Catalog excerpts

2833 Chiya, Ojiya-city, Niigata-pref., 947-8503 JAPAN 930 Muirfield Drive, Hanover Park, IL60133 Western Regional Office 46750 Lakeview Blvd. Fremont, CA 94538 Eastern Regional Office 41 Orchard Street, Ramsey, NJ07446 Boekweitstraat 21, 21 53 GK Nieuw-Vennep, The Netherlands
Open the catalog to page 1
LINEAR SYSTEM
Open the catalog to page 2
CONTENTS NB・LINEAR・SYSTEM TECHNICAL・INFORMATION・ Eng-1〜42 SLIDE GUIDE・ ・・・・・・・・・・・A-1〜79 CONTENTS CONTENTS BALL SPLINE ROTARY BALL SPLINE STROKE BALL SPLINE・ ・・・・・・・・・ B-1〜43 SLIDE BUSH・・・・・・・・・・・・C-1〜139 TOP BALL ・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・ D-1〜21 R STROKE BUSH SLIDE ROTARY BUSH・ ・・ E-1〜29 SHAFT・ ・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・ F-1〜29 SLIDE WAY ・SLIDE TABLE MINIATURE SLIDE GONIO WAY・ ・・・・・・・・・・・・G-1〜64 ACTUATOR・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・・ H-1〜77 SLIDE SCREW・ ・・・・・・・・・・・ TECHNICAL・REFERENCE・ INDEX・ Tech-1〜7 INDEX-1〜10 I-1〜7
Open the catalog to page 3
CONTENTS CONTENTS SLIDE GUIDE SEBS-BS/B/BY P.A-26 SEBS-BSM/BM/BYM P.A-26 SEBS-WBS/WB/WBY P.A-30 SEB-A/AY P.A-34 SGL-HTE P.A-66 SGL-HYE P.A-68 SEB-WA/WAY P.A-38 SER-A P.A-46 SER-WA P.A-48 SGW-TF P.A-76 SGW-TE P.A-78 SGL-F P.A-54 SGL-TF P.A-56 SGL-HTF P.A-58 SGL-HYF P.A-60 SGL-E P.A-62 SGL-TE P.A-64 SGL-HTEX P.A-70
Open the catalog to page 4
CONTENTS BALL SPLINEROTARY BALL SPLINESTROKE BALL SPLINE SSP P.B-18 SSPM P.B-20 SSPF P.B-22 SM-G-L P.C-20 SM-W KB-W SW-W P.C-22 P.C-74 P.C-94 SMF KBF SWF P.C-24 P.C-76 P.C-96 SSPT P.B-24 SSP-S P.B-26 SSP-C P.B-27 SMK KBK SWK P.C-26 P.C-78 P.C-98 SMT P.C-28 SMF-E P.C-30 SPR P.B-34 SPB P.B-36 SPLFS P.B-42 SMK-E P.C-32 SMT-E P.C-34 SMK-G-L P.C-36 SM-AJ KB-AJ SW-AJ P.C-16 P.C-70 P.C-90 SM-OP KB-OP SW-OP P.C-18 P.C-72 P.C-92 SMF-W KBF-W SWF-W P.C- 38 P.C- 80 P.C-100 SMT-W P.C-42 SLIDE BUSH SM KB SW P.C-14 P.C-68 P.C-88 SMK-W KBK-W SWK-W P.C- 40 P.C- 82 P.C-102
Open the catalog to page 5
CONTENTS SMFC KBFC P.C-44 P.C-84 SMKC KBKC P.C-46 P.C-86 SMTC P.C-48 GM GW P.C-104 P.C-106 GM-W P.C-105 SMA P.C-108 SMF-W-E P.C-50 SMK-W-E P.C-52 SMT-W-E P.C-54 SMA-W P.C-110 AK P.C-112 AK-W P.C-114 TRF P.C-56 TRK P.C-58 TRFC P.C-60 SMB P.C-116 SMP P.C-118 SMJ P.C-120 TRKC P.C-62 TRF-E P.C-64 TRK-E P.C-66 SME P.C-122 SME-W P.C-124 SMD P.C-126
Open the catalog to page 6
CONTENTS CE P.C-128 CD P.C-130 SWA P.C-132 TKE P.D-12 TKE-W P.D-13 TKD P.D-14 SWJ P.C-134 SWD P.C-136 RBW P.C-138 TKD-W P.D-15 TWA P.D-16 TWA-W P.D-17 TWJ P.D-18 TWJ-W P.D-19 TWD P.D-20 TWD-W P.D-21 TOPBALL R TK P.D-6 TK-OP TW-OP P.D-8 TKA P.D-6 P.D-10 TW TKA-W P.D-8 P.D-11
Open the catalog to page 7
CONTENTS STROKE BUSHSLIDE ROTARY BUSH SR P.E-4 SR-UU P.E-5 SR-B P.E-6 FR P.E-28 FRA P.E-29 P.F- 6 P.F-10 SNS SNWS P.F- 7 P.F-11 SNT SHAFT SR-BUU P.E-7 SRE P.E-12 SREK P.E-14 SN SNW P.F-8 SMA-R P.E-16 SMA-RW P.E-17 AK-R P.E-18 SNB/SNSB P.F- 9 SNW-PD/SNWS-PD P.F-12 SH-A P.F-15 SH P.F-16 AK-RW P.E-19 SMP-R P.E-20 RK P.E-23 SHF SHF-FC SA P.F-18 WH-A P.F-20 P.F-17
Open the catalog to page 8
CONTENTS WA P.F-22 LWA P.F-23 RV SLIDE WAYSLIDE TABLEMINIATURE SLIDEGONIO WAY NV/NVS P.G-10 SV/SVS P.G-14 SVW/SVWS P.G-22 NVT/NVTS P.G-28 SVT/SVTS P.G-32 SYT/SYTS P.G-38 SYT-D/SYTS-D P.G-42 SYBS P.G-50 RVF P.G-60 P.G-62 ACTUATOR BG P.H-1 SLIDE SCREW SS P.I-7
Open the catalog to page 9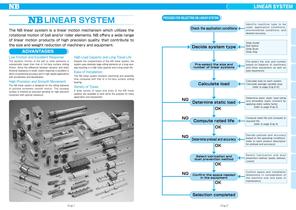
The NB linear system is a linear motion mechanism which utilizes the rotational motion of ball and/or roller elements. NB offers a wide range of linear motion products of high precision quality that contribute to the size and weight reduction of machinery and equipment. Low Friction and Excellent Response The dynamic friction of the ball or roller elements is substantially lower than that of full-face surface sliding friction. Since the difference between dynamic and static frictional resistance is small, motion response is excellent in terms of positioning accuracy and in high speed...
