 Website:
Parker Hannifin France SAS
Website:
Parker Hannifin France SAS
Group: Parker
Catalog excerpts

Visit our homepage for additional support parker.com/pmde Hydraulic Motors Series V12, V14, V16 Variable Displacement
Open the catalog to page 1
Catalogue MSG30-8223/UK General information Hydraulic Motors Series V12/V14/V16 Basic formulas for hydraulic motors Flow (q) ηv – volumetric efficiency ∆p – differential pressure [bar] (between inlet and outlet) ηhm – mechanical efficiency Basic formulas for hydraulic pumps Flow (q) – volumetric efficiency ∆p – differential pressure [bar] (between inlet and outlet) ηhm – mechanical efficiency Conversion factors Conversion factors
Open the catalog to page 2
Hydraulic Motors Series V12/V14/V16 Parker Hannifin Pump & Motor Division Europe Trollhättan, Sweden
Open the catalog to page 3
Catalogue MSG30-8223/UK General product information Hydraulic Motors Series V12/V14/V16 Series V12/V14/V16 Series V12/V14/V16 is a bent-axis, variable displacement motor. Parker Variable Bent-axis motors are designed for both open and closed circuit transmissions with focus on high performance machines. V12 series is available in displacement 60 and 80 cc, Max intermittent pressure 480 bar, continuous pressure to 420 bar. V14 series is available in displacement 110 and 160 cc, Max intermittent pressure 480 bar, continuous pressure to 420 bar. V16 series is available in displacement 220 and...
Open the catalog to page 4
Hydraulic Motors Series V12/V14/V16 Bearing life General information Bearing life can be calculated for that part of the load/ life curve (shown below) that is designated ’Bearing fatigue’. ’Fatigue of rotating parts’ and ’Wear’caused by fluid contamination, etc., should also be taken into consideration when estimating the service life of a motor/ pump in a specific application. In reality, bearing life can vary considerably due to the quality of the hydraulic system (fluid condition, cleanliness, etc.) Bearing life calculations are mainly used when comparing different motor frame sizes....
Open the catalog to page 5
Catalogue MSG30-8223/UK General information Hydraulic Motors Series V12 Parker Hannifin Pump & Motor Division Europe Trollhättan, Sweden
Open the catalog to page 6
Hydraulic Motors Series V12 V12 cross section 1. End cap 2. Servo control valve 3. Setting piston 4. Valve segment 5. Cylinder barrel 6. Spherical piston with laminated piston ring 7. Synchronizing shaft 8. Heavy-duty roller bearings 9. Bearing housing 10. Output shaft Specifications V12 frame size Displacement [cm3/rev] - max, at 35° - min, at 6.5° Operating pressure [bar] - max intermittent 1) - max continuous Operating speed [rpm] - at 35°, max intermittent 1) - at 35°, max continuous - at 6.5° – 20°, max intermittent 1) - at 6.5° – 20°, max continuous - min continuous Flow [l/min] - max...
Open the catalog to page 7
Hydraulic Motors Series V12 Continuous Speed vs. Displacement 8 000 Efficiency diagrams The following diagrams show volumetric and overall efficiencies versus shaft speed at 210 and 420 bar operating pressure, and at full (35°) and reduced (10°) displacements. Information on efficiencies for a specific load condition can be made available from Parker Hannifin. Parker Hannifin Pump & Motor Division Europe Trollhä
Open the catalog to page 8
Controls (general information) The following six V12 controls described below satisfy most application requirements: • AC and AH (Pressure compensator) • EO and HO (Two-position controls) • EP and HP (Proportional controls). All controls utilize a setting piston that connects to the valve segment (refer to the picture on page 7). The built-in four-way servo valve acts on the setting piston and determines the displacement which can vary between 35° (max) and 6.5° (min). Hydraulic Motors Series V12 Servo supply pressure is usually obtained from the main high pressure port through the built-in...
Open the catalog to page 9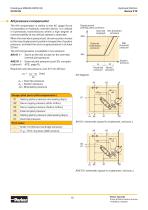
Hydraulic Motors Series V12 AH pressure compensator The AH compensator is similar to the AC (page 9) but incorporates an hydraulic override device. It is utilized in hydrostatic transmissions where a high degree of manoeuvrability at low vehicle speeds is desirable. When the override is pressurized, the servo piston moves to the max displacement position irrespective of system pressure, provided the servo supply pressure is at least 20 bar. The AH compensator is available in two versions: AHI 01 I – Same as the ACI except for the override; internal pilot pressure. AHE 01 I – External pilot...
Open the catalog to page 10
Hydraulic Motors Series V12 EO two-position control The EO is a two-position control, where max and min displacements are governed by a DC solenoid attached to the control cover The EO control is utilized in transmissions where only two operating modes are required: Low speed/high torque or high speed/low torque. The servo piston, normally in the max displacement position, shifts to the min displacement position when the solenoid is activated. Intermediate displacements cannot be obtained with this control. Servo pressure is supplied internally (through the shuttle valve from one of the...
Open the catalog to page 11
Hydraulic Motors Series V12 EP proportional control The EP electrohydraulic proportional control is used in hydrostatic transmissions requiring a continuously variable shaft speed. The position of the setting piston is governed by a DC solenoid attached to the control cover. When the solenoid current increases above the threshold current, the servo piston starts to move from the max towards the min displacement position. The displacement vs. solenoid current is shown in the diagram to the right. Please note, that the shaft speed vs. current is non-linear; refer to the diagram below....
Open the catalog to page 12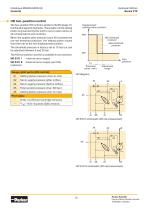
Hydraulic Motors Series V12 HO two-position control The two-position HO control is similar to the EO (page 11) but the pilot signal is hydraulic. The position of the setting piston is governed by the built-in servo valve (same on all compensators and controls). When the applied pilot pressure (port X5) exceeds the pre-set threshold pressure, the setting piston moves from the max to the min displacement position. The threshold pressure is factory set at 10 bar but can be adjusted between 5 and 25 bar. Displacement (setting piston position) Max Max Max The HO two-position control is available...
Open the catalog to page 13All Parker Hannifin France SAS catalogs and technical brochures
-
MPI™ Medium Pressure Products
20 Pages
-
Needle Valves
48 Pages
-
Phastite® Tube Connectors
36 Pages
-
Quick Coupling Products
230 Pages
-
Ball and Plug Valves
72 Pages
-
Aluminium Roller Guides
20 Pages
-
OSPP-Classic
37 Pages
-
Valve Products Isys ISO Series
42 Pages
-
2A Pneumatic Cylinders
48 Pages
-
Stainless Steel Valves
72 Pages
-
Global FRL and P3Y Series
122 Pages
-
MMB Hydraulic Cylinders
24 Pages
-
PWO Water/oil cooler
12 Pages
-
Axial Piston Pumps
28 Pages
-
QDC - Quiet DC Cooler
56 Pages
-
Air Oil Coolers
18 Pages
-
Hydraulic Valves Industrial Standard
817 Pages
-
Quick Couplings Catalog
185 Pages
-
Crankcase Ventilation
12 Pages
-
Condition Monitoring
72 Pages
-
Screw-Driven Positioners
111 Pages
-
Belt Driven Positioners
151 Pages
-
GVI Global Vehicle Inverter
16 Pages
-
GVM142 Global Vehicle Motor
16 Pages



















































