
Catalog excerpts

Computer Vision System Toolbox Design and simulate computer vision and video processing systems Computer Vision System Toolbox™ provides algorithms and tools for the design and simulation of computer vision and video processing systems. The toolbox includes algorithms for feature extraction, motion detection, object detection, object tracking, stereo vision, video processing, and video analysis. Tools include video file I/O, video display, drawing graphics, and compositing. Capabilities are provided as MATLAB® functions, MATLAB System objects™, and Simulink® blocks. For rapid prototyping and embedded system design, the system toolbox supports fixed-point arithmetic and C code generation. Key Features ▪ Feature detection, including FAST, Harris, Shi & Tomasi, SURF, and MSER detectors ▪ Feature extraction and putative feature matching ▪ Object detection and tracking, including Viola-Jones detection and CAMShift tracking ▪ Motion estimation, including block matching, optical flow, and template matching ▪ RANSAC-based estimation of geometric transformations or fundamental matrices ▪ Video processing, video file I/O, video display, graphic overlays, and compositing ▪ Block library for use in Simulink Feature Detection and Extraction A feature is an interesting part of an image, such as a corner, blob, edge, or line. Feature extraction enables you to derive a set of feature vectors, also called descriptors, from a set of detected features. Computer Vision System Toolbox offers capabilities for feature detection and extraction that include: ▪ Corner detection, including Shi & Tomasi, Harris, and FAST methods ▪ SURF and MSER detection for blobs and regions ▪ Extraction of simple pixel neighborhood and SURF descriptors ▪ Visualization of feature location, scale, and orientation Additionally, the system toolbox provides functionality to match two sets of feature vectors and visualize the results. When combined into a single workflow, feature detection, extraction, and matching can be used to solve many computer vision design challenges, such as registration, stereo vision, object detection, and tracking. SURF (left), MSER (center), and corner detection (right) with Computer Vision System Toolbox. Using the same image, the three different feature types are detected and results are plotted over the original image.
Open the catalog to page 1
Registration and Stereo Vision Computer Vision System Toolbox supports automatic image registration by providing algorithms that use features to estimate the geometric relationships between images or video frames. Typical uses include video mosaicking, video stabilization, image fusion, and stereo vision. Feature-Based Registration Feature detection, extraction, and matching are the first steps in the feature-based registration workflow. With a pair of images, you can detect and extract features in each image, using one of several feature types available in the system toolbox. You can then...
Open the catalog to page 2
Results from stereo image rectification. Non-overlapping areas are show in red and cyan. Stereo Vision Stereo vision is the process of reconstructing a 3D scene from two or more views of the scene. Using the system toolbox, you can perform uncalibrated stereo image rectification on a pair of stereo images and match individual pixels along epipolar lines to compute a disparity map. Accelerating the pace of engineering and science
Open the catalog to page 3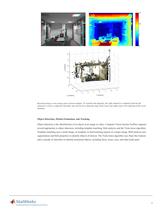
Reconstructing a scene using a pair of stereo images. To visualize the disparity, the right channel is combined with the left channel to create a composite (top left); also shown are a disparity map of the scene (top right) and a 3D rendering of the scene (bottom). Object Detection, Motion Estimation, and Tracking Object detection is the identification of an object in an image or video. Computer Vision System Toolbox supports several approaches to object detection, including template matching, blob analysis, and the Viola-Jones algorithm. Template matching uses a small image, or template,...
Open the catalog to page 4
Face detection using the Viola-Jones algorithm. Motion estimation is the process of determining the movement of blocks between adjacent video frames. The system toolbox provides a variety of motion estimation algorithms, such as optical flow, block matching, template matching, and background estimation using Gaussian mixture models (GMMs). These algorithms create motion vectors, which relate to the whole image, blocks, arbitrary patches, or individual pixels. For block and template matching, the evaluation metrics for finding the best match include MSE, MAD, MaxAD, SAD, and SSD. Detecting...
Open the catalog to page 5
Video deinterlacing in MATLAB. Video I/O Computer Vision System Toolbox can read and write multimedia files in a wide range of formats, including AVI, MPEG, and WMV. You can stream video to and from MMS sources over the Internet or a local network. You can acquire video directly from Web cameras, frame grabbers, DCAM-compatible cameras, and other imaging devices using Image Acquisition Toolbox™. Simulink users can use the MATLAB workspace as a video source or sink. Video Display The system toolbox includes a video viewer that lets you: ▪ View video streams in-the-loop as the data is being...
