
Catalog excerpts

Intel® Core™ i7 Processor Family for LGA2011 Socket Specification Update Supporting Desktop Intel® Core™ i7-4960X Extreme Edition Processor Series for the LGA2011 Socket Supporting Desktop Intel® Core™ i7-49xx and i7-48xx Processor Series for the LGA2011 Socket June 2014 Revision 008
Open the catalog to page 1
By using this document, in addition to any agreements you have with Intel, you accept the terms set forth below. You may not use or facilitate the use of this document in connection with any infringement or other legal analysis concerning Intel products described herein. You agree to grant Intel a non-exclusive, royalty-free license to any patent claim thereafter drafted which includes subject matter disclosed herein. INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH INTEL PRODUCTS. NO LICENSE, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, BY ESTOPPEL OR OTHERWISE, TO ANY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS IS...
Open the catalog to page 2
Specification Update
Open the catalog to page 3
Revision History Version Initial release. Revised erratum CG79 to show only the supported performance monitor counters Added erratum CG104 Specification Update
Open the catalog to page 4
Preface This document is an update to the specifications contained in the Affected documents table below. This document is a compilation of device and documentation errata, specification clarifications, and changes. It is intended for hardware system manufacturers and software developers of applications, operating systems, or tools. Information types defined in Nomenclature are consolidated into the specification update and are no longer published in other documents. This document may also contain information that was not previously published. Note: Throughout this document, the Intel®...
Open the catalog to page 5
Nomenclature Errata are design defects or errors. These may cause the processor behavior to deviate from published specifications. Hardware and software designed to be used with any given stepping must assume that all errata documented for that stepping are present on all devices. Specification changes are modifications to the current published specifications. These changes will be incorporated in any new release of the specification. Specification clarifications describe a specification in greater detail or further highlight a specification’s impact to a complex design situation. These...
Open the catalog to page 6
Identification Information Component Identification using Programming Interface The processor stepping can be identified by the following register contents. Table 1. Processor Signature / Version Notes: 1. The Extended Family, Bits [27:20] are used in conjunction with the Family Code, specified in Bits [11:8], to indicate whether the processor belongs to the Intel® 386, Intel® 486, Pentium®, Pentium 4, or Intel® Core™ processor family. 2. The Extended Model, Bits [19:16] in conjunction with the Model Number, specified in Bits [7:4], are used to identify the model of the processor within the...
Open the catalog to page 7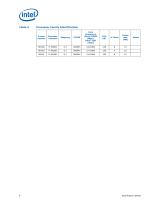
Processor Family Identification S-spec number Core Frequency (GHz)/DDR3 (MHz)/ Intel® QPI (GHz) Specification Update
Open the catalog to page 8
Summary Tables of Changes The following tables indicate the errata, specification changes, specification clarifications, or documentation changes that apply to the processor product. Intel may fix some of the errata in a future stepping of the component, and account for the other outstanding issues through documentation or specification changes as noted. These tables uses the following notations: Codes used in summary tables Stepping X: Errata exists in the stepping indicated. Specification Change or Clarification that applies to this stepping. This erratum is fixed in listed stepping or...
Open the catalog to page 9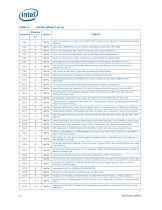
Errata (Sheet 1 of 4) Stepping Core Frequencies at or Below the DRAM DDR Frequency May Result in Unpredictable System Behavior. Quad Rank DIMMs May Not be Properly Refreshed During IBT_OFF Mode. PCIe* TPH Attributes May Result in Unpredictable System Behavior. PCIe* Rx Common Mode Return Loss is Not Meeting the Specification. PCIe* Rx DC Common Mode Impedance is Not Meeting the Specification. QPILS Reports the VNA/VN0 Credits Available for the Processor Rx Rather Than Tx. A PECI RdPciConfigLocal Command Referencing a Non-Existent Device May Return an Unexpected Value. The Vswing of the...
Open the catalog to page 10
Errata (Sheet 2 of 4) Stepping REP MOVSB May Incorrectly Update ECX, ESI, and EDI Performance-Counter Overflow Indication May Cause Undesired Behavior VEX.L is Not Ignored with VCVT*2SI Instructions Concurrently Changing the Memory Type and Page Size May Lead to a System Hang MCI_ADDR May be Incorrect For Cache Parity Errors Instruction Fetches Page-Table Walks May be Made Speculatively to Uncacheable Memory REP MOVS/STOS Executing with Fast Strings Enabled and Crossing Page Boundaries with Inconsistent Memory Types may use an Incorrect Data Size or Lead to Memory-Ordering Violations The...
Open the catalog to page 11
Errata (Sheet 3 of 4) Stepping A Write to the IA32_FIXED_CTR1 MSR May Result in Incorrect Value in Certain Conditions #GP May be Signaled When Invalid VEX Prefix Precedes Conditional Branch Instructions Interrupt From Local APIC Timer May Not Be Detectable While Being Delivered PCMPESTRI, PCMPESTRM, VPCMPESTRI and VPCMPESTRM Always Operate with 32-bit Length Registers MSR_PKG_Cx_RESIDENCY MSRs May Not Be Accurate During Package Power States Repeated PCIe* and/or DMI L1 Transitions May Cause a System Hang MONITOR or CLFLUSH on the Local XAPIC's Address Space Results in Hang PCMPESTRI,...
Open the catalog to page 12
Errata (Sheet 4 of 4) Stepping PMON Counters Overflow May Not Trigger PMON Global Freeze Processor May Log a Machine Check when MSI is signaled by a device PECI May Not be Able to Access IIO CSRs Spurious Patrol Scrub Errors Observed During a Warm Reset Receiver Termination Impedance On PCIe* 3.0 Does Not Comply With The Specification Platform Recovery After a Machine Check May Fail PECI May be Non-responsive When System is in BMC Init Mode Processor May Issue Unexpected NAK DLLP Upon PCIe* L1 Exit Core C-state Residency Counters May Return Stale Data PCIe* Ports Operating at 8 GT/s May...
Open the catalog to page 13All Intel catalogs and technical brochures
-
10th Gen Intel® Core
7 Pages
-
10th Gen
8 Pages
-
nuc-celeron
4 Pages
-
Intel® NUC 8 Home Mini PC
4 Pages
-
Intel® Xeon® Scalable Platform
14 Pages
-
Intel® Ethernet Controller XL710
1726 Pages
-
Intel® Xeon® Processor E3-1200 v5
130 Pages
-
Intel® Quark™ SoC X1000 Series
934 Pages
-
Intel® X99 Chipset
4 Pages
-
Intel® Desktop Board DQ67EP
4 Pages
-
Intel® Ethernet Switch FM4000
270 Pages
-
Intel® NUC Board DE3815TYBE
82 Pages
-
S2600GZ and S2600GL
245 Pages
-
i7-lga2011
314 Pages
-
c600-series
936 Pages
-
b75-express
4 Pages
-
desktop-board
4 Pages
-
3rd-gen-core-desktops
2 Pages
-
/3rd-gen-core
2 Pages
Archived catalogs
-
Intel® Ethernet Controllers
2 Pages
-
Intel® 3450 Chipset
2 Pages
-
Intel® 3000 and 3010 Chipset
4 Pages
-
Intel® X58 Express Chipset
4 Pages
-
Intel® Server Board S1200BT
8 Pages
-
Intel® Desktop Board DX58SO2
4 Pages































