Open the catalog to page 10
ALLOWABLE LOAD A load is applied to the linear system as Figure 1-1 shows. Sometimes moment loads are applied to, for example, slide guides. Load and moment are defined Basic Static Load Rating (compliant with IS014728-2*1) and Allowable Static Moment When excess load or impact load is applied to the linear system while it is stationary or moving slowly, a permanent deformation occurs on the rolling If this deformation exceeds a certain limit, it causes vibration and noise during operation resulting in a non-smooth motion and a shorter life time. To prevent this permanent deformation and...
Open the catalog to page 11
When the travel distance per unit time is constant, the rated life can be expressed in terms of time (hour). Equation (9) shows the relationship between stroke length, number of cycles per minute, and the life In the linear system, the guide rail or shaft works as race way of the rolling elements. Therefore, the hardness of the rail or shaft is an important factor in determining the rated load. The rated load decreases as the hardness decrease below 58HRC. NB products hold appropriate hardness by advanced heat treatment technology. In case of using the rail or shaft of insufficient...
Open the catalog to page 12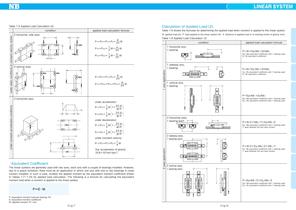
Table 1-5 Applied Load Calculation (2) applied load calculation formula 2 horizontal, side axes velocity diagram time t(sec) direction ofimovement thrust force _ direction otmovement under acceleration under deceleration under constant velocity •Equivalent Coefficient The linear systems are generally used with two axes, each axis with a couple of bearings installed. However, due to a space limitation, there must be an application in which one axis with one or two bearings in close contact installed. In such a case, multiply the applied moment by the equivalent moment coefficient shown in...
Open the catalog to page 13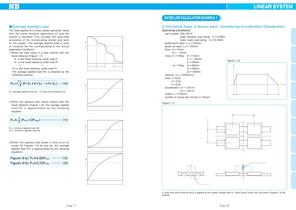
•Average Applied Load The load applied to a linear system generally varies with the travel distance depending on how the system is operated. This includes the start/stop processes of the reciprocating motion and work on the system. The average applied load is used to compute the life corresponding to the actual application conditions. ©When the load varies in a step manner with the travel distance (Figure 1-7). SL\ is the travel distance under load Pi &2 is the travel distance under load P2 in is the travel distance under load Pn The average applied load Pm is obtained by the following...
Open the catalog to page 18
©Calculating Equivalent Load OPr in the vertical direction and Ps in the horizontal direction are calculated by the following equations. LINEAR SYSTEM ©Equation for Dynamic Equivalent Load calculating in the same manner ©Calculating Average Equivalent Load ©Calculating Rated Life Decide each coefficient • hardness coefficient TH=1 for hardness of guide is 58HRC or more •temperature coefficient f T= 1 operating temperature is below 100°C (80°C is maximum for SGL guide) • contact coefficient fc=1 for blocks are not in close contact •applied load coefficient fw=1.5 for Vmax=200mm/s...
Open the catalog to page 20All NB Europe catalogs and technical brochures
-
Interchange table
28 Pages
-
FIT SERIES
2 Pages
-
Topball&Slide shaft products
28 Pages
-
Catalogue general
564 Pages
-
LINEAR SYSTEM
21 Pages
-
SLIDE ROTARY BUSH
4 Pages
-
Stainless Steel SGL Guide
2 Pages
-
SLIDE GUIDE
4 Pages
-
ACTUATOR Type BG15
2 Pages
-
ROTARY BALL SPLINE SPB type
4 Pages
-
NB REVERSE-SEAL
2 Pages
-
LEAFLET OF SHAFT DRAWINGS
9 Pages
-
SLIDE SCREW
4 Pages
-
ACTUATOR
39 Pages
-
SLIDE WAY
33 Pages
-
SHAFT
15 Pages
-
STROKE BUSH
15 Pages
-
TOPBALL
11 Pages
-
SLIDE BUSH
70 Pages
-
BALL SCREW SPLINE
4 Pages
-
BALL SPLINE
22 Pages
-
SLIDE GUIDE
40 Pages
-
TECHNICAL REFERENCE
4 Pages
-
TOPBALL™ Slide Products
28 Pages
-
Rotary Ball Spline SPR Type
2 Pages
-
Slide Rotary Series
14 Pages
-
Gonio Way RVF Type
8 Pages
-
STUDROLLER™ NV/NVT Type
14 Pages
-
Slide Guide SGL-HYF and HYE
8 Pages
-
Slide Bush SM G-L/SMK G-L
2 Pages
-
Shaft Leaf
9 Pages
Archived catalogs
-
Linear Systems
8 Pages







































