Website:
StandexMeder Electronics GmbH
Website:
StandexMeder Electronics GmbH
Group: Standex Electronics
Catalog excerpts

LEADING BRANDS Reed Technology
Open the catalog to page 1
Content Reed Switch Characteristics Reed Switch Operational Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 The Basic Reed Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8 Basic Electrical Parameters of Reed Switch Products . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 How Reed Switches are used with a Permanent Magnet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18...
Open the catalog to page 3
PRODUCT SOLUTIONS. AS DIVERSE AS THE MARKETS WE SERVE.
Open the catalog to page 4
Standex Electronics is a worldwide market leader in the design, development and manufacture of standard and custom electro-magnetic components, including magnetics products and reed switch-based solutions. We offer engineered product solutions for a broad spectrum of product applications in all major markets, including but not limited to: Our magnetic offerings include planar, Rogowski, current, and low- and high-frequency transformers and inductors. Our reed switch-based solutions include KENT, MEDER and KOFU brand reed switches, as well as a complete portfolio of reed relays, and a...
Open the catalog to page 5
CUSTOMER DRIVEN INNOVATION. PREMIER WORLDWIDE CAPABILITIES. COMMITMENT & EXPERTISE Standex Electronics has a commitment to absolute customer satisfaction and customer-driven innovation, with a global organization that offers premier sales support, engineering capabilities, and technical resources worldwide. Headquartered in Cincinnati, Ohio, USA, Standex Electronics has eight manufacturing facilities in six countries, located in the United States, Germany, China, Mexico, the United Kingdom, and Japan • Coil Molding & Packaging • Insert and Thermoset Molding • Low Pressure Molding (Hot Melt)...
Open the catalog to page 6
• Stainless Steel Fabrication and Precise Laser Welding • Transformer Design And Manufacturing • Wave Soldering • Picoammeters • Destructive Pull Testers • Gauss / Teslameters ENGINEERING • Electronic sensor engineering • Circuit Design and PCB Layout • Patented Conductivity Sensors • Patented Inductive Sensors QUALITY/ LAB CAPABILITIES • Certifications: AS9100, ITAR, ISO9000, TS16949 • SPC Data Collection • Fully Equipped Certified Test Labs • 3-D Magnetic Sensor Mapping • Burn-in and Life Testing • Complete, In-House Machine Shop • Corona Discharge Testing Capabilities • Quick Turn...
Open the catalog to page 7
Reed Switch Characteristics Reed Switch Operational Characteristics The Reed Switch was first invented by Bell Labs in the late 1930s. However, it was not until the 1940s when it began to find application widely as a sensor and a Reed Relay. Here it was used in an assortment of stepping/ switching applications, early electronic equipment and test equipment. In the late 1940s Western Electric began using Reed Relays in their central office telephone switching stations, where they are still used in some areas today. The Reed Switch greatly contributed to the development of telecommunications...
Open the catalog to page 9
Reed Switch Characteristics The Basic Reed Switch Fig. #1 The basic hermetically sealed Form 1A (normally open) Reed Switch and its component makeup. Fig. #2 The 1 Form C (single pole double throw) three leaded Reed Switch and its component makeup. A Reed Switch consists of two ferromagnetic blades (generally composed of iron and nickel) hermetically sealpowered in a glass capsule. The blades overlap internally in the glass capsule with a gap between them, and make contact with each other when in the presence of a suitable magnetic field. The contact area on both blades is plated or...
Open the catalog to page 10
Reed Switch Characteristics Figure 3 shows the general function of a Reed Switch with the us of a permanent magnet. Fig. #3 The basic operation of a Reed Switch under the influence of the magnetic field of a permanent magnet. The polarization of the reed blades occurs in such a manner to offer an attractive force at the reed contacts. The use of a coil wound with copper insulated wire. See Figure 4. Fig. #4 A Reed Switch sitting in a solenoid where the magnetic field is strongest in its center. Here the reed blades become polarized and an attractive force exists across the contacts. When a...
