
Catalog excerpts

PLC810PG HiperPLC™ Family Continuous Mode PFC & LLC Controller with Integrated Half-bridge Drivers Product Highlights Features • Highly integrated, eliminates external components • Frequency and phase synchronized PFC and LLC • Reduced noise and EMI • Ripple current reduction in PFC output capacitor • Edge collision-avoidance simplifies layout • Comprehensive PFC and LLC fault handling and current limiting • Proprietary continuous conduction mode PFC for high efficiency with low component cost • High efficiency Zero Voltage Switching (ZVS) LLC • Off-time PFC control eliminates AC input sensing components • Configurable, precise dead time control and frequency limit • Prevents hard MOSFET switching • Tight LLC duty cycle symmetry for balanced O/P diode currents • Lead and halogen free Green package Applications • 32” to 60” LCD TV power supplies • Off-line 150 W to 600 W efficiency-optimized power supplies • LED street lighting The DC-DC controller drives an LLC resonant topology. This variable frequency controller provides high efficiency by switching the power MOSFETs at zero voltage, eliminating most switching losses. The LLC controller is built around a current controlled oscillator with a control range selected to support the traditional frequency of operation found in televisions. To ensure zero voltage switching, the dead time of the LLC switching in the PLC810PG is tightly toleranced and can be adjusted with an external resistor. The highside/lowside duty cycle is also closely matched to provide balanced output currents reducing output diode cost. A typical PLC810PG LLC design operates at 100 kHz (under nominal conditions). Depending on the LLC circuit design, the switching frequency can vary from half to three times the nominal operating frequency as a result of line and load changes. Description The PLC810PG is a combined PFC and LLC off-line controller with integrated high voltage half-bridge drivers. Figure 1 shows a simplified schematic of a PLC810PG based power supply where the LLC resonant inductor is integrated into the Standby Supply transformer. The PFC section of the PLC810PG is a universal input continuous current mode (CCM) design that does not require a sinusoidal input reference, thereby reducing system cost and external components. The PFC converter is frequency locked to the LLC to minimize noise and electromagnetic interference. Increasing the PFC frequency in synchronization with the LLC at light loads reduces the current at which the PFC boost converter GNDP GNDL Typical Application Circuit – LCD TV Power Supply.
Open the catalog to page 1
PLC810PG becomes discontinuous improving light load operation and reducing power line harmonics. PFC and LLC primary side fault management is provided. The phase of the PFC PWM output is dynamically adjusted relative to the LLC phase such that the switching edges do not coincide with noise sensitive events in the PWM and LLC timing circuits. This edge-collision avoidance technology simplifies power supply layout and improves performance. Phase synchronization reduces EMI spectral components and reduces ripple current in the PFC capacitor.
Open the catalog to page 2
PLC810PG Pin Description VCC Pins VCC VCC powers the small signal analog circuitry inside the IC. A bypass capacitor must be connected from the VCC pin to the GND pin. This capacitor needs to be a 10 mF ceramic capacitor, or a parallel combination of a 10 mF electrolytic capacitor and a 0.1 mF ceramic capacitor. VCCL VCCL is the supply pin for the LLC low side driver. It powers only the LLC low side MOSFET driver and the communications circuitry between the analog circuitry and the LLC drivers. A 1 mF ceramic bypass capacitor must be connected from the VCCL pin to the GNDL pin. This...
Open the catalog to page 3
PLC810PG FMAX This pin is for programming maximum LLC frequency with a resistor to VREF. If the frequency commanded by the FBL pin current exceeds 95% of the programmed maximum frequency, the LLC high and low side drivers turn both LLC MOSFETs off. This pin must be decoupled to the GND pin with a 1 nF capacitor. RSVD1, RSVD2, and RSVD3 RSVD1 must be connected to VREF. RSVD2 and RSVD3 must be connected to the GND pin. Pin Numbering and Designation (Top View).
Open the catalog to page 4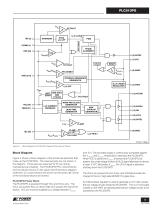
PHASE ALIGNMENT (6) GATEP (7) VCC RESET VUVLO(+) INTERNAL REFERENCE GENERATOR + VREF SOFT ONE SHOT 4096 START CYCLES (13) VCCHB OVL FAULT RAMP AND CLOCK GENERATOR NONOVERLAP GENERATOR DEAD TIME GENERATOR (12) GATEH (14) HB (16) VCCL (10) GATEL Block Diagram of PLC810PG. Reserved Pins are not Shown. Block Diagram Figure 3 shows a block diagram of the functional elements that make up the PLC810PG. The reserved pins are not shown in the diagram. Those pins are reserved for PI use during manufacture and testing. The PLC810PG PFC control blocks and circuits are shown on the upper half of the...
Open the catalog to page 5
PLC810PG PLC810PG PFC Control Block The PLC810PG PFC is a boost converter which conditions the average input current to make it (typically) sinusoidal and in phase with the input voltage. In normal operation the PFC operates in continuous conduction mode (CCM). Under light load, depending on the PFC inductor value, the converter may enter a discontinuous conduction mode (DCM). The PLC810PG PFC controller does not need to sense the input voltage. The PLC810PG PFC controller exploits the fact that the input voltage (VIN) is effectively constant over a few adjacent switching cycles, because...
Open the catalog to page 6
PLC810PG using a resistor connected between the VREF pin and the FMAX pin using the curve in Figure 15. The resistor on the FMAX pin also sets the LLC dead time interval (see Figure 14). The FBL pin provides output voltage regulation. As such the current entering this pin modulates the switching frequency. More current forces a higher switching frequency. The FMAX pin sets an upper limit for the switching frequency to ensure zero voltage switching. Minimum switching frequency is determined by the adjusting minimum bias applied to the FBL pin. If the external feedback circuit attempts to...
Open the catalog to page 7All Power Integrations catalogs and technical brochures
-
InnoSwitch3-AQ
28 Pages
-
InnoSwitch4-CZ
30 Pages
-
LinkSwitch-TNZ
24 Pages
-
2SIS0400T2C0C-33
10 Pages
-
2SMS0220D2C0C-CM1200DC-34X
8 Pages
-
2SML0220D2E0-FF600R17ME4
4 Pages
-
2SIL1200T2A0-33
4 Pages
-
InnoSwitch3-TN
23 Pages
-
ChiPhy
6 Pages
Archived catalogs
-
DPA-Switch
34 Pages
-
CAPZero
8 Pages
-
PeakSwitch™ Family
4 Pages
-
PeakSwitch
24 Pages
-
HiperPLC
26 Pages
-
TOPSwitch-HX
48 Pages
-
TinySwitch-PK
24 Pages
-
TinySwitch-III
24 Pages
-
LinkSwitch-TN
20 Pages
-
LinkSwitch-LP
16 Pages
-
LinkSwitch-II
10 Pages
-
LinkSwitch-CV
20 Pages






