Open the catalog to page 6
■ '£ Edft View Display C-jg'am Simulation Analyse Code Tvu\i Hdp Model with viewers for four videos: (from left) original, estimated background, foreground pixels, and results of tracking. Adding graphics to video helps with visualizing extracted information or debugging a system design. You can insert text to display the number of objects or to keep track of other key information. You can insert graphics, such as markers, lines, and polygons to mark found features, delineate objects, or highlight other key features. The system toolbox functionality fuses text and graphics into the image or...
Open the catalog to page 7
Images with text and graphics inserted. Adding these elements can help you visualize extracted information and debug your design. Stream Processing in MATLAB and Simulink Computer Vision System Toolbox supports a stream processing architecture in both MATLAB and Simulink. In a stream processing architecture, one or more video frames from a continuous stream are processed at a time. This type of processing is appropriate for analysis of large video files or systems with live video. In MATLAB, stream processing is enabled by System objects, which use MATLAB objects to represent time-based and...
Open the catalog to page 8All The MathWorks catalogs and technical brochures
-
MATLAB Production Server
6 Pages
-
Database Toolbox
4 Pages
-
MATLAB Report Generator
4 Pages
-
Stateflow
8 Pages
-
SimEvents
7 Pages
-
SimDriveline
7 Pages
-
SimHydraulics
7 Pages
-
SimPowerSystems
8 Pages
-
Simulink Control Design
5 Pages
-
Aerospace Blockset
5 Pages
-
SimRF
6 Pages
-
Simulink Coder
6 Pages
-
Embedded Coder
8 Pages
-
Simulink PLC Coder
4 Pages
-
Fixed-Point Designer
9 Pages
-
MATLAB Coder
5 Pages
-
Simulink 3D Animation
10 Pages
-
Gauges Blockset
2 Pages
-
Simulink Report Generator
3 Pages
-
Polyspace Bug Finder
6 Pages
-
global-optimization-toolbox
10 Pages
-
Phased Array System Toolbox
9 Pages
-
OPC Toolbox
5 Pages
-
Simulink Design Verifier
7 Pages
-
Simulink Design Optimization
10 Pages
-
Filter Design HDL Coder
5 Pages
-
Bioinformatics Toolbox
9 Pages
-
SimBiology
6 Pages
-
DSP System Toolbox
11 Pages
-
Fuzzy Logic Toolbox
5 Pages
-
Polyspace Client for C/C++
5 Pages
-
xPC Target
5 Pages
-
SimMechanics
7 Pages
-
Simscape
7 Pages
-
Simulink
6 Pages
-
Data Acquisition Toolbox
8 Pages
-
Image Processing Toolbox
7 Pages
-
Signal Processing Toolbox
10 Pages
-
Control System Toolbox
6 Pages
-
Symbolic Math Toolbox?
6 Pages
-
Parallel Computing Toolbox?
7 Pages
-
MATLAB®
6 Pages
-
Mapping Toolbox 3.2
7 Pages
-
Instrument Control Toolbox
7 Pages
-
Optimization Toolbox 6.0
14 Pages
Archived catalogs
-
MATLAB Release Notes
505 Pages
-
C and Fortran API Reference
263 Pages
-
External Interfaces
649 Pages
-
Function Reference: Volume 3 (P-Z)
1696 Pages
-
Function Reference: Volume 2 (F-O)
1568 Pages
-
Function Reference: Volume 1 (A-E)
1298 Pages
-
Creating Graphical User Interfaces
520 Pages
-
3-D Visualization
212 Pages
-
Graphics
667 Pages
-
MATLAB Programming Tips
66 Pages
-
Programming Fundamentals
840 Pages
-
Data Analysis
220 Pages
-
Mathematics
316 Pages
-
MATLAB® Getting Started Guide
250 Pages





































































