
Catalog excerpts

becomes discontinuous improving light load operation and reducing power line harmonics. PFC and LLC primary side fault management is provided. The phase of the PFC PWM output is dynamically adjusted relative to the LLC phase such that the switching edges do not coincide with noise sensitive events in the PWM and LLC timing circuits. This edge-collision avoidance technology simplifi es power supply layout and improves performance. Phase synchronization reduces EMI spectral components and reduces ripple current in the PFC capacitor. 2 > Rev. E 05/09 www.powerint.com size="-1">
Open the catalog to page 2
ISP Ω due to internal offset current requirements for the ISP pin. The average inductor current (measured over several switching cycles) is used for the PFC control algorithm. This pin also Implements pulse-by-pulse current limiting. Current sense, PFC. It is for sensing the negative voltage on the current sense resistor (which describes PFC inductor current). This sense resistor is connected between PFC MOSFET Source and Bridge -ђ terminal. The signal must pass through an RC low-pass fi lter with a time constant between 100 and 200 ns. The resistor must be no greater than 150 ISL s. The...
Open the catalog to page 3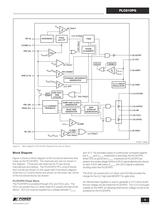
OC +- ISP (3)VCOMP (1)FBP (23) GND (2,19) ISL (22) DVGA and LPF PWM RESETINTERNAL REFERENCEGENERATOR INVERSION 3.3 V LINEARREGULATOR PHASEALIGNMENT > +- PFC FAULT OTAV > FBPREF (6) GATEP(7) VCC (4) VREF(13) VCCHB(12) GATEH(14) HB(16) VCCL(9) GNDL V > +- V > OVH UVLO > +- IN(H) /V > IN(L) V (8) GNDP > +- PFC INHIBIT OC FAULTLLC CLOCK V > UVLO(+) V > UVLO(-) V > SD(H) V > SD(L) +- LLC OFF OVL FAULTLLC OFFLLC FAULTV > REF SOFTSTART CLAMP OVL FAULT OV FAULTV ONE SHOT4096CYCLES LLC CURRENTFEEDBACKRAMP AND CLOCKGENERATOR NON-OVERLAPGENERATOR DEAD TIMEGENERATOR (10) GATEL > +- CLAMP1.2 V FBL...
Open the catalog to page 5
PLC810PG PFC Control Block The voltage developed across the PFC current sense resistor and applied to the ISP pin is compared against an overcurrent threshold (which has built in hysteresis). This implements a pulse-by-pulse current limit to protect the PFC MOSFET against overcurrent.The ISP pin voltage is also averaged (over several switching cycles), and used as an input to the PFC multiplier.The Discrete Variable Gain Amplifi er, DVGA/LPF block is responsible for averaging the ISP pin voltage (over several switching cycles) and implementing a multiplier as part of the PFC control loop,...
Open the catalog to page 6
using a resistor connected between the VREF pin and the FMAX pin using the curve in Figure 15. The resistor on the FMAX pin also sets the LLC dead time interval (see Figure 14).The FBL pin provides output voltage regulation. As such the current entering this pin modulates the switching frequency. More current forces a higher switching frequency. The FMAX pin sets an upper limit for the switching frequency to ensure zero voltage switching. Minimum switching frequency is determined by the adjusting minimum bias applied to the FBL pin.If the external feedback circuit attempts to push the LLC...
Open the catalog to page 7
LLC Outputs The secondary ouputs of transformer T2 are rectifi ed and fi ltered by D9, D10, C38, C39 and C53 to provide the +12 and +24 V outputs. LLC Stage LLC Input Stage Switched +5 V Main Output MOSFETs Q10 and Q11 form the LLC half-bridge. They are driven directly by the PLC810 via gate resistors R56 and R58. Capacitor C39 is the primary resonating capacitor, and should be a low-loss type rated to tolerate the highest RMS current seen at maximum load. Transformer T2 has a large built-in leakage inductance which acts with C39 to form the series resonant tank. Capacitor C40 is used for...
Open the catalog to page 10
OVP Zener diodes VR6-7 and D12, D13 sense any overvoltage condition in the 12 V or 24 V outputs. An overvoltage signal from either output is used to trigger a bipolar latch (Q14, Q15, R70, R73), which turns on transistor Q13. This transistor is used to deactivate the remote on-circuit which turns off the primary bias, and hence the PLC810PG. Voltage Feedback The LLC converter 12 V and 24 V outputs are sensed, weighted, and summed by resistors R64, R66, and R68. Resistor R62 is the main gain-setting resistor. Resistor R63 and C45 form a phase-lead compensator which extends the feedback loops...
Open the catalog to page 11
Ω . The programmed current into the FMAX pin controls two parameters:The LLC drive (GATEL and GATEH) dead-time. The smaller the resistor value, the greater the current and the higher the maximum frequency, see Figure 15. The maximum LLC operating frequency. When the FBL pin current increases above the FMAX pin current, the LLC MOSFETs will be shut down. Switching will restart when the FBL pin current drops below the FMAX pin current. The dead-time should be longer than the actual voltage rise and fall times of the LLC half-bridge center-point (longest times at minimum load). If the...
Open the catalog to page 12
Locating the Bulk Capacitor Ω and 1 Ω . If 2 parallel bulk capacitors are used to meet the ripple current requirement, place 1 near the PFC MOSFET, and the second near the LLC MOSFETs. If only one bulk capacitor is used, it is recommended that a high voltage decoupling capacitor, (10 nF- 100 nF), is connected across the HVDC bus and primary return, connected with short traces to the LLC MOSFETs. (See C40 in schematic in Figure 4, and in PCB layout in Figure 9) The LLC converter MOSFETs see high di/dt, and this high voltage decoupling capacitor will reduce EMI. High Voltage Pins Low Voltage...
Open the catalog to page 14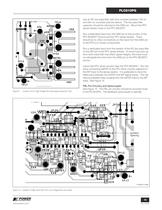
Use an RC low-pass fi lter with time constant between 100 ns and 200 ns, mounted near the device. The low-pass fi lter capacitor should be returned to the GND pin. Mount the PFC sense resistor close to the PFC MOSFET.Run a dedicated trace from the GND pin to the junction of the PFC MOSFET Source and the PFC sense resistor. There should be no other connections on the trace from the GND pin to the PFC/LLC power components.Run a dedicated trace from the resistor of the RC low-pass fi lter on the ISP pin to the PFC sense resistor. To avoid loop pick up from di/dt noise that may effect signal...
Open the catalog to page 15All Power Integrations catalogs and technical brochures
-
InnoSwitch3-AQ
28 Pages
-
InnoSwitch4-CZ
30 Pages
-
LinkSwitch-TNZ
24 Pages
-
2SIS0400T2C0C-33
10 Pages
-
2SMS0220D2C0C-CM1200DC-34X
8 Pages
-
2SML0220D2E0-FF600R17ME4
4 Pages
-
2SIL1200T2A0-33
4 Pages
-
InnoSwitch3-TN
23 Pages
-
ChiPhy
6 Pages
Archived catalogs
-
HiperPLC
26 Pages
-
DPA-Switch
34 Pages
-
CAPZero
8 Pages
-
PeakSwitch™ Family
4 Pages
-
PeakSwitch
24 Pages
-
TOPSwitch-HX
48 Pages
-
TinySwitch-PK
24 Pages
-
TinySwitch-III
24 Pages
-
LinkSwitch-TN
20 Pages
-
LinkSwitch-LP
16 Pages
-
LinkSwitch-II
10 Pages
-
LinkSwitch-CV
20 Pages






















