Catalog excerpts

Finite Stroke LM Guide Advantages of using the ball cage Smooth motion with little rolling fluctuation Compact body with a 4-groove structure
Open the catalog to page 1
Ball Cage Effect The early forms of ball bearings were full-ball types without ball cages. Friction between balls caused loud noise, made high-speed rotation impossible, and shortened the service life. Twenty years later, a Caged Ball design was developed for ball bearings. The new design enabled high-speed rotation at a low noise level and extended the service life, despite the reduced number of balls used. It marked a major development in the history of ball bearings. Similarly, the quality of needle bearings was significantly improved by the caged needle structure. With cage-less,...
Open the catalog to page 2
Finite Stroke LM Guide EPF The spherically shaped cage holds the balls which rotate between the raceways of a precision ground LM rail and the 4 rows of circular arc grooves in the LM block. Smooth motion Since its stroke is finite, the balls do not recirculate and travel smoothly even under a preload. In addition, fluctuation of the rolling resistance is minimum. Therefore, the product is optimal in places where a short stroke and smooth motion are required. • High rigidity Since model EPF adopts a DB structure in 4 rows of circular arc grooves, it has a high rigidity especially against a...
Open the catalog to page 3
● Utilization of the Ball Cage Technology - 1 ● Utilization of the Ball Cage Technology - 2 Since the cage is resin-molded, metal to metal contact between balls is eliminated, and acceptable running noise, low particle generation and long service life are achieved. Since the cage is resin-molded into a spherical shape, the lubricant is retained in a grease pocket and long-term maintenance-free operation is achieved. Model EPF - Product Overview Major Applications emiconductor manufacturing machines / medical equipment / s
Open the catalog to page 4
Model EPF - Product Overview Reverse-radial direction *1: Dimensional table for model EPF ^ See page 9. Model EPF is capable of receiving loads in all four directions: radial, reverse-radial and lateral directions. The basic load ratings are equal in the four directions (radial, reverse-radial and lateral directions). Their actual values are indicated in the dimensional table*1 for model EPF. a Equivalent Load When the LM block of model EPF receives loads in the rad ial, reverse-radial and lateral directions simultaneously, the equivalent load is obtained in the equation below. Pe :...
Open the catalog to page 5
*1: Basic dynamic load rating (C) The basic dynamic load rating (C) indicates the load with constant direction and magnitude, under which the rated life (L) is 50 km when a group of the identical LM Guide units independently operating under the same conditions. Service Life The service life of each LM Guide unit manufactured in the same process is subject to slight variations even under the same operational conditions. Therefore, it is necessary to use the rated life defined below as a reference value for obtaining the service life of the LM Guide. • Rated Life The rated life means the...
Open the catalog to page 6
Model EPF - Product Overview The radial clearance of an LM Guide greatly affects its running accuracy, load carrying capacity and rigidity. The radial clearance of model EPF is optimally adjusted. In general, selecting a negative clearance, (i.e., a preload*1 is applied) while taking into account possible vibrations and impact generated from reciprocating motion, favorably affects the service life and the accuracy. *3:The accuracy measurements represent the values measured at the center point or central area of the LM block. *4: If the stroke exceeds 40 mm, contact THK.
Open the catalog to page 7
a Shoulder Height of the Mounting Base and the Corner Radius Normally, the mounting base for the LM rail and the LM block has a datum plane on the side face of the shoulder of the base in order to allow easy installation and highly accurate positioning. The corner of the mounting shoulder must be machined to have a recess, or machined to be smaller than the corner radius “r,” to prevent interference with the chamfer of the LM rail or the LM block. Note: For the mounting material, we recommend using a highly rigid material such as cast iron. If using a less rigid material such as aluminum,...
Open the catalog to page 8
The following table shows the standard LM rail lengths of model EPF. We recommend the corresponding values for dimension G, as shown in the table below, for rails with non-standard lengths. If the dimension G is longer, the respective part tends to become unstable after installation, which may adversely affect the accuracy. Standard LM rail lengths of model EPF Unit: mm Note: LM rail lengths other than the standard LM rail lengths (Lo) may also be available. Contact THK for details.
Open the catalog to page 9
EPFTYPEDimensional Table for Model EPF Model No. [Mode, number coding) Rail material: stainless steel (standard) Accuracy symbol - see page 6 *: The material of the LM rail is stainless steel as standard. [Note] This model number indicates that an LM rail and an LM block constitute one set.
