
Catalog excerpts

SimHydraulics Model and simulate hydraulic systems SimHydraulics® provides component libraries for modeling and simulating hydraulic systems. It includes models of hydraulic components, such as pumps, valves, actuators, pipelines, and hydraulic resistances. You can use these components to model fluid power systems such as front-loader, power steering, and landing gear actuation systems. Fuel supply and water supply systems can also be modeled using SimHydraulics. SimHydraulics models can be used to develop control systems and test system-level performance. You can parameterize your models using MATLAB® variables and expressions, and design control systems for your hydraulic system in Simulink®. You can add electrical, mechanical, pneumatic, and other components to your hydraulic model using Simscape™ and test them in a single simulation environment. To deploy models to other simulation environments, including hardware-in-the-loop (HIL) systems, SimHydraulics supports C-code generation. Learn more about physical modeling. Key Features ▪ Pump models, including centrifugal, jet, and axial-piston pumps ▪ Directional valve models, including check valves and common configurations for 2-, 4-, and 6-way valves ▪ Flow and pressure control valve models, including ball, poppet, and pressure relief valves ▪ Translational and rotational actuator models, including optional friction and centrifugal forces ▪ Tank and pipe models with elevation effects for modeling fluid transportation systems ▪ Customizable library of common hydraulic fluids ▪ Ability to extend component libraries using the Simscape language ▪ Support for C-code generation Modeling a Hydraulic Actuation System 7:01 Model a hydraulic actuation system. A double-acting hydraulic cylinder controlled by a four-way directional valve is modeled using SimHydraulics® components. SimHydraulics is used to optimize system-level performance and to create plant models for control design. The models you create support your entire development process, including hardware-in-the-loop simulations.
Open the catalog to page 1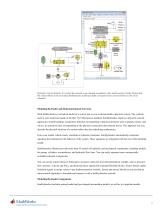
Hydraulic circuit schematic of a system that contains a gas-charged accumulator and a double-acting cylinder (bottom left). The colored blocks in the associated SimHydraulics model (top right) correspond to the colored elements in the circuit schematic. Modeling Hydraulic and Hydromechanical Networks With SimHydraulics you build a model of a system just as you would assemble a physical system. The symbols used in your model are based on the ISO 1219 fluid power standard. SimHydraulics employs a physical network approach to model building: components (blocks) corresponding to physical...
Open the catalog to page 2
■ The standard pipeline block models pipelines with circular and noncircular cross sections and accounts for frictional pressure loss and fluid compressibility. ■ The segmented pipeline block accounts for frictional pressure loss, fluid compressibility, and fluid inertia and enables you to model phenomena, such as water hammer. A library of local resistance blocks lets you include pressure loss associated with elbows, bends, and cross-sectional flow area changes. SimHydraulics provides actuators and pumps that let you: ■ Model hydraulic cylinders and rotary actuators, including effects such...
Open the catalog to page 3
Customizing Models You can combine the blocks in the SimHydraulics libraries to create custom hydraulic models. In addition, Simscape (required by SimHydraulics) contains a foundation library that includes a set of basic building blocks for different physical domains; these blocks define the pressure/flow relationship for basic physical effects, such as fluid compressibility, fluid inertia, mechanical friction, energy transduction, and flow through fixed and variable orifices. You can combine these building blocks with SimHydraulics blocks to model a component that spans different physical...
Open the catalog to page 4
Cross-section illustration of a hydraulic cylinder with snubber (bottom left). The colored blocks in the SimHydraulics model (top left) correspond to colored arrows in the cross-section illustration, which represent typical hydraulic flow paths. The graphs (right) track the velocity and position of the piston, and the pressure of the hydraulic fluid during the simulation. Defining Fluid Properties SimHydraulics employs efficient methods for defining density, viscosity, and bulk modulus—the fluid properties that affect system behavior. SimHydraulics provides 18 commonly used hydraulic...