Open the catalog to page 11
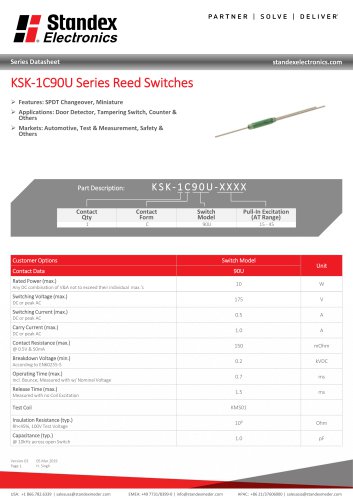
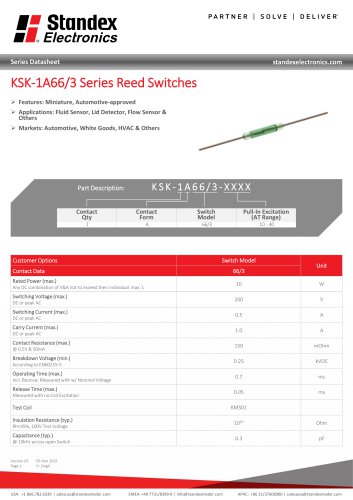
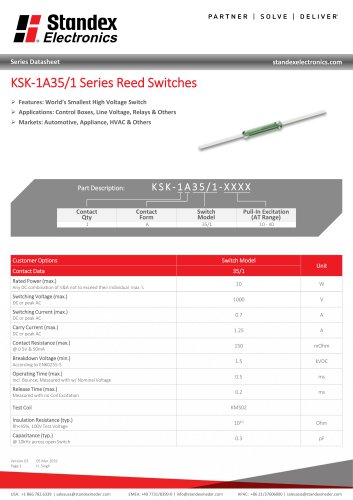
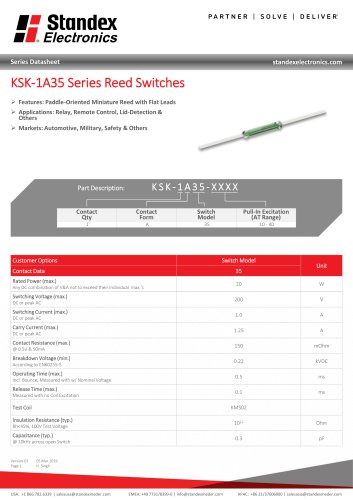
Reed Switch Characteristics Basic Electrical Parameters of Reed Switch Products Pull-In (PI) is described as that point where the contacts close. Using a magnet, it is usually measured as a distance from the Reed Switch to the magnet in mm (inches) or in field strength AT, mTesla, or Gauss. In a coil, the Pull-In is measured in volts across the coil, mA flowing in the coil, or ampere-turns (AT). Generally, this parameter is specified as a maximum. No matter how well the reed blades are annealed, they will still have a slight amount of retentivity (a slight amount of magnetism left in the...
Open the catalog to page 12
Reed Switch Characteristics Drop-Out (DO) is described as that point where the contacts open and has similar characteristics as the Pull-In above. It is also described as release or reset voltage current or AT. Hysteresis exists between the Pull-In and Drop-Out and is usually described in the ratio DO/PI expressed in %. The hysteresis can vary depending upon the Reed Switch design, (Figure #7), where variations in plating or sputtering thickness, blade stiffness, blade overlap, blade length, gap size, seal length, etc. will all influence this parameter. See Figure 7 for example of...
Open the catalog to page 13
Reed Switch Characteristics Fig. #9 A schematic diagram of a typical circuit used for measuring the dynamic contact resistance across the contacts of a Reed Switch. Fig. #10 A typical dynamic contact resistance portrayal showing the first closure, bouncing, dynamic noise and pattern generated by waver-ing contacts Applying the frequency described above to a coil, the contacts will operate and close in approximately ½ mA. The contacts may then bounce for about 100ms and undergo a period of dynamic noise for as much as ½ ms. This dynamic noise is generated by the contacts continuing to bounce...