Open the catalog to page 10
[Note] The cage holding balls moves extremely accurately. However, it may be displaced if it receives the machine’s drive vibrations, inertial force or impact. If you desire to use the product under the following conditions, contact THK. •Vertical installation •A large moment load is applied • Stopping the LM block by letting the external stopper hit the table • The product is used at high acceleration/deceleration If the cage is displaced, it is necessary to force the cage back. The table on the right shows the sliding resistance required in such cases. Make settings so that the thrust at...
Open the catalog to page 11
Precautions on Use • Precautions on handling • Disassembling components may cause dust to enter the system or degrade the mounting accuracy of parts. Do not disassemble the product. • Tilting the LM block or LM rail may cause them to fall by their own weights. • Dropping or hitting the LM Guide may damage it. Applying an impact to the LM Guide could also cause damage to its function even if the guide looks intact. • Lubrication • Thoroughly remove anti-corrosion oil and feed a lubricant before using the product. • Do not mix lubricants of different physical properties. • In locations...
Open the catalog to page 12All THK catalogs and technical brochures
-
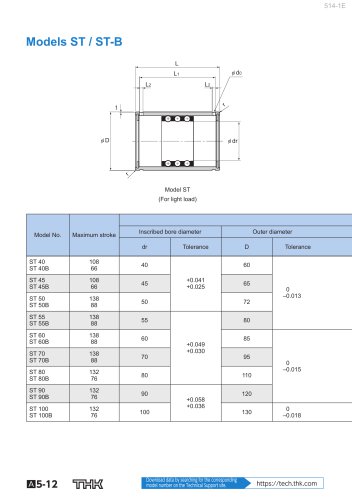
Models ST / ST-B
2 Pages
-
Predicting the Rigidity
5 Pages
-
Features of the LM Guide
16 Pages
-
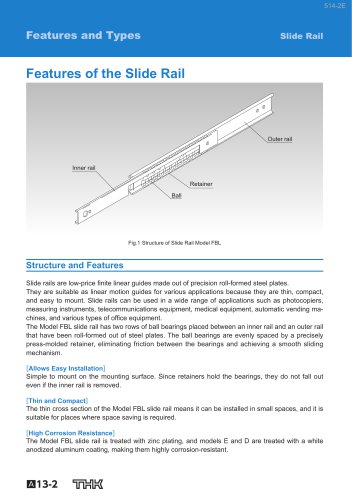
Features of the Slide Rail
1 Pages
-
PCT/PC
40 Pages
-
Models SHS-C and SHS-LC
2 Pages
-
Models SSR-XW and SSR-XWM
2 Pages
-
Models SSR-XV and SSR-XVM
2 Pages
-
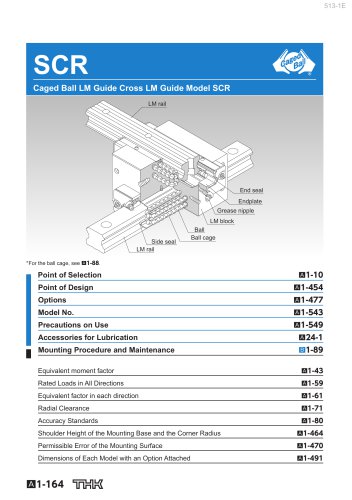
SCR
8 Pages
-
LM ACTUATOR GL
20 Pages
-
HDR
28 Pages
-
RSX
6 Pages
-
Fix Stages
4 Pages
-
LM ACTUATOR GL-N
28 Pages
-
LM Actuator TY
16 Pages
-
Clean-Room Actuator Model CSKR
20 Pages
Archived catalogs
-
Model SSR-XTB
2 Pages
-
Catalogue Caged Ball LM Guide
23 Pages
-
Low Price Actuator Model VLA
16 Pages
-
LM Guide Actuator Model KR
92 Pages
-
Ball Spline Series
24 Pages
-
Cross-Roller Ring Series
28 Pages
-
High-temparature LM Guide Series
28 Pages
-
Model HR Separate Type
20 Pages
-
LM Actuator Model TY
16 Pages
-
Guide Ball Bush LG
8 Pages
-
Limited-stroke LM Guide
12 Pages
-
LM Actuator Model GL-N
28 Pages
-
RoD Actuato
12 Pages
-
Product Ordering Guide
8 Pages
-
LM Guide Actuator KR
68 Pages