
Catalog excerpts

General Catalogue
Open the catalog to page 1
Madrid, Espaha c/ Giiviiynes, ] i Pet. ind. Pfrrto - f rtaciin | 733 20 Pinto j Madrid) Madrid, Espana c/Albatrosr 30 | Pol. Ind. Pinto - L"5tacibn| 28320 Pinta [Madrid; E-mail: jnfoOrtr.es La Estcra n* 66S. | Panamericana Norte, Km 1 7 Lcteo Val.'e Grande Lsmpa.. Chile Oflcina Cornercial 7^ ~ Room 209, Building Q | Focus Square Center, No. 6 FuTong East Avenue Chaoyang District. Beijing I 00 T 02, P.R.C.
Open the catalog to page 2
Electric Capacitors • Electrical function of a capacitor 11 • Voltage influence in capacitors 14 • Three-phase power capacitors 17 • Leakage capacitor's tangent 19 • Handling precautions and security 20 Reactive Energy Compensation • Reactive energy associated troubles 26 • Reactive energy compensation's benefits 27 Reactive energy compensation's economic saving 29 • Capacitive energy calculation needed for compensation 30 • Configurations for reactive energy compensation 32 • Motors and transformers compensation 34 • Quality, installation and protection 37 • Case study: commercial...
Open the catalog to page 3
Índex Reactive Energy Formulary Magnitudes and associated units table; most frequent multiples and submultiples table Capacitors and filter reactances in case of harmonic presence Electric Capacitors Reactive Power of a capacitors bank Capacitors hree phase capacitors with connector T MA/C/CE/TER Series einforced three phase capacitors with connector R MA/C/CE/TER RTF Series hree phase capacitors with connector for harmonics filter applications T MA/C/CE/TER RCT Series hree phase capacitors with connector T DW Series (New Compact Design) hree-phase capacitors T BO/R/TER Series einforced...
Open the catalog to page 4
Automatic Capacitor Banks • Automatic capacitor banks COMPACT-3 Series 98 • Automatic capacitor banks COMPACT-5 Series 100 • Automatic capacitor banks COMPACT-9 Series 102 • Automatic capacitor banks MINI-MURAL Series 104 • Automatic capacitor banks MURAL Series 108 • Automatic capacitor banks MODULAR Series 112 • Thyristor switching automatic capacitor banks ST Series 116 • Automatic capacitor banks with harmonic filters ARM Series 120 Medium Voltage • General information of MV Capacitors 126 • Technical characteristics and dimensions of three-phase MV Capacitors 127 • Technical...
Open the catalog to page 5
• Automatic reactive power controller PR-2D Series 146 • Automatic reactive power controller PR-5D Series 147 • Automatic reactive power controller PR-8D Series 148 • Summation current transformers RT Series 149 • Split core current transformers RT...P Series 150 Lighting Capacitors Ballasts for discharge lamps Ventronic Electronic Ballast
Open the catalog to page 6
General Information A capacitor is an electrical component, which stores electric charge. Its most important application is that of power factor correction (see Reactive compensation chapter). The capacitive element’s constructive material depends on its application. RTR Energía S.L. manufactures cylindrical capacitors with propylene film, metallized with elements such as Al o Zn, which makes it self-healing and reduces the possible losses. This film will have different thicknesses depending on the working voltage. The elements used for metallizing act as current conductors, and the...
Open the catalog to page 10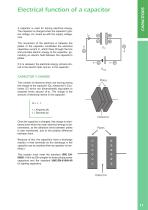
A capacitor is used for storing electrical energy. The capacitor is charged when the capacitor’s plates voltage, Uc, levels up with the supply voltage, Uca. The movement of the electrons in between the plates of the capacitor constitutes the electrical capacitive current Ic, which flows through the line and provides electric energy to the capacitor, generating an electric field between the capacitor’s plates. If Ic is released, the electrical energy remains stored in the electric field, and so, in the capacitor. CAPACITOR´S CHARGE The number of electrons which are moving during the charge...
Open the catalog to page 11
Capacitance and dielectric Voltage is very influential in the behaviour of the capacitor, thus the charge fluctuates with it. Charge (Q) Supply voltage (U) ratio is a constant value, which depends on the capacitor’s frame and is denoted as capacitance (C), measured in Farads (F). Submutiples table Prefix Q = [Coulombs ] U = [Volts ] C = [ Farads ] A capacitor has a 1 Farad capacitance when it stores a charge of 1 Coulomb if a 1 V voltage is applied between the plates. Keeping the basic principle of capacitor’s dependence, which states that the bigger it is the area of the plates, the bigger...
Open the catalog to page 12
Depending on the values of the constants of every dielectric, there is a limit potential difference, which all materials can manage throughout the thickness. This limit is defined as electrical stiffness. Because of determined electric-power system conditions or extreme temperatures, inadmissible for the correct working of the capacitor, this voltage limit can be overfilled. Thus, the dielectric can be bored and an electric arc will be formed between the plates. 1 Electrodes (Metallized Film) 2 Prolypylene Film (Dielectric) 3 Electric connection 4 No metallized area The propylene film...
Open the catalog to page 13
Voltage influence in capacitors DIRECT VOLTAGE When a capacitor is connected to a continuous voltage, Ucc, the current has a very high intensity and is limited by the ohmic resistance, which is tiny in the capacitor. When the voltage between the plates of the capacitor increases, the current gradually decreases. When the charging process is finished, the current intensity becomes zero. In continuous rating and direct voltage, the capacitor behaves as an open circuit. During the discharge process of the capacitor, the voltage and the current decrease with the same ratio, and so they become...
Open the catalog to page 14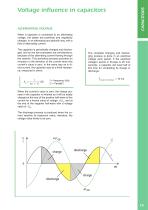
Voltage influence in capacitors ALTERNATING VOLTAGE When a capacitor is connected to an alternating voltage, the plates are positively and negatively charged, in an alternating and periodic way, with a flow of alternating current. The capacitor is periodically charged and discharged, and so the two processes are simultaneous, because of the alternating current flowing through the network. This periodical process provokes an inversion in the direction of the current when this current’s value is zero. In the same way as in direct current, the capacitor acts as a finite resistance, measured in...
Open the catalog to page 15All RTR Energía catalogs and technical brochures
-
LV PFC Capacitors
12 Pages
-
Controller PR-5D & PR-6D
12 Pages
-
Controller PR-2D
12 Pages
-
Lamps General Catalogue
20 Pages
-
Lighting
32 Pages
-
Power Factor Correction
60 Pages
-
Three Phase Harmonic Filters
2 Pages
-
Three Phase Capacitors
2 Pages