Open the catalog to page 14All StandexMeder Electronics GmbH catalogs and technical brochures
-
Magnetic Floats
2 Pages
-
Activate Distance
40 Pages
-
Switch Green
6 Pages
-
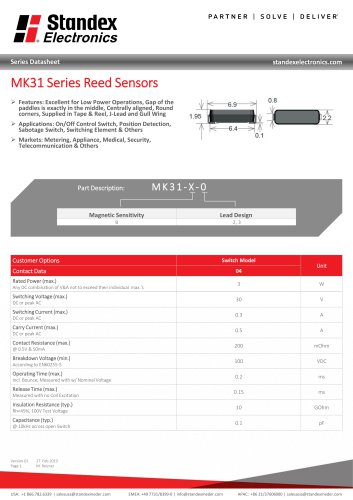
MK31 SERIES REED SENSOR
2 Pages
-
Product Line Brochure Magnetics
24 Pages
-
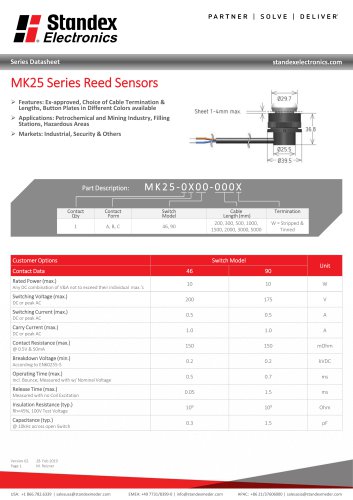
MK25 SERIES REED SENSOR
3 Pages
-
MK28 SERIES REED SENSOR
2 Pages
-
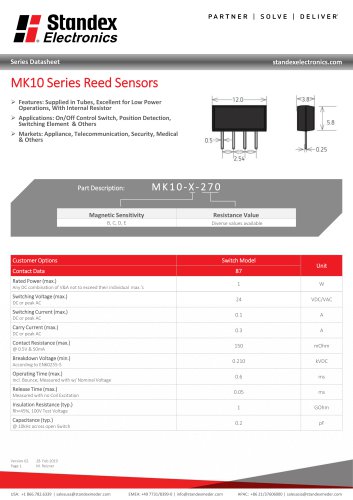
MK10 SERIES REED SENSOR
2 Pages
-
MK02-6 SERIES REED SENSOR
2 Pages
-
MK06 SERIES REED SENSOR
3 Pages
-
MK27 SERIES REED SENSOR
3 Pages
-
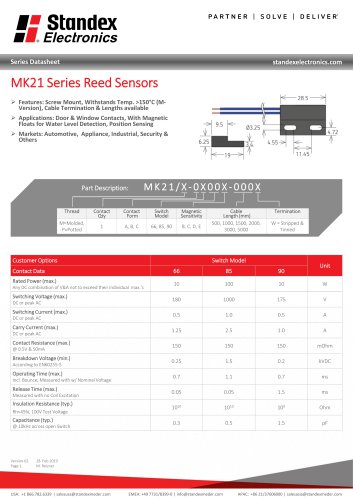
MK21 SERIES REED SENSOR
3 Pages
-
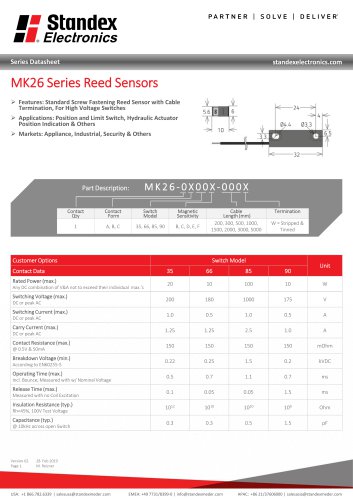
MK26 SERIES REED SENSOR
3 Pages
-
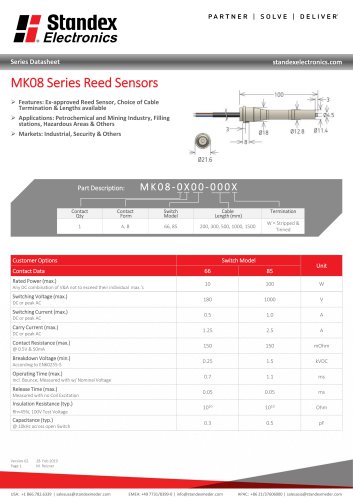
MK08 SERIES REED SENSOR
