Catalog excerpts

Why Q-Motion... ? “I‘m pleased to now be able to offer positioning solutions to our customers where classical drive technologies could only fulfill expectations to a limited extent. ” Mark Freyer, Head of Product Division Inertia Drives Why did we develop this product line? Q-Motion stands for a series of miniaturized stages with piezomotor drive principle. Because PI received a large number of enquiries, we noted an increased demand for these very small positioning axes and manipulators, for example, in mobile applications for measuring and medical devices, in industrial microassembly or...
Open the catalog to page 2
Closes a Gap PI draws from a wealth of experience when it comes to implementing piezo ceramic drives in positioning systems. However, PI is certainly not restricted to a special drive technology, but is always able to offer the optimum solution for the many different requirements in the field of motion and positioning. All piezomotor drive principles are distinguished by: ■ ■ Piezo motors combine the high position resolution of the piezo actuators with the unlimited travel ranges of classical drives. The drives in the Q-Motion series are based on one piezoelectric inertia drive that can now...
Open the catalog to page 3
Maximum Flexibility The piezoceramic actuators form the heart of the piezo inertia drive. It can be customized to the special installation conditions of the customer. The electronics are made available from the OEM module to the „intelligence on the chip“ This . makes it easy to integrate the circuitry into customer-specific drivers. Individual axes can be stacked for multi-axis applications such as sample manipulation and adjustment of optical elements, detectors and fiber arrays. Parallel kinematic systems with six degrees of freedom that fit onto the palm of the hand are interesting with...
Open the catalog to page 4
Operating Principle Piezo inertia drives are space-saving and inexpensive piezo-based drives with relatively high holding forces and a virtually unlimited travel range. They make use of the stick-slip effect (inertia effect) – a cyclical alternation of static and sliding friction between a moving runner and the drive element generated by the piezo element – for a continuous feed of the runner. The operating frequency of more than 20 kHz enables the runner to be directly driven at velocities in excess of 10 mm/s (70°/s). Tangential Drive A drive element mounted on the side of the runner...
Open the catalog to page 5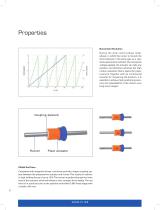
Properties Nanometer Resolution During the slow control phase (stickphase), in which the runner is moved, the drive behaves in the same way as a classical piezoceramic actuator. By varying the voltage applied, the actuator can take any position and therefore achieves the high motion resolution that is typical for piezoceramics. Together with an incremental encoder for measuring the position, it is possible to achieve high positioning accuracy and repeatability of the motion over long travel ranges. PIShift Rod Drive Compared with tangential drives, rod drives provide a larger coupling...
Open the catalog to page 6
The minimum incremental motion is specified with 2 nm for closed-loop linear stages with incremental encoders (1 nm resolution). The small steps are performed reliably with the analog expansion of the piezoelectric actuator. The maximum velocity is 10 mm/s with 20 kHz operating frequency. The graph shows position vs. time over a short range of 0.3 ms and 3 µm travel. Even with a sample frequency of 133 kHz, the profile is linear and the velocity constant. The unidirectional repeatability of a Q-522 with 1 nm encoder resolution is 25 nm. Cost-Effective Piezo inertia drives are based on a...
Open the catalog to page 7
Q-Motion Miniature Stages HIGH RESOLUTION, AFFORDABLE PRICE ½ Linear stages, rotary stages and parallel kinematic robots with six degrees of freedom ½ Direct position measurement with incremental encoder with up to 1 nm resolution (optional) ½ Piezomotor driving principle: Self-locking when at rest, therefore no holding current, no power consumption, no heat generation and no servo jitter Applications Applications can be found in industry and research. The small form factor and the vacuum compatibility make Q-Motion stages ideal positioning tasks in Beamline Instrumentation or electron...
Open the catalog to page 8
Q-Motion Linear Stages Q-521 Q-Motion Miniature Linear Positioning Stage Very Small Linear Positioning Stage with Position Control, High Resolution and Attractive Price Q-522 Q-Motion Miniature Linear Stage Piezomotors for Small Dimensions, High Resolution and a Favorable Price Q-545 Q-Motion Precision Linear Stage High Forces and Small Size Through Piezomotors Q-Motion Rotary Stages Q-614 Q-Motion Miniature Rotation Stage Minimum Dimensions: 14 mm Turntable Diameter Q-622 Q-Motion Miniature Rotation Stage Minimum Dimensions: 22 mm Turntable Diameter Q-632 Q-Motion Rotation Stage Compact...
