
Catalog excerpts

TIA-4000 O/E Converter Optical Oscilloscope Probe Benefits: • Wavelength Response 950 nm to 1650 nm • Bandwidth 30 KHz to 7 GHz typical • Low Noise, High Gain • SMA type K Output Electrical Connector • Gain Settings from 2 to 7 • FC/APC Style Fiber Optic Input Connector The TIA-4000 is comprised of a fiber coupled InGaAs APD detector combined with a variable reverse bias voltage network and fast transimpedance amplifier. The output of the unit brought out to a type K female SMA connector. Light falling on the detector generates a positive-going proportional current. This current, multiplied by the transimpedance produces a voltage that is proportional to the light incident on the detector surface. Normally the unit is used to drive a coaxial cable, this cable should have a 50 ohm characteristic impedance and be terminated with a 50 ohm load at the oscilloscope or other measuring device to be used. The active area of the TIA-4000 is 30 microns in diameter. It is coupled to a single mode optical fiber. Typical optical return loss is 52 dB and is caused primarily by the FC/APC connector employed. The applied bias voltage controls the gain of the APD. This voltage in turn, is controlled by means of the two push buttons on the top panel. The rightmost button increases the gain and the leftmost button decreases the gain. There are 64 discrete gain settings that are retained in non-volatile memory when the power is turned off. Thus the gain setting will be retained even though power is disconnected from the unit. Pressing a button once causes the unit to advance in the selected direction by one step. Holding the button down causes the unit to advance automatically until a limit is reached.
Open the catalog to page 1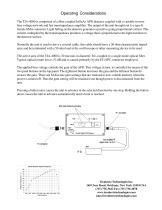
Operating Considerations The TIA-4000 is comprised of a fiber coupled InGaAs APD detector coupled with a variable reverse bias voltage network and fast transimpedance amplifier. The output of the unit brought out to a type K female SMA connector. Light falling on the detector generates a positive-going proportional current. This current, multiplied by the transimpedance produces a voltage that is proportional to the light incident on the detector surface. Normally the unit is used to drive a coaxial cable, this cable should have a 50 ohm characteristic impedance and be terminated with a 50...
Open the catalog to page 2All Scitec Instruments catalogs and technical brochures
-
MPL-N-257
1 Pages
-
DCS500PA
1 Pages
-
C-995
2 Pages
-
360C
2 Pages
-
340CD
2 Pages
-
HPT-5100
2 Pages
-
FPM-250
2 Pages
-
FLS-1350
1 Pages
-
V-250
2 Pages
-
LTX-5525
2 Pages
-
LTX-5510
2 Pages
-
LTX-5520
2 Pages
-
LTX-510
1 Pages
-
TIA-3000
2 Pages
-
TIA-1200
2 Pages
-
TIA-950
2 Pages
-
TIA-527
2 Pages
-
TIA-525
2 Pages
-
LTX-5515
2 Pages
-
LTS-1500
2 Pages
-
C995
2 Pages
-
360C OEM
2 Pages
-
350CD
2 Pages
-
300CD
2 Pages
-
IR Source Series 70
9 Pages
-
Infra Red Source Series 50
2 Pages
-
IR Source Series 40
1 Pages
-
IR Source Series 30
2 Pages
-
Infrared Source Series 20
6 Pages
-
IR Source Series 18-19
4 Pages
-
IR Source Series 12
6 Pages
-
Model 310CD
2 Pages
-
Optical Chopper
2 Pages
-
Energy Sensor Heads
2 Pages
-
Power Measuring
1 Pages
-
Mini-spectrometer
4 Pages
-
Motorized Filter Wheel
2 Pages
-
UV LOG USB and UV LOG 485
4 Pages
-
UVLOG
3 Pages
-
ZA - Laser with Ø 20mm
1 Pages
-
ZM-18H
2 Pages
-
Z-LASER - Laser for positioning
32 Pages
-
Laser – Powermeter
1 Pages
-
UV Probe Selection Process
3 Pages
-
CH 10
2 Pages

























































