
Catalog excerpts

CONET Local Area Network Conet LAN Token Passing Local Area Network. DATASHEET CONET FEATURES • True Token-passing Local Area Network (Peer to Peer communications) - no master device dependency High system reliability Easy “Multi-master” systems. Switchable data rate enables network to be optimised for the installation - high data rate for high performance and low data rate for low grade cable and/or longer distance. Transformer isolation 1500V rms at every node yields high noise immunity. Defined data formats and standard built-in network services enable total compatibility between different products. Conet computer interface cards for direct network connection to PC with ISA or PCI buses. Automatic error detection and retransmission for very secure data communications without false messages. Up to 127 nodes on one network to keep pace with expanding plant requirements. Conet Development Conet was developed in response to a need from plant operators who wished to bring field data back to the control room or supervisor’s office in the most cost effective way. The only solutions that existed were very expensive and beyond the reach of the smaller operator. Thus one of the most important features of Conet is its ability to operate on low cost cabling which, in many instances, is already available as a free pair in a multi-core cable. Conet’s design was influenced by the requirements of the Mining industry who required a reliable network to run from surface to the underground levels of the mine often with power cables etc. Major Uses - two broad categories: 1. Multidrop Telemetry Systems: Digital and analog signals are transmitted from one or many transmitting stations to one or many receiving stations without the need for a master computer station on the network. The telemetry devices, such as Conet Squeezers, are programmed with built-in software to communicate with each other while Conet itself takes care of error checking and data integrity. In this category, Conet Squeezer systems may share a network with other intelligent users (e.g. PCs) but operate completely independently. 2. Computer I/O: Data Acquisition Multiple host computers may communicate with field I/O devices such as PLCs, Remote Terminal Units, Analog and Digital front end systems etc.. This data would typically be used by the computer for monitoring, control, reporting or re-transmission back to other field outputs via the same Conet network. Product Compatibility Omniflex has developed a number of intelligent devices which communicate via Conet and has an on-going development program of making Conet compatible with third party vendors of hardware and software. Based on the ISO OSI 7 Layer Model Conet complies with the Networking Standards making Interface to other products possible. Conet permits easy communications between any of these different intelligent devices on the same network by making use of a Data Interchange Table (DIT) in memory at each node. This DIT stores all I/O and supervisory/control analog and digital variables in set registers in a block of memory which is accessible from the device itself and from the network. It also contains Copyright Omniflex Subject to change without notice
Open the catalog to page 1
CONET Local Area Network Conet LAN Token Passing Local Area Network. system variables which are unique to the product, such as setpoints, dead-band levels, time delays etc.. All a system programmer needs to know about any device in order to read or write to the DIT is the register number and the format of its contents. Token Passing Protocol Conet is a token-passing network. Peer to peer with no master. In order to maintain orderly communications between all the devices, a specially formatted message, known as the ‘token’, is passed from node to node. The node which has the token at any...
Open the catalog to page 2
CONET Local Area Network Conet LAN Token Passing Local Area Network. CONET NETWORK TOPOLOGIES The Flexible Network The NIM extends the versatility of Conet installations by providing the following benefits: 1. The ability to extend branches off a Conet cable to provide “Star” or “T” configurations, with the only limitation being the longest end to end distance of each network.(i.e. 10km) 2. The ability to break a Conet network into functionally independent pieces so that a fault in any one section will not affect the operation of any other section. 3. The ability to extend the length of a...
Open the catalog to page 3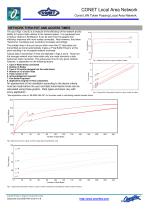
CONET Local Area Network Conet LAN Token Passing Local Area Network. NETWORK THRU-PUT AND ACCESS TIMES 1. Type of Node device connected 2. Number of Nodes 3. Type of I/O card(s) plugged into the node device 4. Number of I/O at each node 5. Total number of I/O 6. Acknowledgement requests* 7. Free Buffer Enquiries* 8. Application program in Host computer(s) Thru-put (Figs 1 and 3) is a measure of the efficiency of the network and its abilitty to transmit data relative to the network speed. It is expressed here in kbaud, relative to 62.5kbaud. It can be seen from the graphs that efficiency...
