Catalog excerpts

ETH Electro Cylinder Parker High Force Electro Thrust Cylinder
Open the catalog to page 1
WARNING — USER RESPONSIBILITY FAILURE OR IMPROPER SELECTION OR IMPROPER USE OF THE PRODUCTS DESCRIBED HEREIN OR RELATED ITEMS CAN CAUSE DEATH, PERSONAL INJURY AND PROPERTY DAMAGE. • This document and other information from Parker-Hannifin Corporation, its subsidiaries and authorized distributors provide product or system options for further investigation by users having technical expertise. • The user, through its own analysis and testing, is solely responsible for making the final selection of the system and components and assuring that all performance, endurance, maintenance, safety and...
Open the catalog to page 2
High Force Electro Thrust Cylinder - ETH Overview 5 Technical Characteristics 8 Step by Step Selection Process 10 Calculating Required Axial Force 11 Selection of the Size and Screw Lead 12 ETH - Electro Thrust Cylinder for ATEX Environment 12 Service Life 13 Permissible Torque with motor in parallel 15 Permissible Axial Thrust Forces 16 Permissible Side Load 18 Stroke, Usable Stroke and Safety Travel 20 Relubrication 21 Dimensions 22 Motor Mounting Options 1)23 Motor and Gearbox Selection 26 Mounting Methods 27 Standard 27 Center Trunnion Mounting 27 Rear Clevis 28 Front Plate
Open the catalog to page 3
Parker Hannifin The global leader in motion and control technologies A world class player on a local stage Global Product Design Parker Hannifin has more than 40 years experience in the design and manufacturing of drives, controls, motors and mechanical products. With dedicated global product development teams, Parker draws on industry-leading technological leadership and experience from engineering teams in Europe, North America and Asia. Local Application Expertise Parker has local engineering resources committed to adapting and applying our current products and technologies to best fit...
Open the catalog to page 4
ETH Electro Cylinder www.parker.com/eme/eth High Force Electro Thrust Cylinder - ETH Overview Description The ETH electro cylinder closes the gap between pneumatic and hydraulic actuators; it can act as a suitable alternative to both in many applications and can have the added benefit of increasing the reliability of the production process. Taking the costs for air and oil into consideration, you will find that in most cases an electromechanical system such as the ETH electro cylinder offers the more economical solution. Combined with a wide choice of accessories, the ETH becomes a highly...
Open the catalog to page 5
ETH - Electro Cylinder Overview Parker High Force Electro Thrust Cylinder ETH032/050/080 ATEX: End caps and drive housing are not anodized
Open the catalog to page 6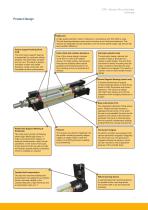
ETH - Electro Thrust Cylinder Overview Product Design Ballscrew A high-quality precision class 7 ballscrew in accordance with ISO 3408 is used. The ball bearings between screw and nut ensure a low frictional resistance. This ensures an especially smooth operation over the entire speed range, high service life and excellent efficiency. Screw support bearing (front end) The front screw support bearing is supported by a polymer sliding bearing. This eliminates vibration and run-out. The result is quieter, smoother motion with better precision, longer screw life, and increased dynamic...
Open the catalog to page 7
ETH - Electro Cylinder Technical Characteristics Technical Characteristics Cylinder size type Screw lead Screw diameter Travels, speeds and accelerations [mm] Available strokes 1) 2) Max. permissible speed at stroke = 50-400 mm 600 mm 800 mm 1000 mm 1200 mm 1400 mm 1600 mm Max. Acceleration continuous from 50continuous from 50continuous from 1001000 & standard strokes 1200 & standard strokes 1600 & standard strokes 333 286 196 146 4 Forces Max. axial traction/thrust force motor inline Max. axial traction/thrust force 3) Motor parallel Equivalent dynamic axial force at a lifetime of 2500 km...
Open the catalog to page 8
ETH - Electro Cylinder Technical Characteristics Cylinder size type Screw lead Screw diameter Travels, speeds and accelerations [mm] Available strokes 1) 2) Max. permissible speed at stroke = 100-400 mm 500 mm 600 mm 800 mm 1000 mm 1200 mm 1400 mm 1600 mm 2000 mm Max. Acceleration Forces Max. axial traction/thrust force motor inline Max. axial traction/thrust. 3) Motor parallel Equivalent dynamic axial force at a lifetime of 2500 km Max. transmissible torque / force constant Max. transmissible torque inline motor Max. transmissible torque. 3) Motor parallel Force constant motor inline 5)...
Open the catalog to page 9
ETH - Electro Cylinder Step by Step Selection Process Step by Step Selection Process The following steps help you to specify the most suitable electro cylinder for your application. If your application’s requirements exceed a maximum value, please choose a larger electro cylinder and recheck the maximum values. In some cases a smaller electro cylinder can also meet the requirements. Application data ATEX or non-ATEX environment If used in an ATEX environment, check if the ETH corresponds to the ATEX requirements of your application "Electro Thrust Cylinder for ATEX Environment" (page 12)...
Open the catalog to page 10
ETH Electro Cylinder Calculating Required Axial Force Calculating Required Axial Force Formulas 1 & 2 below give the mathematical equation for calculating the thrust required to extend or retract the piston rod. With the aid of the axial forces, it is possible to check if the electro cylinder is able to provide the required forces and if the maximum buckling load is respected. The axial forces are also used as the calculation basis for the service life. Formula symbols (Formula 1-2) = Axial forces during extension in N Fx,a,j FG,Kse FG,Ks = Mass of the cylinder rod at zero stroke in kg =...
Open the catalog to page 11
ETH - Electro Cylinder Selection of the Size and Screw Lead Selection of the Size and Screw Lead Required maximum axial force Determine the maximum axial force (page 11) that the electro cylinder must provide. Preselection of the electro cylinder Using the calculated force required, compare the actual electro cylinder specifications (page 8) to determine which profile size will produce enough force. Once you have determined a profile size, determine that the unit will physically fit in the space allowed by the application (including parallel or inline motor mounts). Required maximum...
Open the catalog to page 12All Parker Electromechanical and Drives Division Europ catalogs and technical brochures
-
AC15 Variable Speed Drive
16 Pages
-
Belt Driven
32 Pages
-
SensoNODETM
2 Pages
-
Medical solutions
2 Pages
-
RS and AXEM Series
14 Pages
-
DC590P
28 Pages
-
AC890
25 Pages
-
HPLA Linear Actuators
40 Pages
-
AC10 Variable Speed Drive
26 Pages
-
AC30 Variable Speed Drive
42 Pages
-
Parker Automation Controller
20 Pages
-
Explosion Proof Servo Motors
44 Pages
-
Parker Gearboxes
36 Pages
-
GVI Global Vehicle Inverter
16 Pages
-
RTS, RS, RX and AXEM Series
24 Pages
-
TMW Series Torque Motors
32 Pages
-
PSD1 Parker Servo Drive
16 Pages
-
DC590+ Product Catalog
20 Pages
-
Torque Motors – Kit version
111 Pages
-
Frameless Servo Motors
44 Pages
-
HKW Series
133 Pages
-
GVM Global Vehicle Motor
24 Pages
-
PSD1 Parker Servo Drive
12 Pages
-
Belt Driven Positioners
151 Pages
-
PS / RS Series
16 Pages
-
PTN Planetary Gearbox
4 Pages
-
PE Series
12 Pages
-
Motion Solutions
16 Pages
-
ETHERNET Powerlink
20 Pages
-
SMB Motors
28 Pages
Archived catalogs
-
ETH Electro Cylinder_2012
56 Pages












