3 Pages
-
MK02 SERIES REED SENSOR
3 Pages
-
MK13 SERIES REED SENSOR
3 Pages
-
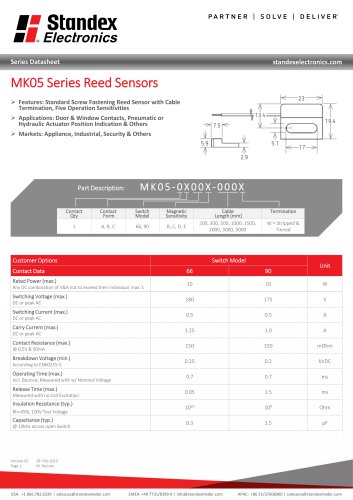
MK05 SERIES REED SENSOR
3 Pages
-
MK04 SERIES REED SENSOR
3 Pages
-
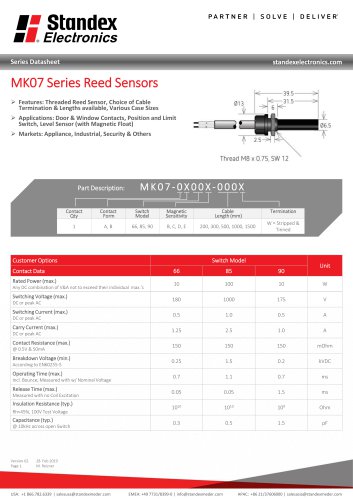
MK07 SERIES REED SENSOR
3 Pages
-
MK03 SERIES REED SENSOR
2 Pages
-
MK14 SERIES REED SENSOR
3 Pages
-
MK18 SERIES REED SENSOR
2 Pages
-
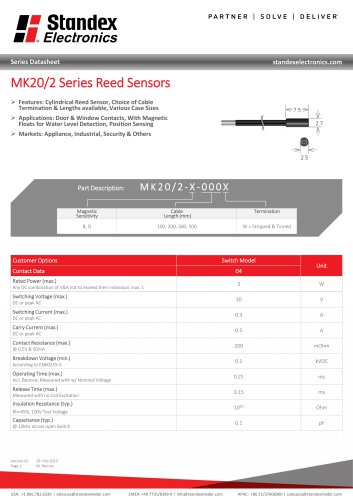
MK20/2 SERIES REED SENSOR
2 Pages
-
MK01 SERIES REED SENSOR
3 Pages
-
MK30 SERIES REED SENSOR
2 Pages
-
MK15 SERIES REED SENSOR
2 Pages
-
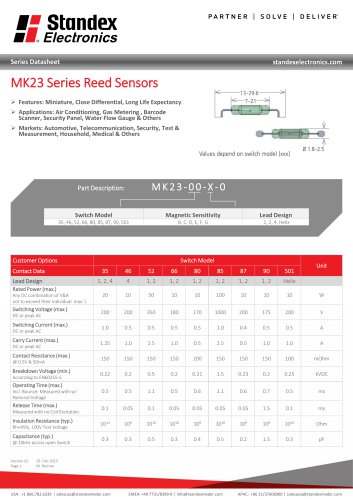
MK23 SERIES REED SENSOR
4 Pages
-
MK22 SERIES REED SENSOR
2 Pages
-
MK17 SERIES REED SENSOR
2 Pages
-
MK16 SERIES REED SENSOR
2 Pages
-
MK24 SERIES REED SENSOR
2 Pages
-
LS05 Series Data Sheet