Open the catalog to page 4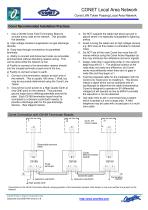
CONET Local Area Network Conet LAN Token Passing Local Area Network. Conet Recommended Installation Practices 1. Use a C6169 Conet Field Termination Board to connect every node to the network. This provides five benefits: a) High voltage transient suppression via gas discharge devices; b) Easy loop-through connections via paralleled terminals; c) Ability to connect and disconnect node via removable terminal block without disturbing network wiring. This can be done while the network is live; d) Facility to connect a line termination resistor directly into the unused terminals at each end of...
Open the catalog to page 5
CONET Local Area Network Conet LAN Token Passing Local Area Network. SPECIFICATIONS Within 3 metres of each other but it is recommended that one board is used at each node. General Polarity Polarity insensitive Only a single path may connect any two nodes on the network. Any branch off the main line should not exceed 20m unless a suitable impedance tap is used. Data transmission Terminate only at each end of transmission line, on C6169 Field Termination Board. Resistance value Termination resistors should be equal to the characteristics impedance of the cable (refer to cable manufacturer’s...
Open the catalog to page 6All Omniflex catalogs and technical brochures
-
MAXIFLEX Bases
3 Pages
-
Model M1267B CPU P3e-R
8 Pages
-
Model M1265A CPU A3e
8 Pages
-
Model M1586A CONET PNIM
2 Pages
-
Model M1588D HARWELL NIM
2 Pages
-
Model M1711A HSC
2 Pages
-
Model M1322A 16DI-24
2 Pages
-
Model M1323A 16DI-48
2 Pages
-
Model M1326A 32DI-24
2 Pages
-
Model M1327A 64DI-24
2 Pages
-
Model M1341B 16DO
2 Pages
-
Model M1330A 8DI8RO
2 Pages
-
Model M1342A 32DO
2 Pages
-
Model M1372A 8RO
2 Pages
-
Maxilarm
15 Pages
-
Model C2321A Teleterm M2S
8 Pages
-
Model C2330B-11-0
6 Pages
-
Model C2330B-12-0
6 Pages
-
Model M1403A 16AI
2 Pages
-
Model M1412A 8AO
2 Pages
-
Model M1431B 8 VC ISO
2 Pages
-
Model M1432C 8 TC/mV ISO
3 Pages
-
Model M1433B 6 RTD ISO
2 Pages
-
Model C2360C-0-0 Teleterm M2
6 Pages
-
Model C2360B-0-0 Teleterm M2
8 Pages
-
C2404B
4 Pages
-
C118xB series
4 Pages
-
Model M1589D HART NIM
3 Pages
-
Model M1580A Dual Serial NIM
2 Pages
-
Model M1240B CPU T2
6 Pages
-
Model MT8150x OIT 15 Inch
2 Pages
-
Model MT8121x OIT 12.1 Inch
2 Pages
-
Model MT8070iH OIT 7 Inch
2 Pages
-
Model MT8100i OIT 10 Inch
2 Pages
-
Model M1022B BASE
3 Pages
-
Model C2475A OMNITERM LZD
6 Pages
-
Model C2474A OMNITERM LZI
6 Pages
-
Model C2166A PT-2000 24Vdc
3 Pages
-
Model MT8104xh OIT 10.4 Inch
2 Pages
-
Model M1102A PSU
2 Pages
-
Model MT6070ih OIT 7 Inch
2 Pages
-
Model MT6050i OIT 4.3 Inch
2 Pages
-
Model M1023B BASE
3 Pages
-
Model C2063B OMNITERM LPI
12 Pages
-
Model M1021B BASE
3 Pages
-
Model C2462A OT LPD
12 Pages
-
Next Generation Signal Conditioners
12 Pages
-
Industry Standard Alarm Annunciators
10 Pages





























































































