 Website:
Swan Analytical Instruments
Website:
Swan Analytical Instruments
Group: SWAN Systeme / Seres OL
Catalog excerpts

Analytical Instruments in Water Steam Cycles
Open the catalog to page 1
Online Instruments in Power Cycles 5 Typical Water Steam Cycle 6 Remarks and Recommendations on Specific Individual Parameters 8 Sampling and Sample Distribution 10 Calculating pH from Differential Conductivity 20 Free Residual Chlorine 30 Automated Quality Assurance 32 Additional Recommended Papers and Literature 34 The outcome of an engineering project such as the design, installation, and commissioning of an analytical system in a power plant will to a large extent depend on specifying the requirements at the outset. Expertise from many different sources are involved. Station chemists,...
Open the catalog to page 2
Why Use Analytical Instruments? The aim of power cycle chemistry is to prevent corrosion and to avoid deposits in the power cycle. This will reduce downtime and protect expensive components such as boilers, turbines and condensers. All in all, the goal of power plant chemistry is to maintain the designed plant efficiency, the designed life time and to abide by all environmental rules and regulations. With the exception of precious metals, metallic surfaces are subject to water-induced corrosion when unprotected. In power plants, oxide layers provide the necessary protection. These layers...
Open the catalog to page 3
Typical Water Steam Cycle Example locations for On-line Monitoring in Water-Steam Cycle EXAMPLE LOCATIONS FOR ONLINE MONITORING IN THE WATER STEAM CYCLE 7 Monitoring points and key parameters in the Monitoring points and key parameters at Water-Steam Cycle Monitoring points and key parameters at Water-Steam Cycle water steam cycle: Steam turbine Steam generator FW tank FW Tank deaerator Deaerator Make-up water Cond. Cond. polisher Polisher pH, SC, CACE,(Na, SiO2, PO4, TURB) SC,CACE, (Na, SiO2, PO4, TURB) pH, SC,CACE, (Na, SiO2, PO4, TURB) Saturated steam Saturated steam Superheated/Reheated...
Open the catalog to page 4
Remarks and Recommendations on Specific Individual Parameters Conductivity After Cation Exchange and Degassed Conductivity The online measurement of conductivity after water has passed through a column of strongly acidic cation exchange resin is used to indicate the presence of potentially corrosive ionic contaminants. The technique may be referred to as "cation conductivity" or "acid conductivity" in some documentation. As per IAPWS, the accepted abbreviation is CACE. This parameter can only be measured online and under no circumstances may it be replaced by grab samples and analysis in...
Open the catalog to page 5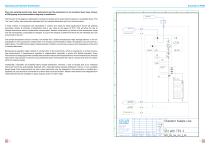
Once the sampling points have been determined and the parameters to be monitored have been chosen, a P&ID (piping and instrumentation diagram) is established. The first part of the diagram is dedicated to cooling the sample and to reducing the pressure to acceptable levels. This "hot" part is often, also physically, separated from the sample distribution and from the instruments. A small number of companies have specialized in coolers and valves for these applications. Some will propose secondary coolers to maintain a temperature that is very close to the region of 25°C. This will allow the...
Open the catalog to page 6
Instrument Panels Sample 10QUB30 Main Steam Sodium Instrument Panels Sample 10QUG10 Make-up Water Sample 10QUC70 Condensate Hotwell ANALYTICAL INSTRUMENTS Acid Conductivity SYSTEMS ENGINEERING ANALYTICAL INSTRUMENTS Specific Conductivity Acid Conductivity ENGINEERING SYSTEMS ANALYTICAL INSTRUMENTS Dissolved Oxygen SYSTEMS ENGINEERING It is common practice to mount the instruments in groups according to their physical properties. All transmitters are mounted on one side, and all the analyzers (silica, sodium, phosphate) on the other. Grab sampling lines are put together over a discharge...
Open the catalog to page 7
Acid Conductivity Conductivity is by far the most important parameter in power cycle monitoring. It is measured as "specific" (also direct or total) conductivity, as "acid" (also cationic) conductivity after a strongly acidic ion-exchanger, and as degassed cation conductivity. Analytical Method Conductivity sensors for use in the low microsiemens range consist of two electrodes made of stainless steel or titanium. The cell constant expresses the ratio of the distance between the electrodes to the area of the electrodes. A transmitter provides a constant alternating voltage. The current that...
Open the catalog to page 8
All treatment methods involve maintaining a certain pH range. However, measuring pH in water with low ionic strength is not an easy job. The measurement of the oxidation reduction potential provides insight into the redox condition in the feedwater. Some plants require an ORP measurement for optimum operation. Analytical Method A pH measurement consists of a potential difference (mV) between two electrodes. The reference electrode provides direct contact between the sample and an electrolyte. The measuring electrode is separated by an ion-sensitive membrane from the sample. The potential...
Open the catalog to page 9
Calculating pH from Differential Conductivity Experimental Data This method for determining the sample pH has been known for many years, and is also recommended by VGB and IAPWS. It is in fact very simple, stable and reliable, and requires low maintenance. It might not have been used widely due to a lack of adequate instruments. Analytical Method Modern electronics with advanced software can provide a suitable instrument that measures specific and acid (cation) conductivity and calculates the sample pH. It is ideally suitable for combined cycle plants with many sampling points for pH and...
Open the catalog to page 11
Dissolved Oxygen Faraday Verification Different treatment methods require different levels of dissolved oxygen. With the exception of oxygenated The AMI Oxytrace instruments do not require a great deal of maintenance. It is sufficient to check the sensor in the air treatments, low levels are required. once in a while. The transmitter automatically checks electrolyte consumption and membrane integrity. Analytical Method The sensor consists of a cathode (gold) and an anode (silver), an electrolyte and a membrane. Oxygen diffuses across the membrane due to partial pressure differences. When a...
Open the catalog to page 12All Swan Analytical Instruments catalogs and technical brochures
-
AMI ISE Universal
2 Pages
-
AMI Hydrazine
2 Pages
-
AMI Codes-II TC
2 Pages
-
AMI Codes-II
2 Pages
-
AMI CACE
2 Pages
-
AMI pH/Redox
2 Pages
-
Pautbac II
2 Pages
-
Opal
2 Pages
-
TOC Evolution VUV
2 Pages
-
Topaz Analyzer
2 Pages
-
Automated Quality Assurance
6 Pages
-
Seven Sins of Steam Sampling
16 Pages






















