
Catalog excerpts

0MA3NAFLJUX Faraday Road, South Dorcan Industrial Estate, Swindon SN3 5HE, UK +44 (0) 1793 524566 sales.eu@magnaflux.com www.magnaflux.eu
Open the catalog to page 1
Fluorescent Liquid Penetrant Inspection Penetrants, Emulsifiers, Developers, & Removers
Open the catalog to page 2
Technical Info The Importance of Liquid Penetrant Inspection Liquid penetrant inspection is a nondestructive test method which does not harm the parts being inspected. The testing methods detect cracks, fractures, laps, seams and other flaws that are open to the surface that may have been caused by fatigue, impact, quenching, machining, grinding, forging or overload. The process is used on machined parts, castings, forgings and other items that will be placed into service or already in service requiring maintenance. The process involves applying a penetrant chemical, visible or fluorescent,...
Open the catalog to page 3
Selecting the Correct Penetrant Method Per AMS 2644 Penetrant Types • Type 1: Fluorescent dye • Type 2: Visible dye Penetrant Methods • Method A: Water washable • Method B: Post emulsifiable, lipophilic • Method C: Solvent removable • Method D: Post emulsifiable, hydrophilic Developer Forms • Form a: Dry powder • Form b: Water soluble • Form c: Water suspendible • Form d: Nonaqueous Type 1 fluorescent • Form e: Nonaqueous Type 2 visible dye Differences Between Sensitivity AMS 2644 Penetrant Sensitivity Levels Sensitivity levels are a classification system for fluorescent liquid penetrants...
Open the catalog to page 4
Technical Info Common Applications Common Terms Background – the surface of the test part against which the indication is viewed. It may be the natural surface of the test part or the developer coating on the surface. Bleedout – the action of an entrapped liquid penetrant in surfacing from discontinuities to form indications. Developer – a material that is applied to Aerospace processes commonly use Method D Level 4 penetrants for safety critical rotating parts including turbine blades. the test surface to accelerate bleedout and to enhance the contrast of indications. Developing Time – the...
Open the catalog to page 5
Fluorescent Liquid Penetrant Testing Method A Water Washable Preclean with Aqueous Cleaner Post Emulsifiable Preclean with Aqueous Cleaner Solvent Removable Preclean Apply Penetrant Dwell for 10−30 min. Apply Penetrant Dwell 10–30 min. Apply Penetrant Method B Apply Emulsifier Apply Emulsifier Remove Excess Penetrant Apply cleaner on cloth and then wipe the part Form a Apply Developer Apply Developer Dwell 10 min. – 4 hr. Apply Developer Apply Developer Dwell 10–60 min. Apply Developer
Open the catalog to page 6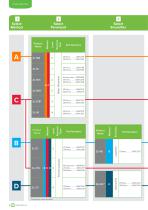
Product Selection Select Emulsifier Part Numbers Water Washable *Commonly used product 5 Part Numbers Post Emulsifiable Product Name Part Numbers Removal Type Removal Type Product Name Select Penetrant Select Method Product Name
Open the catalog to page 7
Select Developer Select Cleaner/Accessories Product Name Part Numbers Product Name
Open the catalog to page 8All Magnaflux catalogs and technical brochures
-
ProductCatalogueEMEAR2022
70 Pages
-
Magnetic Particle Inspection
7 Pages
-
EV6500
2 Pages
-
EV6000 Hand-Held LED UV Lamp
2 Pages











