
Catalog excerpts
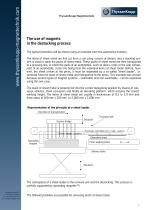
ThyssenKrupp Magnettechnik The use of magnets in the destacking process The typical procedure will be shown using an example from the automotive industry. The items of sheet metal are first cut from a coil using a press or shears, and a stacking system is used to stack the packs of sheet metal. These packs of sheet metal are then transported to a pressing line, in which the parts of an automobile, such as doors, roofs or the side component of an automobile, come into being from the individual items of sheet metal. Before, however, the sheet arrives at the press, it must be separated by a so-called "sheet loader", i.e. removed from the stack of sheet metal and transported to the press. This example was chosen because several types of magnet systems - switchable and non-switchable - can be explained using this one case. The stack of sheet metal is properly fed into the correct destacking position by means of conveyor vehicles, chain conveyors and finally an elevating platform, which ensures the correct working height. The items of sheet metal are usually in thicknesses of 0.5 to 3.0 mm and have areas of 200 mm x 200 mm to 2,000 mm x 2,000 mm. Representation of the principle of a sheet loader Direction of transportation Transport belt Suction bridge Perm. magn. systems Electrically switchable perm. magn. systems Deposited sheet Spreading magnet Press walking beam Delivery table The centrepiece of a sheet loader is the removal unit and the destacking. This process is usefully supported by spreading magnets (2). Johanniskirchstraße 71 45329 Essen, Germany Tel. +49 (0)201 946161-0 Fax +49 (0)201 946161-555 The following facilities are possible for removing items of sheet metal: 1
Open the catalog to page 1
ThyssenKrupp Magnettechnik 1. Use of pneumatic suction equipment This requires an appropriate conditioning system for the air, suction bellows and a quite complicated suction adjustment system. The sheets which are to be destacked may have almost any geometry as well as having punchouts. Pneumatic suction units therefore involve specific setting of the suction equipment in terms of the sheet geometry. It must be possible to switch on and off each item of suction equipment individually, and each item of suction equipment has a valve of its own for the elevation movement and for the vacuum....
Open the catalog to page 2
ThyssenKrupp Magnettechnik Air gaps between sheet metal and magnet are, however, to be avoided in the case of a configuration of this kind, since the small deep action would cause the holding power to be greatly reduced. The advantage of holding magnets in comparison with suction units is that there is no need to generate a vacuum and no electric lines have to track the elevation of the suction unit. There is the disadvantage, however, that the sheet must be torn from the holding magnet at the uppermost position of the magnetic suction unit. This does not, however, generally represent a...
Open the catalog to page 3
ThyssenKrupp Magnettechnik Disadvantages: - an elevating movement is necessary - holding power cannot be switched off in the upper position - provision of the holding power is a function of the system design 4. Permanent magnetic walking beams These are even wider than the magnetic strips (about 120 mm), making them heavier also. It is here possible to maintain the elevation of the magnetic beam constant. This is done in a simple way by means of a crank gear. The elevating platform now takes over alone the task of performing follow-on cycles, with the result that the uppermost sheet on the...
Open the catalog to page 4
ThyssenKrupp Magnettechnik 5. Electrically settable permanent magnets This solution is related to Points 2 and 3. Monostable magnet systems which can be set in terms of holding power are used instead of the permanent holding magnets (1). They have an adhesion area of 30 mm x 90 mm, and they will be described at this point in somewhat greater detail because they can be used universally. The operation is based on the principle of field displacement, i.e. when the current is flowing, the magnetic field of the permanent magnet is switched off, thus contrary to the operation of electromagnets....
Open the catalog to page 5
ThyssenKrupp Magnettechnik The following problem underlies removal from the stack of sheets. Spreading magnets generally ensure a spreading of the upper sheets, so that only the uppermost sheet of a stack is held by the magnet systems. It is absolutely essential to avoid removing two sheets at once. For this purpose, it is necessary to achieve a settable adhesive power and thus deep action. The adhesive power should again be compensated for deposition. The range of sheets usually extends from 0.5 mm to 3 mm thick metal sheets, the system then having to meet the following contradictory...
Open the catalog to page 6
ThyssenKrupp ThyssenKrupp Magnettechnik this demand ideally, the magnet system comprises a permanent magnetic and electromagnet part. The electromagnet part is activated for „sucking“ the sheet, the permanent magnet part is activated for securely holding and further transporting the sheet. This combination has the advantage that a brief current surge is required only at a quite specific time (namely, during the suction). Since the time of the current flow can remain brief, allowing the switch-on period of the electro magnetically operating part also to be brief, the switch-on period in...
Open the catalog to page 7
ThyssenKrupp Magnettechnik Permanent magnetic part Since the pole pitch is a measure of the deep action of the magnet system, this means that the permanent magnet part of the system has only a small range, but it has a high adhesive power even in the case of thin sheets. This is because, as a result of iron saturation, the adhesive power/area can be increased in the case of thin sheets only by means of a greater number of magnetic poles, and precisely this fact then leads to the fine pole pitch. The fine pole pitch has only a small deep action. This corresponds also to the application in a...
Open the catalog to page 8
ThyssenKrupp Magnettechnik „Area take-up“ should be understood to be the ratio of the active area of the magnet system to the sheet area. An area take-up of 50% means that the sheet area is twice as large as that of the magnet system. Fig. 4 also presents the transfer height of that part of the system which operates purely by permanent magnets. The range of secure destacking can be seen from the difference between the two pertinent curves for the same thickness of sheet metal. This range should be as large as possible, so as not to have constantly to optimize the height of the elevating...
Open the catalog to page 9All ThyssenKrupp Magnettechnik catalogs and technical brochures
-
Filter magnets
2 Pages
-
Magnetic sheet separators
3 Pages
-
Pot magnets
8 Pages
-
Hard ferrite magnets
4 Pages
-
Magnets move us
9 Pages
-
Spreading Magnets
8 Pages
-
holding magnets
40 Pages
-
AlNiCo-Magnets
40 Pages
















