
Catalog excerpts

Engineered Fastening Threaded Fasteners
Open the catalog to page 1
Fastening & Assembly Solutions for Plastic Applications Plastics continue to open up a world of design opportunities, yet present some unique fastening problems. Whether you’re fastening plastic to plastic or plastic to another material, STANLEY Engineered Fastening offers a wide selection of high-performance fasteners engineered to meet the requirements of your application. Why use Special Fasteners for Plastics? Each type of plastic has its own set of performance issues, such as ductility, thermal expansion and clamp retention. Selecting a fastener that can best match these requirements...
Open the catalog to page 2
Engineered Threaded Fasteners for Plastics Table of Contents Threaded Fasteners for Plastics Threaded Fasteners for Thermoplastics Threaded Fasteners for Thermoset Plastics Other Threaded Fastening Solutions
Open the catalog to page 3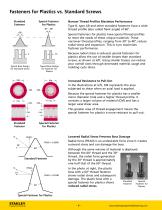
Fasteners for Plastics vs. Standard Screws Standard Fastener Special Fastener for Plastics 30° – 48° Special fasteners for plastics have special thread profiles to meet the needs of these unique materials. These narrower thread profiles, ranging from 30° to 48°, reduce radial stress and expansion. This in turn maximizes fastener performance. /3 S Typical Boss Design for Standard Screw Typical Boss Design for Fastener for Plastics Increased Resistance to Pull-Out In the illustrations at left, CM represents the area subjected to shear when an axial load is applied. Because the special...
Open the catalog to page 4
The Properties of Plastics The fastening performance of plastics is affected by several factors: • Flexural modulus (stiffness of material) • Filler and/or reinforcement content (amount of glass, etc. added to material) • Thermal expansion rate • Creep rate Flexural Modulus Flexural modulus is the best indicator of how a plastic will respond to fasteners. Generally, the lower the flexural modulus, the more the material will flow and allow the formation of threads. Thermoplastics with a higher flexural modulus also allow the formation of threads, but usually require a fastener with a low...
Open the catalog to page 5
Installing a Threaded Fastener in Plastics 3. strip/failure torque 1. Thread forming begins Torque clamping load 2. Screw head in contact with plastic; clamp load generated thread forming torque Thread forming and Stripping Torque Because friction increases as penetration increases, the differential between the thread forming torque and the strip (failure) torque must be maximized. Proper seating torque varies from application to application, so contact a STANLEY Engineered Fastening applications engineer for assistance. Penetration Depth 3. Strip-out torque level met or exceeded; boss...
Open the catalog to page 6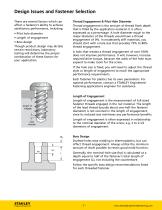
Design Issues and Fastener Selection There are several factors which can affect a fastener’s ability to achieve satisfactory performance, including: • Pilot hole diameter • Length of engagement • Boss design Though product design may dictate certain restrictions, laboratory testing will determine the proper combination of these factors for your application. Thread Engagement & Pilot Hole Diameter Thread engagement is the amount of thread flank depth that is filled by the application material. It is often expressed as a percentage. A hole diameter equal to the major diameter of the threads...
Open the catalog to page 7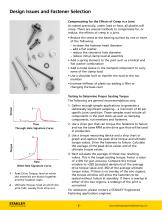
Design Issues and Fastener Selection Compensating for the Effects of Creep in a Joint As stated previously, under load or heat, all plastics will creep. There are several methods to compensate for, or reduce, the effects of creep in a joint. • Reduce the stress at the bearing surface by one or more of the following: – increase the fastener head diameter – add a flat washer – reduce the clearance hole diameter – reduce initial clamp load at assembly • Add a spring element to the joint such as a helical and flat washer combination • Add a metal sleeve in the clamped component to carry some of...
