Catalog excerpts

Measuring concentration of liquids Comparison of measuring methods
Open the catalog to page 1
Increase quality, save resources: LiquiSonic®. With high-quality, innovative sensor technology. Robust, precise, user-friendly. LiquiSonic® LiquiSonic® is an inline analytical system for determining the concentration in liquids directly in the production process. The analyzer is also used for phase separation and reaction monitoring. Sensor installation within the product stream means an extremely fast measurement that responds immediately to process changes. User benefits include: • • • • • • • • optimal plant control through online and real-time information about process states maximized...
Open the catalog to page 2
Inline process analysis Contents Sonic velocity Alternative measuring methods
Open the catalog to page 3
Sonic velocity Measuring the sonic velocity relies on the measurement of running time. An ultrasonic signal is sent through the liquid from a sender to a receiver. The speed of the signal is calculated by measuring the time the signal needs to travel from the sender to the receiver. Because the distance between the sender and receiver is constant, the sonic velocity can be determined. transmitter receiver v: sonic velocity s: distance between sender and receiver t: signal delay Measuring principle of sonic velocity For example, at 20 °C the sonic velocity of water is 1.483 m/s. Depending on...
Open the catalog to page 4
Sonic velocity
Open the catalog to page 5
Alternative measuring methods Density Density measurement is based on a spring-mass system in which a tube is made to oscillate mechanically. The frequency of oscillation is dependent on the spring constant and on the mass of the tube, including its content. Assuming the mass and volume of the tube remain constant, the density of liquid contained in the tube can be determined by measuring the frequency. The spring rigidity of a tube is dependent on temperature. Generally, the temperature is measured in the device to compensate for its dependency. Measuring principle of density Sonic...
Open the catalog to page 6
Conductivity Electrolytic conductivity measures the ability of a solution to transport ionic charges. It is dependent on the type and concentration of ions in the solution, in addition to temperature (up to 3 % per °C). With the help of a coil, inductive conductivity sensors trigger a current in the liquid. This current is then measured and analyzed by a second coil. The accuracy of the conductivity measurement amounts to 0.5 % of the measuring range, though accuracy decreases in cases of temperature fluctuations and when inadequate installation conditions are present. Measuring principle...
Open the catalog to page 7
Refractometry The refractometer determines the refractive index of liquids and solids. Calculating the refractive index depends on refraction of light, which is reflected or scattered by a liquid. Light scatters differently depending on the type and concentration of dissolved solid. Therefore, the refractive index is determined by the concentration of the dissolved solid. An optimal sensor (window) measures the reflection of a light beam from an LED light source upon reaching the sample. Measuring principle of refractometry Sonic velocity sensor concentration determination specific sonic...
Open the catalog to page 8
Radiometry A radioactive source sends its rays through the material that is received by the detector. A scintillator uses light flashes to convert and determine the number of radioactive rays. Because the penetration of gamma rays is dependent on the type of matter, density is determined by the intensity of the incoming rays. Measuring principle of radiometry Sonic velocity sensor concentration determination specific sonic velocity is required; (laboratory testing or media databases) density can be calculated from intensity of incoming radiation; sufficient documentation calibration liquid...
Open the catalog to page 9
Clamp-on The clamp-on method is based on measuring the ultrasonic transit-time differential. To this end, the two ultrasonic sensors are installed to the pipe from the outside. An ultrasonic signal is sent from one sensor and received by another. Ultrasonic signals are emitted alternately in the flow direction and against it. The duration of sonic signals is shorter in the flow direction than in the one against it. Sonic velocity is the ratio of the ultrasonic signals in the liquid and the duration. Duration functions as an average of the duration of both sensor signals in the liquid,...
Open the catalog to page 10
Spectroscopy Spectroscopic examination methods facilitate the characterization of atoms, ions and molecules through specific wavelengths that can be measured using emission, absorption, distribution, etc. In atomic spectroscopy, the type of spectroscopic procedure used to analyze the chemical elements of atoms is differentiated based on emission, absorption or fluorescence processes (for example, gamma-ray spectroscopy, atomic spectroscopy AFS). Molecular spectroscopy is based on the excitation and evaluation of rotation, oscillation and electronic states in molecules. In the process,...
Open the catalog to page 11
pH-value One of the oldest chemical parameters in laboratory and industry is the pH-value. It is a measure for the alkalinity or basicity of a solution and is defined as the negative decadic logarithm of the hydrogen ion activity. In laboratories pH-sensors are common practice, whereby inline sensors can be in use directly in the process too. Thereby, it is necessary to pay attention to operation site, material resistance and durability, because pH-sensors are well known as very susceptible measuring technology. Offline, rarely inline pH-titrators can be found in the industrial environment,...
Open the catalog to page 12
Alternative measuring methods
Open the catalog to page 13
Quality and Support Enthusiasm for technical progress is the driving force behind our company as we seek to shape the market of tomorrow. As our customer you are at the center of all our efforts and we are committed to serving you with maximum efficiency. We work closely with you to develop innovative solutions for your measurement challenges and individual system requirements. The growing complexity of application-specific requirements means it is essential to have an understanding of the relationships and interactions involved. Creative research is another pillar of our company. The...
Open the catalog to page 14All SensoTech catalogs and technical brochures
-
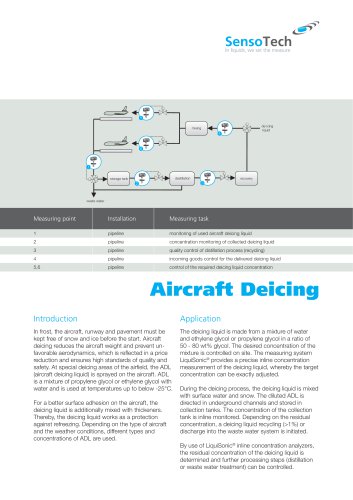
Aircraft Deicingy
3 Pages
-
Company Profile
8 Pages