Catalog excerpts

Official Journal of the European Union COMMISSION REGULATION (EC) No 640/2009 of 22 July 2009 implementing Directive 2005/32/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council with regard to ecodesign requirements for electric motors (Text with EEA relevance) (4) Electric motor systems include a number of energy-using products, such as motors, drives, pumps or fans. Motors and variable speed drives are an important part of these products. This is why this Regulation requires that certain types of motors be equipped with variable speed drives. Having regard to Directive 2005/32/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 6 July 2005 establishing a framework for the setting of ecodesign requirements for energyusing products and amending Council Directive 92/42/EEC and Directives 96/57/EC and 2000/55/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council (1) and in particular Article 15(1) thereof, Many motors are integrated in other products without being separately placed on the market or put into service in the meaning of Article 5 of Directive 2005/32/EC and of Directive 2006/42/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council (2). To achieve the full cost-efficient energy saving potential, motors integrated in other products should be subject to the provisions of this Regulation. After consulting the Ecodesign Consultation Forum, The Commission has carried out a preparatory study which analysed the technical, environmental and economic aspects of electric motors. The study has been developed together with stakeholders and interested parties from the EU and third countries, and the results have been made publicly available. The preparatory study shows that electric motors are placed on the Community market in large quantities, with their use-phase energy consumption being the most significant environmental aspect of all life-cycle phases, and their annual electricity consumption amounting to 1 067 TWh in 2005, corresponding to 427 Mt of CO2 emissions. In the absence of measures to limit this consumption, it is predicted that energy consumption will increase to 1 252 TWh in 2020. It has been concluded that the life-cycle energy consumption and the use-phase electricity consumption can be improved significantly, in particular if motors in variable speed and load applications are equipped with drives. The preparatory study shows that electricity consumption in use is the only significant ecodesign parameter related to product design as referred to in Annex I, Part 1, to Directive 2005/32/EC. Improvements in the electricity consumption of electric motors should be achieved by applying existing nonproprietary cost-effective technologies that can reduce the total combined costs of purchasing and operating them. THE COMMISSION OF THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES, Having regard to the Treaty establishing the European Community, Under Directive 2005/32/EC ecodesign requirements are to be set by the Commission for energy-using products representing significant volumes of sales and trade, having a significant environmental impact and presenting significant potential for improvement in terms of their environmental impact without entailing excessive costs. Article 16(2) first indent of Directive 2005/32/EC provides that in accordance with the procedure referred to in Article 19(3) and the criteria set out in Article 15(2), and after consulting the Ecodesign Consul tation Forum, the Commission shall, as appropriate, introduce an implementing measure for products used in electric motor systems. Electric motors are the most important type of electric load in industries within the Community where motors are used in the production processes. The systems in which these motors are operated account for about 70 % of the electricity consumed by the industry. There is a total potential for cost-effective improvement of the energy efficiency of these motor systems by about 20 % to 30 %. One of the major factors in such improvements is the use of energy efficient motors. Consequently, motors in electric motor systems represent a priority product for which ecodesign requirements should be established.
Open the catalog to page 1
Official Journal of the European Union Ecodesign requirements should harmonise power consumption requirements for motors throughout the Community, thus contributing to the functioning of the internal market and to the improvement of the environ mental performance of these products. The measures provided for in this Regulation are in accordance with the opinion of the Committee estab lished by Article 19(1) of Directive 2005/32/EC, HAS ADOPTED THE FOLLOWING REGULATION: (11) An appropriate timeframe should be provided for manu facturers to redesign products. The timing should be such that...
Open the catalog to page 2
Official Journal of the European Union Article 2 Definitions In addition to the definitions set out in Directive 2005/32/EC, the following definitions shall apply: 1. ‘Motor’ means an electric single speed, three-phase 50 Hz or 50/60 Hz, squirrel cage induction motor that: Each ecodesign requirement shall apply in accordance with the following timetable: 1. from 16 June 2011, motors shall not be less efficient than the IE2 efficiency level, as defined in Annex I, point 1; 2. from 1 January 2015: (i) motors with a rated output of 7,5-375 kW shall not be less efficient than the IE3 efficiency...
Open the catalog to page 3
Official Journal of the European Union Article 8 Entry into force This Regulation shall enter into force on the 20th day following its publication in the Official Journal of the European Union. This Regulation shall be binding in its entirety and directly applicable in all Member States. Done at Brussels, 22 July 2009. For the Commission Andris PIEBALGS
Open the catalog to page 4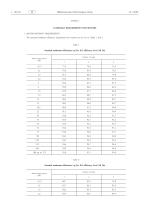
Official Journal of the European Union ANNEX I ECODESIGN REQUIREMENTS FOR MOTORS 1. MOTOR EFFICIENCY REQUIREMENTS The nominal minimum efficiency requirements for motors are set out in Tables 1 and 2. Table 1 Nominal minimum efficiencies (η) for IE2 efficiency level (50 Hz) Rated output power (kW) Table 2 Nominal minimum efficiencies (η) for IE3 efficiency level (50 Hz) Rated output power (kW)
Open the catalog to page 5All HW Ventilation catalogs and technical brochures
-
ISO9001 CERTIFICATION
1 Pages
-
ATEX certificate
1 Pages
-
Company profile
8 Pages
-
Fan-clutch systems
8 Pages
-
ATEX ventilators brochure
4 Pages
-
Q fan case study
8 Pages
-
ErP Directive Fans 2011
14 Pages
-
QUALYFAN user manual
20 Pages
-
Metal Axial Ventilators
10 Pages





























