 Website:
NTN Europe
Website:
NTN Europe
Group: NTN
Catalog excerpts

WE GET YOU MOVING... NTN-SNR as part of the NTN Corporation has been one of the most innovative companies in this sector for decades. The NTN Group is one of the largest roller bearing manufacturers in the world. This position allows us to provide our customers with a high level of added value regarding service, quality and product range. As a result, we have been able to build a strong image as a competent partner for our customers. Our companies are characterized by global presence and a consistent quality system. This technical catalogue forms the basis of our discussions with you. Our...
Open the catalog to page 2
Table of contents 1. Basics of linear guides. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Design principles. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 Ball chain technology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8 Characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12 Selection criteria . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13 Arrangement of the installation surfaces ....
Open the catalog to page 4
5. Accessories. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70-73 5.1 Sealing Options. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70 5.1.1 Descriptions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70 5.1.2 Combination options. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71 5.1.3 Dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72 5.2 Rail caps. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ....
Open the catalog to page 5
1. Basics of linear guides Man has moved heavy loads since ancient times using rotation and linear movement or a combination of both. These movements are still found in many machines. The friction bearings initially used have mostly been replaced by roller bearings. Rolling elements in machines were established more than a hundred years ago, while rolling elements for linear movements have only become common in the last few decades. Figure 1.1 Movement of heavy loads Sliding Rolling
Open the catalog to page 6
1.1 Design principles High surface pressure results when a ball touches a flat surface at one point (Figure 1.2). Grooves in modern linear guides are manufactured with a defined radius to increase the contact area. The ratio of the race way radius to the ball diameter in percent is called osculation. This significantly increases the load capacity, service life time and rigidity of the balls for equal surface pressure. Point contact Area contact Figure 1.2 NTN-SNR linear guides maximum surface pressure Ó Ball diameter Race way radius
Open the catalog to page 7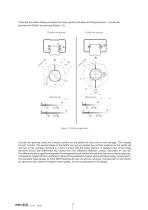
There are two basic design principles for linear guides with balls as rolling elements - circular arc grooves and Gothic arc grooves (Figure 1.3). Circular arc groove Differential slip Differential slip Figure 1.3 Groove geometry Circular arc grooves have one contact surface on the profile rail and one on the carriage. This creates 2-point contact. The special shape of the Gothic-arc groove creates two contact surfaces on the profile rail and two on the carriage, resulting in 4-point contact with the rolling element. A detailed view of the rolling elements shows that differential slip...
Open the catalog to page 8
The race way configuration is another characteristic of linear guides. The following alternatives are used: DF-configuration and DB-configuration of the race ways, corresponding to the terms used for roller bearing systems (Figure 1.4). Linear guide with DF-configuration Linear guide with DB-configuration Linear guide systems can be exposed to torque stress resulting from installation faults (Figure 1.5). When the distance between the active points is low, the resulting internal loads is low as well. The NTN-SNR linear guides are therefore produced using the DF-configuration. Linear guide...
Open the catalog to page 9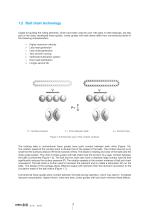
1.2 Ball chain technology Cages for guiding the rolling elements, which have been used for over 100 years in roller bearings, are also part of the newly developed linear guides. Linear guides with ball chains differ from conventional series in the following characteristics: Higher maximum velocity Less heat generation Less noise generation Very smooth running Optimised lubrication system Even load distribution Longer service life F = Force between balls Figure 1.6 Schematic view of the contact surfaces The rotating balls in conventional linear guides have point contact between each other...
Open the catalog to page 10
Figure 1.7 Linear guides with ball chains The noise generation of linear guides is mainly determined by their design. Direct knocking of balls against each other is the main reason for increased noise generation in conventional models. In addition, the contact of the balls with the surfaces of the re-circulating hole affects noise generation (Figure 1.8). These effects are significantly reduced by the use of ball chains. The patented structure of the ball chain further contains gaps for lubricant depots. The combination of the flexibility of the ball chain and the lubricant acts like a...
Open the catalog to page 11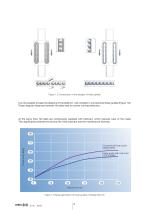
Figure 1.8 Comparison of the designs of linear guides It is not possible to keep the distance of the balls (C1, C2) constant in conventional linear guides (Figure 1.8). These irregular distances between the balls lead to uneven running behaviour. At the same time, the balls are continuously supplied with lubricant, which reduces wear of the metal. This significantly extends the service life of the lubricant and the maintenance intervals. 70 Conventional linear guide LGBXH25FN 60 Linear guide with ball chain LGBCH25FN Velocity (m/min) Figure 1.9 Noise generation of linear guides of Design...
Open the catalog to page 12
The chain in linear guides with ball chain has the function of a cage. It holds the balls at a constant distance from each other and controls their circulation. The structure of the carriages makes it impossible to implement a closed ball chain circulation. At the end of the ball chains, a space of about 1 ball diameter remains. The design of the ends of the NTN-SNR ball chain and the use of a spacer ball compensate for this space (Figure 1.10). NTN-SNR ball chain with spacer ball Figure 1.10 NTN-SNR ball chain This design of the ball chain ends in connection with the spacer ball closes the...
Open the catalog to page 13All NTN Europe catalogs and technical brochures
-
NTN Large Bearings
337 Pages
-
TAPERED ROLLER BEARINGS
32 Pages
-
Topline
16 Pages
-
Megaohm
7 Pages
-
KIT ALL IN ONE
14 Pages
-
Spherical Roller Bearings
80 Pages
-
POLIPUMP
6 Pages
-
Hydraulic Nuts
2 Pages
-
SmartTEMP
4 Pages
-
Deep-Groove Ball Bearings
4 Pages
-
Lubrication
44 Pages
-
Maintenance Tools
56 Pages
-
Linear Motion: Ball Screws
116 Pages
-
Linear Motion : Balls Bushings
84 Pages
-
Linear Axis Range
2 Pages
-
Linear Axis
260 Pages
-
Linear Axis AXE
4 Pages
-
AXE Linear Axis
100 Pages
-
Linear Motion: Range
4 Pages
-
Self-Aligning Bearing Units
125 Pages
-
Precision Rolling Bearings
327 Pages
-
Ball and Roller Bearings
407 Pages
-
OUR RANGE FOR YOUR INDUSTRY
32 Pages
-
SOLUTIONS FOR MACHINE TOOL
6 Pages
-
CYLINDRICAL ROLLER BEARINGS
5 Pages
-
SNC The Pillow Block Range
88 Pages
-
Needle Roller Bearings
84 Pages


































