
Catalog excerpts

Sumitomo DriveTechnologTes Motion Control Drives FINE CYCLO®
Open the catalog to page 1
Motion Control Drives FINE CYCLO® Ring gear housing Output flange Grease is sealed inside the reducer. Simple construction with less number of parts Customers are released from the sealing work. than single stage reducer mechanism.
Open the catalog to page 3
Ring gear housing Slow speed shaft pin Slow speed shaft roller High speed shaft bearing Eccentric high speed shaft Ring gear housing pin Output flange Servo motor Industral Robot I Machine Tool I Welding Positioner Axis Driving, Robot Slider I Automatic Pallet Changer Drive Machine Tool I Liquid Crystal Transfer Robot I Liquid Crystal Transfer Robot Automatic Pallet Pool Drive I Axis Driving, Robot Slider
Open the catalog to page 4
Specification suffix Reduction ratio Standard: − Special specification: S Shape of Ring gear housing Farm of a cylinder With flange 2C(Output shaft with angular contact ball bearing) Symbol of Fine CYCLO 4. Products Mark : Model Lineup Reduction ratio Frame size 59 5. Speed Ratio & Rotation Direction Fig. C-2 Slow Speed Shaft Ring Gear Housing High Speed Shaft Reducer Input : High Speed Shaft Output : Slow Speed Shaft Fixed : Ring Gear Housing i = -1/n 6 Increaser Input : Ring Gear Housing Output : High Speed Shaft Fixed : Slow Speed Shaft i = n+1 Reducer Input : High Speed Shaft Output :...
Open the catalog to page 5
6. Operating Principles The reducer portion of the FINE CYCLO® is fundamentaly different in principle and mechanism from the involute gearing mechanism of competitive gearmotors. The unique speed reducer portion is an ingenious combination of the following two mechanisms: A combination of a planet gear and a fixed internal sun gear. In the FINE CYCLO®, the planet gear has cycloidal-shaped teeth and the sun gear has circular pin teeth. The number of teeth in the planet gear is one or two less than the sun gear. A constant speed internal gearing mechanism. Principle of internal Planetary...
Open the catalog to page 6
7. Rating Table C-1 Rating Table (Input rotation base) Input speed n1(r/min) Model Frame size Table C-2 Maximum acceleration or deceleration torque Frame size C25 C35 C45 C55 C65 Maximum acceleration or deceleration torque (N m) 1030 1962 3188 4316 6278 Rated output Output Allowable Rated output Output Allowable Rated output Output Allowable Rated output Output Allowable torque torque torque torque speed input power speed input power speed input power speed input power (Upper/N m) (Upper/N m) (Upper/N m) (Upper/N m) (Lower/kgf m) (r/min) (kW) (Lower/kgf m) (r/min) (kW) (Lower/kgf m) (r/min)...
Open the catalog to page 7
1000 Rated output torque (Upper/N m) (Lower/kgf m) Output Allowable Rated output torque speed input power (Upper/N m) (r/min) (kW) (Lower/kgf m) Output Allowable Rated output torque speed input power (Upper/N m) (r/min) (kW) (Lower/kgf m) maximum Output Allowable input speed speed input power (r/min) (r/min) (kW) Allowable maximum input speed(r/min) Equivalent On input shaft Upper/Moment of inertia (x10 -4kg m 2) Lower/GD2 (x10-4kgf m2) Notes: 1. Rated output torque Rated output torque implies allowable mean load torque at each output speed. Rated output torque for below 600r/min input is...
Open the catalog to page 8
8-1. Stiffness and lost motion •Hysteresis curve Table C-3 Engineering data •Lost Motion Relationship between load and displacement of output flange (rotational angle) when load is removed slowly from allowable torque to zero torque, with fixed input shaft. Torsional deflected angle at ±3% allowable output Slope of the straight line connecting two points, when allowable torque is 50% and 100% on the hysteresis curve. Hysteresis loss 8-2. No Load Running Torque No load running torque indicates torque on input shaft for rotating reducer under no-load condition. Input speed r/min
Open the catalog to page 9
8-3. No-Load Friction Torque on Output Shaft Indicates torque necessary to start rotation from output side of reducer from stop without load. Table C-4 Value of no-load friction torque on output shaft Frame No-load friction torque on output shaft size Nm kgf m Accuracy in assembled dimensions Standard grease Notes: 1. Table C-4 shows average data after reducers have been run. 2. Measurement Conditions 8-4. Efficiency Fig. C-10 (Frame size C55-C65) Fig. C-9 Efficiency Curve (Frame size C25-C45) Input speed r/min Input speed r/min Efficiency varies by input speed, load torque, grease...
