
Catalog excerpts

Maurer Magnetic AG – White paper Demagnetization of large surface objects before welding Demagnetization of construction pipes Demagnetization of a steel box girder Demagnetizer for large pipes (concept) Maurer Magnetic AG & Schuler Pressen GmbH Maurer Magnetic AG 8627 Grüningen Switzerland
Open the catalog to page 1
Demagnetization of large surface objects Introduction This white paper provides an overview over known demagnetization methods (also known as degaussing) in the field of welding processes. These methods are however limited in demagnetizing large surface objects. For such cases, a new method is introduced for complete demagnetization of large surface steel objects before final assembly. Some examples of large surface steel objects: • Construction pipes and pipelines • Ship construction modules • Offshore modules • Pressure vessels and tanks • Large girders and trusses • Steel panels • Heat...
Open the catalog to page 2
The art of dealing with interfering magnetic fields during welding process The most common problem with excessive residual magnetism on steel objects is the disturbance of welding processes. The phenomenon is known as "magnetic arc blow". The total magnetic field in the joint preparation causes a deflection of the arc by the Lorentz force [4]. Notations used for magnetic fields and their explanations: Ambient field Ha: Residual magnetism B,: Welding current field Hw: Reversing field Hrev: Total field Htot: The ambient field induces in the steel object a magnetic flux. The ambient magnetic...
Open the catalog to page 3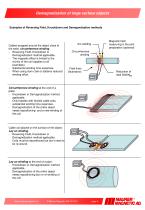
Demagnetization of large surface objects Examples of Reversing Field, Knockdown and Demagnetization methods Cables wrapped around the object close to the weld: circumference winding - Reversing Field, Knockdown or Demagnetization method applicable. - The magnetic effect is limited to the vicinity of the coil (applies to all examples). - Substantial winding time expenses. - When using clam coils or bobbins reduced winding effort. Magnetic field measuring in the joint preparation (optional) Arc welding Circumference winding Field lines (illustrative) Reduction of total field Htot...
Open the catalog to page 4
Demagnetization of large surface objects The magnetic state of the material The magnetic state (domain structure) in the ferromagnetic material can be illustrated by looking at the initial magnetization curve. This curve describes the magnetization processes in the material as a function of applied field H. The magnetic domains are always magnetized up to saturation and bounded by walls (Bloch walls). The magnetization direction of the adjacent domains rotates in the domain wall. By intensifying field strength H, the magnetization direction of the domains increasingly turns in the direction...
Open the catalog to page 5
Demagnetization of large surface objects Description of the procedures 1) Reversing Field The disturbing magnetic fields in the joint preparation are tried to be neutralized by Reversing Fields of a specific amplitude. A direct current is adjusted at the power source which generates the Reversing Field in the coil. This Reversing Field superimposes with the disturbing total field in the joint preparation. In the optimum case the total field may largely be neutralized when applying the correct coil current. The following happens in the material: B = µ0(H + M) Btot magnetic initial curve...
Open the catalog to page 6
Demagnetization of large surface objects 2) Knockdown As a first step, the wound steel portion is magnetized directionally as possible to magnetic saturation. Multipole fields are rectified prior to the Knockdown through that. The second step is to apply a defined Reversing Field in a way that after removal of the Reversing Field, the total field drops to zero in the joint preparation [9]. Hysteresis curve Notes on Hrev, Ha, Hw, Br according to page 3. Hx: field, wherein the flux B becomes zero after removal of Hrev. The material is magnetized first to saturation (Bsat, Hsat). ...
Open the catalog to page 7
Demagnetization of large surface objects 3) Demagnetization (Degaussing) This method is based on an decaying alternating magnetic field produced by a coil. The power source generates therefore reversing DC (or AC) currents with decreasing amplitude. The process causes the demagnetization of the material by the successive reduction of the hysteresis loop. The materiall is first fully magnetized (rectifying of all the magnetic domains). Thereafter, reversing the polarity of the magnetic zones and reducing the field amplitude leads to a statistical distribution of the domain magnetization...
Open the catalog to page 8
Demagnetization of large surface objects 3.2) Demagnetization by High Intensity Sine Pulse field strength high number of pole reversals and high decay precision small hysteresis loop at the end of the pulse high peak field The following pulse parameters were identified in practical experiments and are preferably used for demagnetization of large surface steel objects (up to ~60mm wall thickness): • High field strength (about 50...100kA/m) for reversing hard magnetic zones and to increase the penetration depth. • Demagnetization frequency approximately between 5Hz and 20Hz. • Pulse duration...
Open the catalog to page 9
Demagnetization of large surface subcomponents prior to assembly This method has already been used in the past, but often with limited success. The reasons for this are described with insufficient effect of the demagnetization or with the too cumbersome and time consuming implementation [1,5]. Maurer Magnetic AG has developed a new demagnetization procedure for subcomponents by use of the above described High Intensity Sine Pulse Demagnetization. The procedure has been successfully used several times. It is protected by several patents. The procedure eliminates the residual magnetism of the...
Open the catalog to page 10
Demagnetization of large surface objects Demagnetization procedure: The demagnetization of the whole object is done by demagnetizing all surface subareas. The surface subarea is overlapped by the coil an demagnetized entirely by one pulse (duration ~6...20s). Between the pulses the coil is moved to the next subarea. During the pulse the coil remains stationary. crane hook demagnetized surface coil component power module moving direction of the coil coil: 3x flexible demagnetizing cable K8/10-30 construction pipe turning rolls
Open the catalog to page 11All Maurer Magnetic catalogs and technical brochures
-
Loop Demagnetizers CT
2 Pages
-
Plate Demagnetizers MM PE
4 Pages
-
Magnetic field viewer
2 Pages
-
Teslameter M-Test Mk4
2 Pages
-
Magnetizer MPA 400
1 Pages
-
Zero-Gauss Chamber
2 Pages
-
General brochure
4 Pages
