Open the catalog to page 5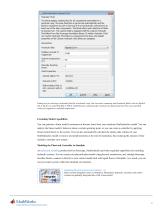
1*^1 Block Parameters: Hydraulic Fluid Hydraulic Fluid The block assigns working fluid for all components assembled in a particular loop. The loop detection is performed automatically and the block is considered as part of the loop if it is hydraulically connected to at least one of the loop components. The block offers wide selection of fluids to choose from. The custom fluid is assigned with the Custom Hydraulic Fluid block from the Simscape foundation library. If neither Hydraulic Fluid nor Custom Hydraulic Fluid block is connected to the loop, the default properties of the Custom...
Open the catalog to page 6
Resources Product Details, Examples, and System Requirements www.mathworks.com/products/simhydraulics Online User Community www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral Trial Software www.mathworks.com/trialrequest Training Services www.mathworks.com/training Sales www.mathworks.com/contactsales Third-Party Products and Services www.mathworks.com/connections Technical Support www.mathworks.com/support Worldwide Contacts www.mathworks.com/contact © 2012 The MathWorks, Inc. MATLAB and Simulink are registered trademarks of The MathWorks, Inc. See www.mathworks.com/trademarks for a list of additional...
Open the catalog to page 7All The MathWorks catalogs and technical brochures
-
MATLAB Production Server
6 Pages
-
Database Toolbox
4 Pages
-
MATLAB Report Generator
4 Pages
-
Stateflow
8 Pages
-
SimEvents
7 Pages
-
SimDriveline
7 Pages
-
SimPowerSystems
8 Pages
-
Simulink Control Design
5 Pages
-
Aerospace Blockset
5 Pages
-
SimRF
6 Pages
-
Simulink Coder
6 Pages
-
Embedded Coder
8 Pages
-
Simulink PLC Coder
4 Pages
-
Fixed-Point Designer
9 Pages
-
MATLAB Coder
5 Pages
-
Simulink 3D Animation
10 Pages
-
Gauges Blockset
2 Pages
-
Simulink Report Generator
3 Pages
-
Polyspace Bug Finder
6 Pages
-
global-optimization-toolbox
10 Pages
-
Phased Array System Toolbox
9 Pages
-
OPC Toolbox
5 Pages
-
Simulink Design Verifier
7 Pages
-
Simulink Design Optimization
10 Pages
-
Filter Design HDL Coder
5 Pages
-
Bioinformatics Toolbox
9 Pages
-
SimBiology
6 Pages
-
Computer Vision System Toolbox
10 Pages
-
DSP System Toolbox
11 Pages
-
Fuzzy Logic Toolbox
5 Pages
-
Polyspace Client for C/C++
5 Pages
-
xPC Target
5 Pages
-
SimMechanics
7 Pages
-
Simscape
7 Pages
-
Simulink
6 Pages
-
Data Acquisition Toolbox
8 Pages
-
Image Processing Toolbox
7 Pages
-
Signal Processing Toolbox
10 Pages
-
Control System Toolbox
6 Pages
-
Symbolic Math Toolbox?
6 Pages
-
Parallel Computing Toolbox?
7 Pages
-
MATLAB®
6 Pages
-
Mapping Toolbox 3.2
7 Pages
-
Instrument Control Toolbox
7 Pages
-
Optimization Toolbox 6.0
14 Pages
Archived catalogs
-
MATLAB Release Notes
505 Pages
-
C and Fortran API Reference
263 Pages
-
External Interfaces
649 Pages
-
Function Reference: Volume 3 (P-Z)
1696 Pages
-
Function Reference: Volume 2 (F-O)
1568 Pages
-
Function Reference: Volume 1 (A-E)
1298 Pages
-
Creating Graphical User Interfaces
520 Pages
-
3-D Visualization
212 Pages
-
Graphics
667 Pages
-
MATLAB Programming Tips
66 Pages
-
Programming Fundamentals
840 Pages
-
Data Analysis
220 Pages
-
Mathematics
316 Pages
-
MATLAB® Getting Started Guide
250 Pages





































