Open the catalog to page 9
Q-Motion Miniature Linear Positioning Stage W I T H P O S I T I O N C O N T R O L , H I G H R E S O L U T I O N A N D AT T R A C T I V E P R I C E Q-521 ½ Only 21 mm wide and 10 mm high ½ Direct position measurement with integrated incremental encoder (optional) ½ Up to 2 nm minimum incremental motion ½ XY mounting without adapter ½ Travel range 12, 22 or 32 mm ½ Velocity 10 mm/s ½ Feed force 1 N ½ Versions vacuum-compatible to 10-9 hPa Precision-class micropositioning stage Q-Motion stages are distinguished by their extremely small design and high position resolution in the nanometer...
Open the catalog to page 10
Preliminary Data 12 mm travel range, resolution 4 nm 12 mm travel range, resolution 1 nm, UHV version Q-521.14U 22 mm travel range, resolution 4 nm 22 mm travel range, resolution 1 nm, UHV version Q-521.24U 32 mm travel range, resolution 4 nm 32 mm travel range, resolution 1 nm, UHV version Q-521.34U 12 mm to 32 mm travel range, open-loop, UHV versions Q-521.x0U Active axis Travel range Integrated sensor Linear encoder Linear encoder Linear encoder Linear encoder Linear encoder Linear encoder Unidirectional repeatability over entire travel range Bidirectional repeatability over entire...
Open the catalog to page 11All Physik Instrumente catalogs and technical brochures
-
A-143
5 Pages
-
A-811.CE
3 Pages
-
G-902.RxI
5 Pages
-
P-405
4 Pages
-
PRYY
7 Pages
-
A-523
5 Pages
-
M-110 • M-111 • M-112 V6
4 Pages
-
L-812
18 Pages
-
RS-40 V7
4 Pages
-
A-68x
4 Pages
-
G-901
9 Pages
-
G-910.RC02
6 Pages
-
F-712.IRP
6 Pages
-
G-910.RC01 • RC03
4 Pages
-
C-663.12
3 Pages
-
C-887.53x
5 Pages
-
Piezoelectric Discs
7 Pages
-
L-402
5 Pages
-
P-840
4 Pages
-
M-238
5 Pages
-
L-220
5 Pages
-
P-725
9 Pages
-
C-413
3 Pages
-
P-518 • P-528 • P-558
6 Pages
-
PL112 – PL140
4 Pages
-
U-628
3 Pages
-
P-545.3D8S
5 Pages
-
P-611.XZ • P-611.2
4 Pages
-
P-541.2 • P-542.2
5 Pages
-
Leading in Precision Positioning
12 Pages
-
Engineered Systems
8 Pages
-
Precision Motion Control
4 Pages
-
Drivetrain Elements
4 Pages
-
Motors and Drives
3 Pages
-
Positioning with Piezo Systems
248 Pages
-
Hexapod Positioning Systems
133 Pages
-
PIRest Actuators - P-131
4 Pages
-
High-Load Linear Stage - L-417
12 Pages
-
PICA piezo amplifier module
3 Pages
-
V-412 • V-418 • V-423
2 Pages
-
S-335 Fast Tip/Tilt Platform
3 Pages
-
Q-Motion® SpaceFAB
4 Pages
-
A-131
5 Pages
-
d-891
1 Pages
-
PI Datasheet V-275
5 Pages
-
PI Datasheet V-273
5 Pages
-
PI Datasheet VT-80
3 Pages
-
A-65x
4 Pages
-
A-60x.MTT
1 Pages
-
A-80x
3 Pages
-
A-322
3 Pages
-
A-110
3 Pages
-
A-141
3 Pages
-
A-123
5 Pages
-
A-121
5 Pages
-
DT-34
4 Pages
-
D-015 • D-050 • D-100
5 Pages
-
A-10x
3 Pages
-
New Products 2015
48 Pages
-
PI Products for Microscopy
36 Pages
-
PI Electron Microscopy
16 Pages
-
Piezo Motors and Stages
48 Pages
-
Piezo Mike Linear Actuators
16 Pages
-
PI Product Overview
34 Pages
-
PILine® Ultrasonic Piezomotors
20 Pages
-
Piezoelectric Actuators
74 Pages
-
Hexapods 6-Axis Stages
56 Pages
-
Piezo Amplifiers & Controllers
44 Pages