Open the catalog to page 10
8-5. ALLOWABLE RADIAL LOAD & AXIAL LOAD OF HIGH SPEED SHAFT When a gear or sheave is mounted on the high speed shaft, radial load and axial load should be equal to or less than allowable value. Check radial & axial load by following the next formula (1)-(3). (1) Radial load Pr (3) When radial and axial load co-exist Pr Lf Pro Table C-5 Actual radial load Pro(Up: N/Down: kgf ) Frame size : Actual radial load [N, kgf ] : Equivalent torque on input shaft [N m, kgf m] : Pitch circle radius of sprocket, gear, or sheave [m] : Allowable radial load [N, kgf ] (Table C-5) : Actual axial load [N, kgf...
Open the catalog to page 11
9. Main Bearings Pr: Actual radial load(N, kgf ) Pa: Actual axial load(N, kgf ) Table C-10 Span of Loading Points(mm) Frame size C25 C35 C45 C55 C65 Span of Loading Points Fig. C-13 Span between each loading point Note) Consult us if: Lr > 4 x L1 Table C-13 Coupling Factor Cf Load connection factor General purpose chain Machine gear or pinion Timing belt Table C-14 Shock factor FS1 Load Classification Uniform load (no shock) Moderate shocks Equivalent axial load Pae(N) Equivalent axial load Pae(N) Heavy shocks Fig. C-14 Diagram of Allowable Moment & Axial Load
Open the catalog to page 12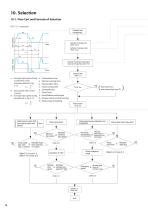
10. Selection 10-1. Flow Cart and Formula of Selection FIG. C-15 Load cycle Evaluate load characteristic Calculate of average input speed nE Calculate of average output torque TE Calculate of allowable rating output torque at average input speed TOE Selection Table (Table C-1) nA : Average input speed during tA : Acceleration time acceleration under tR : Normal running time condition defined in Fig. tB : Deceleration time nR C-15 tO tP nR : Input speed with normal T running nB : Average input speed during TA TR deceleration in Fig. C-15 TB nR nA = : Total running time : Standstill time :...
Open the catalog to page 13All SUMITOMO (SHI) Cyclo Drive Germany GmbH catalogs and technical brochures
-
Paramax 9000 series
281 Pages
-
Helical Shaft Mount (HSM)
58 Pages
-
Bevel Buddybox 4
60 Pages
-
SERVO 6000
38 Pages
-
Motion Control DrivesE CYCLO
28 Pages
-
BEVEL BUDDYBOX 4
248 Pages
-
Cyclo® BBB5
270 Pages
-
Fine Cyclo®
123 Pages
-
PARAMAX ® 9000 Series
281 Pages
-
Fine Cyclo UA Brochure
2 Pages
-
Fine Cyclo Flyer
2 Pages
-
Precision Drives Product Catalog
20 Pages
-
Fine Cyclo F4CF – UA 25
2 Pages
-
Fine Cyclo F4CFS–UA 115
4 Pages
-
Fine Cyclo F4C–C 25
4 Pages
-
Paramax 9000
352 Pages
-
Neo Hyponic
120 Pages
-
Servo 100
58 Pages
-
Servo 6000 series
6 Pages
-
Cyclo® Drive 6000
139 Pages
-
Paramax® 9000
352 Pages
-
HSM series
58 Pages
-
Astero series
186 Pages
-
IB Series catalogues
94 Pages
-
Servo Planetary Gears EPG
6 Pages
-
Servo-Planetary Gears
4 Pages
-
Centrifuge reducers
2 Pages
-
Fine Cyclo®
114 Pages
Archived catalogs
-
Product overview
16 Pages









