2 Pages
-
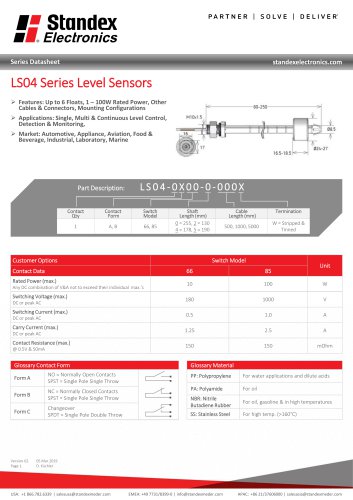
LS04 Series Data Sheet
2 Pages
-
LS03 Series Data Sheet
3 Pages
-
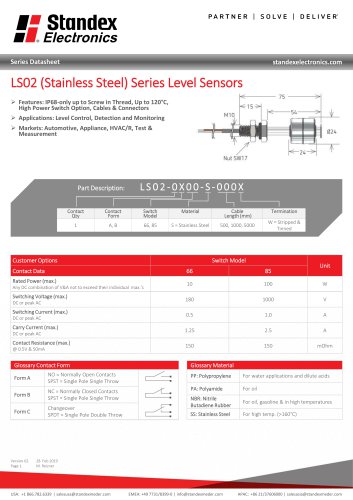
LS02-S Series Data Sheet
2 Pages
-
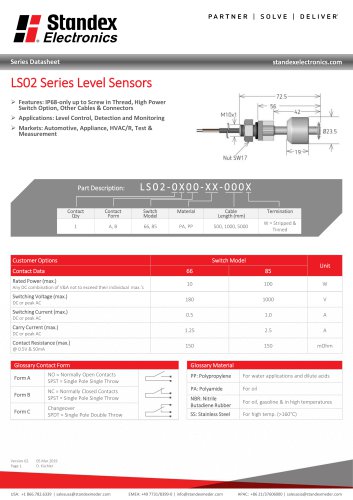
LS02 Series Data Sheet
2 Pages
-
LS01 Series Data Sheet
2 Pages
-
PQ32 Planar Inductors
1 Pages
-
UMS SERIES REED RELAY
3 Pages
-
SIL SERIES REED RELAY
3 Pages
-
SIL RF SERIES REED RELAY
3 Pages
-
SIL HV SERIES REED RELAY
3 Pages
-
RM05-8A-S SERIES REED RELAY
3 Pages
-
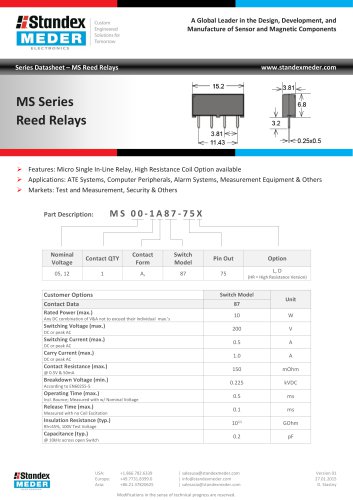
MS SERIES REED RELAY
3 Pages
-
MRX SERIES REED RELAY
3 Pages
-
LI SERIES REED RELAY
3 Pages
-
KT SERIES REED RELAY
3 Pages
-
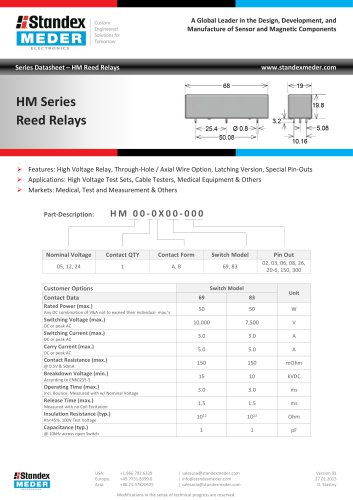
HM SERIES REED RELAY
3 Pages
-
HI SERIES REED RELAY
3 Pages
-