Open the catalog to page 8
Selecting the Right Threaded Fastener The following chart is intended only as a starting point in the selection of fasteners. The fastener must be matched to the properties of the material. Drive to strip ratios, clamp retention, and other performance issues are directly affected by the fastener you choose. Please contact a STANLEY Engineered Fastening applications engineer for assistance in selecting the optimum fastener for your design. Included Materials Polypropylene, 40% talc fill (PP40) Polypheylene Sulfide Polyamide 66, 12% glass fill Polycarbonate, 20% glass fill (PC20) Polybutylene...
Open the catalog to page 9
Delta PT® Thread Forming Fasteners Delta PT® fasteners are engineered to provide maximum performance in a wide range of thermoplastics. The improved design results in a stronger fastener that creates optimal material flow during installation, providing higher performance, better clamp loads and increased joint life. engineered flank geometry optimal material flow Key Advantages • Provides optimal performance in all types of thermoplastics • Provides increased torsional and tensile strength over PT fasteners • Provides high strength and in-place reliability • Can achieve higher clamp loads...
Open the catalog to page 10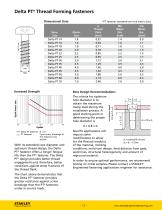
Delta PT® Thread Forming Fasteners Dimensional Data Nom. Size Delta PT 14 Delta PT 16 Delta PT 18 Delta PT 20 Delta PT 22 Delta PT 25 Delta PT 30 Delta PT 35 Delta PT 40 Delta PT 45 Delta PT 50 Delta PT 60 Delta PT 70 Increased Strength *PT fastener standards are true metric sizes. Boss Design Recommendations The criteria for optimum hole diameter is to obtain the maximum clamp load during the installation process. A good starting point in determining the proper hole diameter is d = 0.8 x d1 Delta PT fastener R = 0.1 PT fastener Cycle stress; breakage of the fastener cross section With its...
Open the catalog to page 11
PT® Thread Forming Fasteners With a high thread profile and recessed thread root, the PT® fastener provides increased thread engagement with minimal stress on the boss. It provides optimal performance in a wide range of thermoplastics. 30° thread profile narrow thread pitch recessed thread root Key Advantages • Optimizes performance in all types of thermoplastics • Provides maximum resistance to back-out and pull-out • Minimizes boss failure • Increases product reliability Specifications • Sizes: K15 – K100 in diameter up to 127mm under head • Head Styles: Can be used with any head design •...
Open the catalog to page 12All STANLEY Engineered Fastening catalogs and technical brochures
-
ENGINEERED FASTENING SOLUTIONS
200 Pages
-
Pro Weld Model Type AG-804
1 Pages
-
Pro Weld Model Type AG-805
1 Pages
-
Pro Weld Model Type AG-900
1 Pages
-
ARC-656
2 Pages
-
Cold formed Specials
12 Pages
-
Taptite 2000
12 Pages
-
Engineered Standards®
32 Pages
-
Torx Plus
16 Pages
-
NeoSpeed
4 Pages
-
SAT Catalog EFS Europe
160 Pages
-
Octolok imperial
4 Pages
-
Lockbolt Systems
96 Pages
-
NeoBolt® Lockbolt System
12 Pages
-
SAT Catalog EFS
180 Pages
-
Speed Fastening Systems
96 Pages
-
Breakstem Riveting Systems NA
128 Pages
-
ProSert XTN20
2 Pages
-
734 AV? Series
6 Pages
-
MULTI-GRIP RIVET DATA SHEET
2 Pages
-
LS RIVET DATA SHEET
2 Pages
-
Spiralock Fastener
19 Pages
-
POP Blind Riveting Systems
68 Pages
-
HeliCoil
40 Pages
-
Heli-Coil Aftermarket Products
24 Pages
-
Tucker Emhart Plastics
8 Pages
-
POP NUT Manual & Power Tools
8 Pages
-
Heli-Coil Tangless
6 Pages
-
QA Socket Trays
2 Pages
Archived catalogs
-
Intelligent Air Tools Brochure
12 Pages
-
Air Tool Configuration Catalog
40 Pages




















































