Catalog excerpts

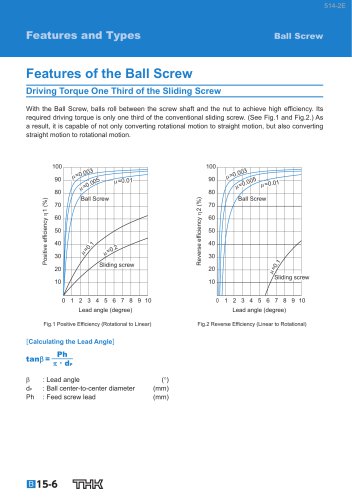
Ball Screw Features of the Ball Screw Driving Torque One Third of the Sliding Screw With the Ball Screw, balls roll between the screw shaft and the nut to achieve high efficiency. Its required driving torque is only one third of the conventional sliding screw. (See Fig.1 and Fig.2.) As a result, it is capable of not only converting rotational motion to straight motion, but also converting straight motion to rotational motion. Ball Screw Sliding screw Sliding screw Lead angle (degree) Lead angle (degree) Fig.2 Reverse Efficiency (Linear to Rotational) : Lead angle : Ball center-to-center diameter : Feed screw lead [Calculating the Lead Angle] Fig.1 Positive Efficiency (Rotational to Linear)
Open the catalog to page 1
Features and Types Features of the Ball Screw [Relationship between Thrust and Torque] The torque or thrust generated when thrust or torque is applied is obtained from equations (1) to (3). Driving Torque Required to Gain Thrust T : Driving torque (N·mm) Fa : Frictional resistance on the guide surface (N) Fa=×mg : Frictional coefficient of the guide surface g : Gravitational acceleration (9.8 m/s2) m: Mass of the transferred object (kg) Ph : Feed screw lead (mm) 1 : Positive efficiency of feed screw (see Fig.1 on B15-6) m: Mass T: Driving torque Feed screw Guide surface Thrust Generated...
Open the catalog to page 2
Examples of Calculating Driving Torque When moving an object with a mass of 500 kg using a screw with an eective diameter of 33 mm and a lead length of 10 mm (lead angle: 530’), the required torque is obtained as follows. Rolling guide (= 0.003) Ball Screw (from = 0.003, = 0.96) Fa: Frictional resistance 14.7 N m: Mass 500 kg Feed screw (Ball screw efficiency = 96) Guide surface (Rolling friction coefficient = 0.003) Frictional resistance on the guide surface Fa=0.003×500×9.8=14.7 N Driving torque Rolling guide (= 0.003) Ball Screw (from = 0.2, = 0.32) Fa: Frictional resistance 14.7N m:...
Open the catalog to page 3
Features and Types Features of the Ball Screw Ensuring High Accuracy The Ball Screw is ground with the highest-level facilities and equipment at a strictly temperaturecontrolled factory, Its accuracy is assured under a thorough quality control system that covers assembly to inspection. Automatic lead-measuring machine using laser ACCUMULATED LEAD –20 Fig.3 Lead Accuracy Measurement Table1 Lead Accuracy Measurement Item Directional target point Representative travel distance error Fluctuation Actual Standard value measurement 0 Ball Screw Lead deviati
Open the catalog to page 4
Capable of Micro Feeding The Ball Screw requires a minimal starting torque due to its rolling motion, and does not cause a slip, which is inevitable with a sliding motion. Therefore, it is capable of an accurate micro feeding. Fig.4 shows a travel distance of the Ball Screw in one-pulse, 0.1-m feeding. (LM Guide is used for the guide surface.) Time (s) Fig.4 Data on Travel in 0.1-m Feeding
Open the catalog to page 5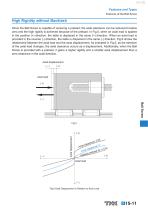
Features and Types Features of the Ball Screw High Rigidity without Backlash Since the Ball Screw is capable of receiving a preload, the axial clearance can be reduced to below zero and the high rigidity is achieved because of the preload. In Fig.5, when an axial load is applied in the positive (+) direction, the table is displaced in the same (+) direction. When an axial load is provided in the reverse (-) direction, the table is displaced in the same (-) direction. Fig.6 shows the relationship between the axial load and the axial displacement. As indicated in Fig.6, as the direction of...
Open the catalog to page 6
Capable of Fast Feed Since the Ball Screw is highly efficient and generates little heat, it is capable of a fast feed. [Example of High Speed] Fig.7 shows a speed diagram for a large lead rolled Ball Screw operating at 2 m/s. [Conditions] Item Large Lead Rolled Ball Screw WTF3060 (Shaft diameter: 30 mm; lead: 60 mm) Maximum speed 2 m/s (Ball Screw rotational speed: 2,000 min-1) Guide surface
Open the catalog to page 7
Features and Types Features of the Ball Screw Ball Screw
Open the catalog to page 8All THK catalogs and technical brochures
-
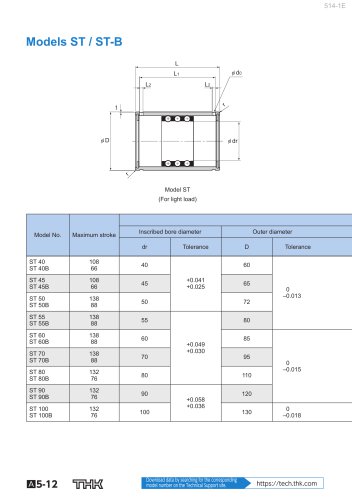
Models ST / ST-B
2 Pages
-
Predicting the Rigidity
5 Pages
-
Features of the LM Guide
16 Pages
-
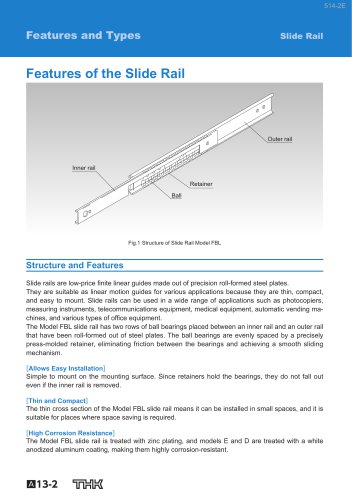
Features of the Slide Rail
1 Pages
-
PCT/PC
40 Pages
-
Models SHS-C and SHS-LC
2 Pages
-
Models SSR-XW and SSR-XWM
2 Pages
-
Models SSR-XV and SSR-XVM
2 Pages
-
SCR
8 Pages
-
LM ACTUATOR GL
20 Pages
-
HDR
28 Pages
-
RSX
6 Pages
-
Fix Stages
4 Pages
-
Finite Stroke LM Guide EPF
12 Pages
-
LM ACTUATOR GL-N
28 Pages
-
LM Actuator TY
16 Pages
-
Clean-Room Actuator Model CSKR
20 Pages
Archived catalogs
-
Model SSR-XTB
2 Pages
-
Catalogue Caged Ball LM Guide
23 Pages
-
Low Price Actuator Model VLA
16 Pages
-
LM Guide Actuator Model KR
92 Pages
-
Ball Spline Series
24 Pages
-
Cross-Roller Ring Series
28 Pages
-
High-temparature LM Guide Series
28 Pages
-
Model HR Separate Type
20 Pages
-
LM Actuator Model TY
16 Pages
-
Guide Ball Bush LG
8 Pages
-
Limited-stroke LM Guide
12 Pages
-
LM Actuator Model GL-N
28 Pages
-
RoD Actuato
12 Pages
-
Product Ordering Guide
8 Pages
-
LM Guide Actuator KR
68 Pages