1: Pixel Data Format Tearing Effect Signal (TE) The Tearing Effect Signal (TE) is a feedback signal from the LCD Controller to MCU. This signal reveals the display status of LCD controller. In the non-display period, the TE signal will go high. Therefore, this signal enables the MCU to send data by observing the non-display period to avoid tearing. Figure 7-1 shows how the TE signal helps to avoid tearing. If the MCU writing speed is slower than the display speed, the display data should be updated after the LCD controller start to scan the frame buffer. Then the LCD controller will...
Open the catalog to page 17
Figure 7-1: Relationship between Tearing Effect Signal and MCU Memory Writing In SSD1963, users can configure the TE signal to reflect the vertical non-display period only or reflect both vertical and horizontal non-display period. With the additional horizontal non-display period information, the MCU can control the refresh action in more accurately by counting the horizontal line scanned by the LCD controller. Usually, a fast MCU will not need horizontal non-display period. But a slow MCU will need it to ensure the frame buffer update process always lags behind the LCD controller. System...
Open the catalog to page 18
Figure 7-2: Clock Control Diagram set_pll bit 1 set_pll bit 0 EXTERNAL CRYSTAL Frame Buffer There are 1215K bytes built-in SRAM inside SSD1963 to use as frame buffer. When the frame buffer is written or read, the “address counter” will automatically increase by one or decrease by one depends on the frame buffer settings. Table 7-2: Frame Buffer Settings regarding to set_address_mode command 0x36 System Clock and Reset Manager The “System Clock and Reset Manager” distributes the reset signal and clock signal to the entire system. It controls the Clock Generator and contains clock gating...
Open the catalog to page 19All TOPWAY LCD catalogs and technical brochures
-
Topway Display main product
1 Pages
-
TOPWAY Smart LCD SGTools Handbook
108 Pages
-
10.1" TFT LCD Module
1 Pages
-
MONO Product
2 Pages
-
LMT050DNCFWU-NNA-2
15 Pages
-
LMT080TDGP01
16 Pages
-
HKT035BTB-1D
36 Pages
-
HMT050AMC-C
17 Pages
-
HMT043ATA-6C
31 Pages
-
TM035PDHG09
42 Pages
-
TM035PDHG03
31 Pages
-
TM028HDZP01
28 Pages
-
LM256160DCW-1
14 Pages
-
LM12896FCW-1
17 Pages
-
LM12832KCW
13 Pages
-
LM2088EFW-9
12 Pages
-
LM3122AGG-2
12 Pages
-
LM240160YCW
18 Pages
-
LM6093ACW
14 Pages
-
HMT104ATA-C
11 Pages
-
HMT101ATA-D
36 Pages
-
HKT080ATA-C
1 Pages
-
HMT080ATA
1 Pages
-
HKT070DTA-1C
11 Pages
-
HMT070DTA-D
1 Pages
-
HKT070DMC-2C
19 Pages
-
HMT070ETD-C
31 Pages
-
HMT070ETD-1D
34 Pages
-
HMT056ATA-C
1 Pages
-
HMT050CB-1C
31 Pages
-
HMT050DTA-D
1 Pages
-
HKT050ATA-C
1 Pages
-
HMT043ATA-7C
32 Pages
-
HMT043GTA-1D
37 Pages
-
HKT043BMC-2C
17 Pages
-
HMT043ATA-3C
11 Pages
-
HMT043BMC-C
1 Pages
-
HMT043ATA-4C
11 Pages
-
HKT043BMC-C
1 Pages
-
HKT043ATA-1C
12 Pages
-
HMT035ATA-D
13 Pages
-
HMT028ATB-C
12 Pages
-
HKT104ATA-C
31 Pages
-
HMT068BTA-C
33 Pages
-
HMT070ATA-1C
32 Pages
-
HMT080ATA-C
33 Pages
-
HMT090ATA-C
30 Pages
-
HMT101ATA-C
33 Pages
-
HMT050ATA-2C
31 Pages
-
HMT043ATA-2C
32 Pages
-
IC Raio RA6963 LCD Controller
42 Pages
-
IC Epson S1D13L01 LCD Controller
118 Pages
-
IC EPSON S1D13700 LCD Controller
133 Pages
-
EPSON S1D13709 LCD Controller
192 Pages
-
Samsung S6B0108 LCD Driver
23 Pages
-
Avant SBN0064G LCD Driver
37 Pages
-
Avant SBN6400G LCD Driver
34 Pages
-
EPSON SED1335 LCD Controller
95 Pages
-
SGS-THOMSON ST7282
23 Pages
-
Raio RA6963 LCD Controller
42 Pages
-
Raio RA8875 TFT LCD Controller
174 Pages
-
Raio RA8835 LCD Controller
93 Pages
-
RAIO RA8803 LCD Controller
8 Pages
-
HMT035ATA-1C
1 Pages
-
Smart LCD introduction
14 Pages
-
Topway company introduction
14 Pages
-
TFT module in bezel
1 Pages
-
Topway TFT LCD
1 Pages
-
LM12864L Series
1 Pages
-
LM12864T Series
1 Pages
-
LM12864F Series
1 Pages
-
LM6060C Series
1 Pages
-
LM12864M Series
1 Pages
-
LM6029A Series
1 Pages
-
LM6059B Series
1 Pages
-
LM24048A Series
1 Pages
-
LM13232A Series
1 Pages
-
LM160160A Series
1 Pages
-
LMB402C Series
1 Pages
-
LMB242A Series
1 Pages
-
LMB204C Series
1 Pages
-
LM3121 Series
1 Pages
-
LMB404A Series
1 Pages
-
HMT043FC-1C
1 Pages
-
LM3123 Series
1 Pages
-
LMB204B Series
1 Pages
-
LMB202E Series
1 Pages
-
LMB202D Series
1 Pages
-
LMB164A Series
1 Pages
-
LMB162G Series
1 Pages
-
LMB162H Series
1 Pages
-
LMB162N Series
1 Pages
-
LMB162A Series
1 Pages
-
LMB0820D Series
1 Pages
-
LMB0820C Series
1 Pages
-
LMB0820A Series
1 Pages
-
LMB081N Series
1 Pages
-
LMB081A Series
1 Pages
-
LMB162X series
1 Pages
-
LMT057DNAFWU-AAN series
1 Pages
-
LMT057DNAFWU-AAA series
1 Pages
-
LMT104SDH01 Series
1 Pages
-
TOPWAY Product List (Y2012)
4 Pages
-
TFT LCD module
1 Pages
-
Without controller
1 Pages
-
Chinese fonts
1 Pages
-
Built-in controller
1 Pages
-
Character module
1 Pages