HF SERIES REED RELAY
3 Pages
-
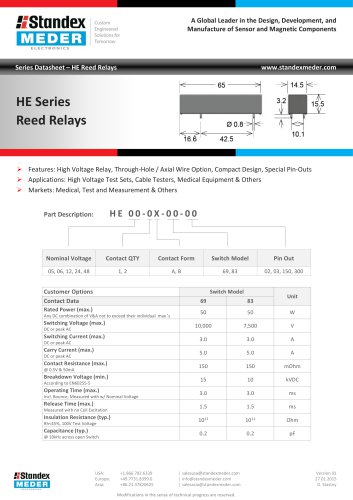
HE SERIES REED RELAY
3 Pages
-
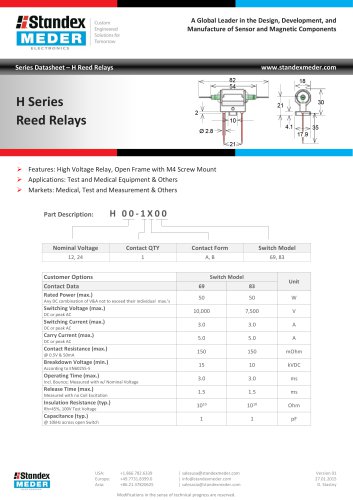
H SERIES REED RELAY
2 Pages
-
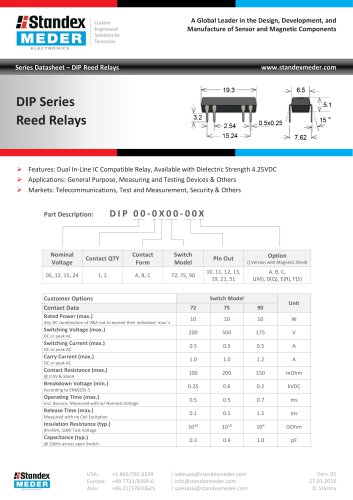
DIP SERIES REED RELAY
3 Pages
-
DIL SERIES REED RELAY
3 Pages
-
CRR SERIES REED RELAY
3 Pages
-
CRF SERIES REED RELAY
3 Pages
-
BT SERIES REED RELAY
3 Pages
-
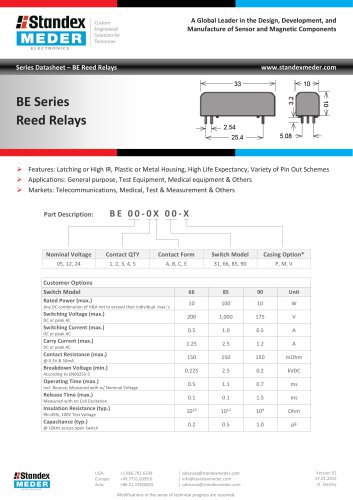
BE SERIES REED RELAY
3 Pages
-
Optocoupler 567 Series
2 Pages
-
Optocoupler 535 Series
2 Pages
-
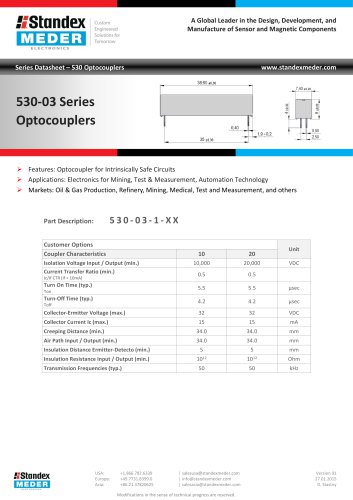
Optocoupler 530-03 Series
2 Pages
-
Optocoupler 530-70 Series
2 Pages
-
Optocoupler 528 Series
2 Pages
-
Optocoupler 525 Series
2 Pages
-
Optocoupler 522 Series
2 Pages
-
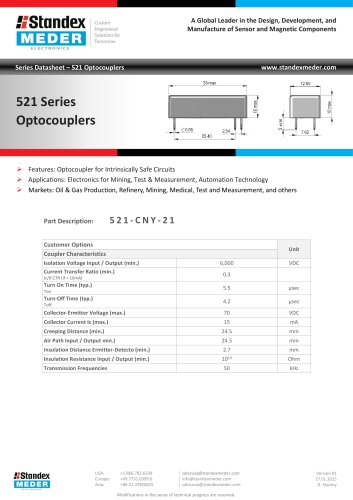
Optocoupler 521 Series
2 Pages