Website:
PRECITEC OPTRONIK
Website:
PRECITEC OPTRONIK
Group: PRECITEC
Catalog excerpts

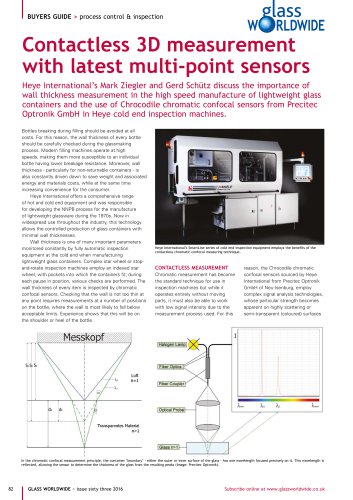
THICKNESS MEASUREMENTS ON BALLOON CATHETERS NONCONTACT MEASUREMENT OF MEDICAL PLASTICS Vision Ballon Testing© MPT Europe It is almost impossible for the wall thickness of balloons and thin-walled tubes (from which balloon catheters are manufactured) to be measured from the inside. The wall thicknesses can merely be estimated mechanically. But a simple solution exists in the form of optical noncontact measuring techniques which offer thickness measurements as a starting point, because these techniques offer so much more. Balloons for angioplasty are usually produced from continuous thin-walled tubes. They are used to widen narrowed or obstructed arteries and veins. The inflated balloon forces expansion of the narrowing within the vessel, opening it up with resulting improved blood flow. The balloon is then deflated and withdrawn. The starting materials are mostly polyurethanes, Nylons or PET with wall thicknesses of 0.015 mm to 0.06 mm (for balloons), comparable to the thickness of human hair. The physical properties of these materials mean that they are globally used for numerous applications (not only in the medical sector). Of particular importance in the medical fields are properties such as resistance to sterilization, gliding properties, mechanical flexibility, processability as well as mechanical and chemical resistance. Historically, parameters such as angles, lengths and diameters were measured with optical measurement systems because they are accessible. Wall thicknesses were determined by compressing the two tube walls together, measuring with a micrometer gauge and halving the result. The accuracy of this procedure is compromised by varying textures and definitely by the soft and yielding material and its low
Open the catalog to page 1
thickness. In addition the subjective nature of the measurement and its influence on results cannot be neglected. Measurement techniques are being extended beyond their capabilities with new, higher quality catheter balloons because of more frequent checking, the need to test at higher mechanical loading plus the analysis being performed under clean-room conditions due to hygiene regulations. Additionally, with the increased use of higher quantities, manufacturing operations require the parallel use of multiple blow-moulding units, further stressing the need for a robust testing technology....
Open the catalog to page 2
thickness decreases with time, while the balloon is still growing. Even silicone breast implants can be measured; such implants are significantly thicker with wall thickness of 2 mm. This can be done nondestructively, while the implant still sits in the mould. As always, the wall thickness is the most interesting part to analyze, due to the probability of it varying in thickness during the manufacturing process (Dip Coating). Balloon dilatation is usually used to expand stents, which remain in the contracted area when the water or contrast media filled balloon (no air is used to fill the...
Open the catalog to page 3All PRECITEC OPTRONIK catalogs and technical brochures
-
CHRocodile MPS 2 L
2 Pages
-
CHRomatic Sensors
2 Pages
-
Heads
2 Pages
-
CHRocodile 2 DPS
2 Pages
-
CHRomatic Vision Camera
2 Pages
-
CHRocodile C Extension Box
1 Pages
-
Flying Spot Scanner
2 Pages
-
Measuring Sensors
2 Pages
-
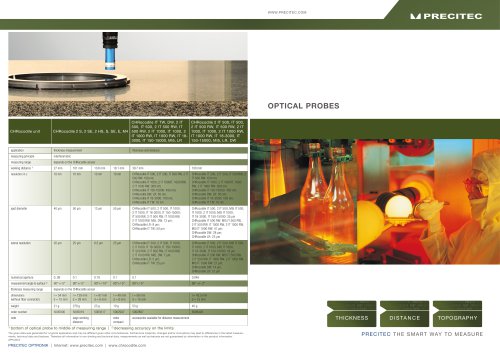
Optical Probes
2 Pages