Catalog excerpts

DATA SHEET MR02D02_04 Issue 04, 11th July 2023 MR Bonded Radial Incremental Magnetic Rings VARIOUS SIZES AND MOUNTING OPTIONS The robust RLS radial magnetic incremental rings consist of an elastoferrite layer firmly bonded on a stainless steel hub. The elasto-ferrite layer is magnetised with 2 mm long alternating magnetic poles, which form an incremental magnetic pattern. A unique or distance-coded (DCRM) reference marks option can also be added to the incremental magnetic pattern. Radial magnetic rings offer reliable solutions for high performance applications. ROBUST DESIGN HIGH OPERATING SPEED Non-contact technology Easy mounting Compatible with RLS LM and RoLin family readheads Different shaft diameters available High speed operation Excellent resistance to dirt and dust Unique or periodic reference mark ROBOTIC JOINTS PAN/TILT POSITIONING
Open the catalog to page 1
General information The bonded radial incremental magnetic rings are a reliable solution for high performance applications. They can be installed with fasteners, by press-fitting or by gluing. To assure safety and reliability at high speeds and temperatures, the rings can optionally be covered with a protective stainless steel foil. For maximum protection and use in particulary harsh environments, the cover foil can be fully welded to the ring. This protective layer also protects the elasto-ferrite from swarfs (e.g. metal, stone, glass, wood, etc.), chemical fluids (oils, coolants, grease,...
Open the catalog to page 2
Storage and handling Storage temperature Operating temperature ߌ High resistance to humidity For higher operating temperatures contact RLS. The magnetic ring should not be exposed to magnetic field densities higher than 25 mT on its surface, as this can damage the ring. HANDLE WITH CARE The use of industrial tools during installation or exposure to strong magnets such as a magnetic base is not recommended as it carries the risk of damaging parts of the system which as a result might not perform in accordance with specifications. Use of tools such as drift, punch or similar are expressly...
Open the catalog to page 3
Accuracy of ring encoder systems The accuracy of the ring encoder measurement is influenced by encoder accuracy errors and installation-dependent errors. In order to evaluate the total accuracy, each of the significant errors must be considered. Fig. 1 shows a typical accuracy error plot with marked particular influences. Encoder accuracy errors System error consists of a magnetisation error, crosstalk and SDE. System error [°] Magnetisation error The following factors influence the result: ⦁ the magnetic inhomogeneity of the elasto-ferrite layer, the ring installation tolerances during the...
Open the catalog to page 4
Crosstalk is an undesirable effect of reference mark magnetisation on the incremental track magnetisation, which leads to accuracy peaks. It depends on both the ride height and the lateral offset. An example of crosstalk is shown in Fig. 2. Rotation [°] Fig. 2. Crosstalk representation. The crosstalk (Ri magnetisation) is circled. Sub divisional error (SDE) or interpolation error The sub divisional or interpolation error is a periodical accuracy error. It is influenced by the following factors: ⦁ the length of poles, ⦁ the homogeneity and cycle definition of magnetic poles, the quality of...
Open the catalog to page 5
Installation-dependent errors Installation and adjustment of the ring and the readhead, in addition to the given encoder-specific error, normally have a significant effect on the overall accuracy of a system. Of particular importance are the installation eccentricity and the effect of deformations resulting from the ring installation. Installation eccentricity Eccentricity can be caused by the misalignment of the ring’s center towards the rotational axis, as can be seen on Fig. 4. The error caused by eccentricity can be calculated by the following formula where Eaccuracy is eccentricity...
Open the catalog to page 6
Technical specifications Mechanical data Material of magnetic layer Hub thermal expansion coefficient (CTE) 11.2 x 10-6 K-1 Environmental data Storage and operating temperature –40 °C to +85 °C For higher operating temperatures contact RLS. Magnetic ring design Structure, appearance and markings The position of the magnetised reference mark is always the same, on the engraved side of the ring as shown in the figure below. OPTIONAL: Protective cover foil Incremental track Magnetic field viewer Reference mark Magnetic layer Stainless steel carrier The shape of the reference mark may vary. The...
Open the catalog to page 7
Reference mark Unique reference mark The readhead must be ordered with reference mark option A (see corresponding readhead data sheet). The magnetic ring must be ordered with reference mark option A (see Part numbering). The shape and position of the magnetised reference mark are critical so this option is only available as factory order. Distance coded reference mark (DCRM) The readhead should be ordered with reference mark option A. The distance coded reference mark option provides multiple reference marks that are individually spaced according to specific mathematical algorithm. Absolute...
Open the catalog to page 8
Installation instructions Machine the mounting shaft according to the dimensions given in the table below. Values in orange represent option with cover foil. Radial ring Shaft diameter (clearance fit installation, fasteners, gluing) - Ds 20 g6 20 g6 30 g6 30 g6 See mounting instructions on page 10 Shaft outer diameter (press-fit) - Dspd
Open the catalog to page 9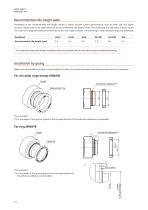
Recommended ride height table Installation at the recommended ride height results in better encoder system performance, such as lower SDE and higher accuracy. Please refer to the table below for the recommended ride height values. The readheads are calibrated at these values. The maximum range of installation tolerances for the ride height is shown in the drawings of the individual rings and readheads. Shaft* Recommended ride height [mm] For maximum range (ride height installation tolerances) please refer to individual ring and readhead drawings. Shaft* Installation by gluing For all radial...
Open the catalog to page 10All RLS catalogs and technical brochures
-
ArtosTM_DBD01_05
21 Pages
-
Artos_DRD01_03
21 Pages
-
RE58_RE58D04_04
22 Pages
-
RE22_RE22D01_10
9 Pages
-
RM22_RM22D01_05
9 Pages
-
MR_MR01D01_06
55 Pages
-
LM13_LM13D01_13
17 Pages
-
LM10 Series
20 Pages
-
AksIM-2_MBD07_05
14 Pages
-
RE16 / RM16
15 Pages
-
SpinCoTM_SP3D01_07
31 Pages
-
AksIM-2_MBD01_11
53 Pages
-
FlexINTM
2 Pages
-
OnAxis™ Redundant_RDD01_01
14 Pages
-
Orbis™
2 Pages
-
DRD01_03
21 Pages
-
SARD01_02
15 Pages
-
ArtosTM_DBD01_05
21 Pages
-
MS Incremental Magnetic Scales
26 Pages
-
AksIM-4
14 Pages

























