
Catalog excerpts

for Offshore and Marine Application, flood- and seawater-proof
Open the catalog to page 1
Stromag Founded in 1932, Stromag has grown to become a globally recognized leader in the development and manufacture of innovative power transmission components for industrial drivetrain applications. Stromag engineers utilize the latest design technologies and materials to provide creative, energy-efficient solutions that meet their customer’s most challenging requirements. Stromag’s extensive product range includes flexible couplings, disc brakes, limit switches, an array of hydraulically, pneumatically, and electrically actuated brakes, and a complete line of electric, hydraulic and...
Open the catalog to page 2
Applications • Holding and working brake variations for off shore and industrial applications where high protection against harsh environment is essential • Usable for windlasses, anchor winches, shipboard cranes, cargo winches, trawler winches Optional extras • Micro switch for monitoring switching states or wear detection • Terminal box • Standstill heater • Preparation for speedometer installation Switching modules • Half wave or full wave • Quick switching units • Built in terminal box • Attached for mounting into the motor terminal box
Open the catalog to page 3
Advantages • Comprehensive torque range 63 - 11,000 Nm • Operative without cover • Type approvals: GL, LRS, ABS, DNV, BV, RR (on request) • Simple assembly to motor, no dismantling of brake required • Less wear • Compatibility of consumable spares • Simple maintenance, one time wear re-adjustment by reversing of the brake disc • Proven reliable design • Sealed inspection holes for air gap or lining wear • Extremely low inertia • High heat dissipation • Free from axial loads when braking and running • Suitable for vertical mounting, please consult Stromag Dessau GmbH • Many optional extras...
Open the catalog to page 4
02) Friction disc with friction lining 32) Armature disc 05) Pinion Brake operation The brake 4 BZFM is a spring-loaded electromagnetic double-face brake which brakes without current and is released electromagnetically. The brake is screwed to a motor or any other machine part by means of cyl. screws via the flange (04). The coil body (01) contains a coil (33) which is potted with a synthetic resin compound in accordance with thermal class 155, (max. limit of temperature 155°C). If the coil (33) is not excited, the springs (34) press the armature disc (32) against the friction disc...
Open the catalog to page 5
4 BZFM – Electromagnetic Spring-Applied Brake Micro switch Optional availability, inboard proving switch, one common contact, one normally open contact and one normally closed contact. This can be interlocked with motor contactor for parking brake duty, i.e. brake release before starting motor. Brake termination Three standard versions: • Flying leads usually 1,5 meter long, axial with a cable bushing and radial through cable gland in flange. • IP 66 terminal box, for easy connection and removal, at execution with terminal box the brake complies with protection IP 66! • Versions for AC...
Open the catalog to page 6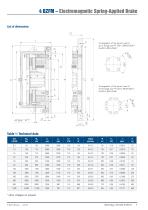
Arrangement of the bores k and kl up to flange size FF 350 to DIN EN 50347 (A400 to DIN 42948) Arrangement of the bores k and kl from flange size FF 400 to DIN EN 50347 (A450 to DIN 42948) Table 1: Technical data
Open the catalog to page 7
Keyways to DIN 6885/1 Standard flange to DIN 42948
Open the catalog to page 8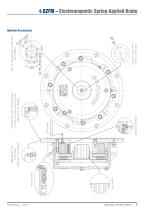
4 BZFM – Electromagnetic Spring-Applied Brake Optional Accessories
Open the catalog to page 9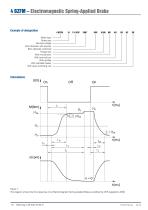
4 BZFM – Electromagnetic Spring-Applied Brake Brake type Brake size Nominal voltage Bore diameter with keyway Bore diameter, prebored Flange size With microswitch With terminal box With rectifier With standstill heater With quick switching unit Figure 1: The diagram shows the time response of an Electromagnetic Spring-Applied Brake as defined by VDE regulations 0580
Open the catalog to page 10
4 BZFM – Electromagnetic Spring-Applied Brake M1 = Switchable torque [Nm] The switchable (dynamic) torque is the torque which can be transmitted by a brake under slip condition depending on the friction coefficient and at working temperature. (M1 = 0,9MSN) M3 = Synchronization torque [Nm] The synchronization torque is the torque which arises for a short time after finishing the switching process. Mü = Transmissible torque [Nm] The transmissible (static) torque is the max. torque that can be applied to a brake without the risk of slipping. MSN = Switchable nominal torque [Nm] The switchable...
Open the catalog to page 11
4 BZFM – Electromagnetic Spring-Applied Brake Nomenclature AR cm2 Friction surface Heat quantity Specific heat Braking time kJ kJ Steel c = 0,46 — Cast iron c = 0,54 — kgK kgK Slipping time Mass moment of inertia J [kgm2] The mass moment of inertia J stated in the formula is the total mass moment of inertia of all the masses to be retarded referred to the brake. Reduction of moments of inertia The reduction of moments of inertia is calculated from the formula n2 J1 = J2 * ( — )2 [kgm2] n1 Moments of inertia of linear masses The equivalent moment of inertia JErs for a linear mass m and a...
Open the catalog to page 12
When expressing the decelerating torque MA by means of the pulse principle, we obtain after corresponding conversion. If a brake slips with constant slipping speed under operation, the dissipated energy is calculated from the formula Working brake The brake has to brake a shaft with switching frequency ”X” from speed ”Y” to speed zero and has to hold it. Holding brake with emergency stop function The brake actuates with shaft speed zero and has to hold; in case of emergency, however, it must be able to brake from shaft speed ”Y” to zero.
Open the catalog to page 13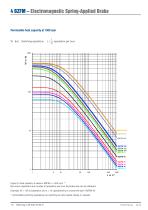
4 BZFM – Electromagnetic Spring-Applied Brake Permissible heat capacity at 1500 rpm Switching operations Figure 2: Heat capacity of series 4 BZFM n =1500 rpm **. By known operations and number of operations per hour the brake size can be obtained. Example: W = 100 kJ/operation and z = 10 operations/hour choose the size 4 BZFM 40 ** permissible switching operations per switching at other speed ratings on request
Open the catalog to page 14All STROMAG catalogs and technical brochures
-
Carbon Fiber Shaft
1 Pages
-
Stromag KMS...THC
1 Pages
-
Stromag Vector Couplings
12 Pages
-
NFF Brake
16 Pages
-
Clutches and Brakes
8 Pages
-
brakes type 600
2 Pages
-
Lever Switches, Serie HHEV
9 Pages
-
Geared Switches, Serie HGE
24 Pages
-
Geared Switches, Serie HEG
10 Pages
-
Determination of Clutches
24 Pages
-
Spidex®, Dentex®
28 Pages
-
Periflex® VN Disc Coupling
36 Pages
-
Disc Coupling
36 Pages
-
highly-flexible ring couplings
31 Pages
-
couplings for Cardan Shaft
34 Pages
-
Stromag: safety in motion
20 Pages
-
Two-in-one 1
4 Pages
-
Two-in-one 2
4 Pages
-
Wind Turbine Catalogue
7 Pages
-
Hydrid Clutches and Brakes
8 Pages
-
High Protection Brake Catalogue
16 Pages
-
Flexible Couplings
2 Pages
-
Highly-flexible TRI-R Couplings
31 Pages
-
Highly-flexible TRI Couplings
33 Pages
-
Highly-flexible GE Couplings
28 Pages
Archived catalogs
-
Electromagnetic Tooth Clutches
36 Pages
-
Driveshaft
44 Pages

































































