Website:
HORIBA STEC
Website:
HORIBA STEC
Group: Horiba
Catalog excerpts

Feature Article Conductivity Meter with Carbon Electrodes and Application for Densitometers Conductivity Meter with Carbon Electrodes and Application for Densitometers Technologies for a Practical Densitometer Riichiro SUZUKI HORIBA developed 2-pole electrical conductivity sensors with chemical-resistant carbon electrodes in 2002. These sensors are installed in semiconductor wet processes and are put into practical use as densitometers. In addition, HORIBA developed a new circuit for 4-pole conductivity measurement, which was an innovation that improved the precision with any 4-pole sensors. Concentration of single-component such as hydrofluoric acid or TMAH are measured based on precise electrical conductivity and temperature measurements. Temperature compensation calculations for the conductivity of the individual component are necessary to convert the conductivity into the concentration. Etching and developing solutions, etc. need to be controlled at a constant level, and the demand for various types of densitometers that use electrical conductivity systems is increasing. Introduction Dozens of types of aqueous solutions are used for cleaning and etching in semiconductor wet processes. These are often prepared by diluting stock solutions on site, and densitometers are needed to check the operation of the dilution devices and adjust the concentrations. With electrolytes, there is a correlation between concentration and electrical conductivity, and concentrations can be converted from electrical conductivity. Electrical conductivity measurement systems that can obtain concentration information in real time don’t need reagents and can easily be incorporated into in-line processes, so these are essential for measuring single-component concentrations. Metals cannot be used as a material of electrode for semiconductor applications because of problems with chemical resistance. On the other hand, carbon has durability when exposed to normal acids and alkalis such as hydrofluoric acid, and also has the feature of having few surface impurities. This paper will discuss the performance, features, and applications of densitometers with carbon electrodes used as standard equipment in semiconductor processes. Electrical conductivity of aqueous solutions Water molecules have one oxygen atom in the center with 2 hydrogen atoms configured at approximately 104degree angles, and the electric charge is distributed so that the hydrogen atoms have a positive electric charge and the oxygen atom has a negative electric charge. For English Edition No.47 June 2017 that reason, water is a dissolving agent that has polarity. When electrolytes dissolve in water, the oxygen in the water molecules orients toward the positive ions, the hydrogen in the water molecules orients around the negative ions, ionizing the ions in the thermal motion. Ion crystals such as sodium chloride (NaCl) that have weak bonding are 100% ionized in dilute solutions, but there are some substances with strong bonding such as silver chloride (AgCl) that only ionize slightly, and mostly don’t dissolve in water.[1] Ions in aqueous solutions receive Coulomb force through electric fields and move, so that movement can be detected using current meter. The electrical conductivity of aqueous solutions depends on the concentration of the ions and the mobility. Electrical conductivity is equivalent to the inverse of the resistance of a sample cut into a 1-m3 shape, and the unit is expressed as S/m. Two-pole method, four-pole method, and electromagnetic induction method Even if constant voltage is applied to a pair of electrodes located in an aqueous solution, the electric field in the aqueous solution is not constant over time, and the current also is not constant. The rate of change in the current also depends on the electrical conductivity. This is because with electrodes and aqueous solutions, the electric charge is carried by the respective electrons and ions, and these can’t penetrate each other’s territories, so a phe
Open the catalog to page 1
Technical Reports occurs in which both electric charges approach each other on the junction surface, forming a so-called electrical dielectric layer. The electrical dielectric layer demonstrates the same characteristics as an electric circuit capacitor, and the potential difference concentrates on the junction surface as time passes, so the electric field (potential gradient) in the aqueous solution decreases. When this happens, current doesn’t flow, so in the 2-pole method, electrical conductivity is measured using a method in which alternating-current (AC) potential is applied to the...
Open the catalog to page 2
eature Article Conductivity Meter with Carbon Electrodes and Application for Densitometers Table 1 Extracted metals from the carbon surface by Hydrogen chloride this sensor that can obtain hydrofluoric acid concentrations and hydrochloric acid and ammonia concentrations from electrical conductivity. The 4-pole carbon sensor has leeway to measure up to 200 S/m with linearity. We provide a densitometer for this sensor that works for up to 50% hydrofluoric acid, 10% hydrochloric acid, and 10% TMAH (tetramethylammo-nium hydroxide). The nature of the carbon electrodes is somewhere between that...
Open the catalog to page 3
Technical Reports Electrical conductivity of chemicals S/m Electrical conductivity S/m 25°C Figure 5 Conductivity characteristics of concerned chemical solution (S/m) (Measured by HORIBA Advanced Techno) Electrical conductivity of various chemicals Figure 5 shows the relationship between various chemical concentrations and electrical conductivity (25°C). The electrical conductivity of hydrofluoric acid is distinctive, and has the characteristic that in low concentrations, the electrical conductivity is low, but in high concentrations of up to 50%, it increases monotonically. Substances such...
Open the catalog to page 4
Conductivity Meter with Carbon Electrodes and Application for Densitometers Electrical conductivity of phosphoric acid solution using inorganic alkalis and oxalic-acid-based etching of ITO (indium tin oxide) transparent electrodes. Conclusion Carbon has higher chemical resistance performance than metal, it is possible to increase the contact area during etching processing, and the catalytic effect of hydrogen peroxide breaking down is low, which makes it an optimal material for electrically conductive electrodes. However, the difficult point is that there is little freedom in things such as...
Open the catalog to page 5All HORIBA STEC catalogs and technical brochures
-
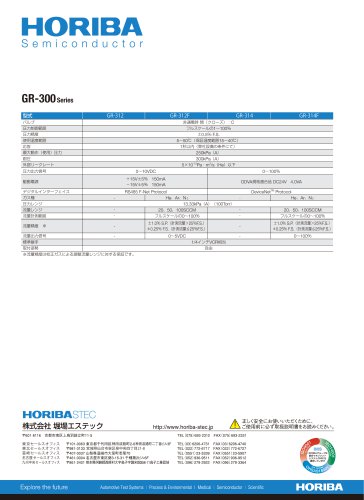
GR-300 Series
1 Pages
-
1000M Series
2 Pages
-
ru1000
4 Pages
-
HF HD-960L
5 Pages
-
CVS-ONE Brochure
4 Pages
-
CEMS
4 Pages
-
Cathodoluminescence H-CLUE
5 Pages
-
Cathodoluminescence F-CLUE
5 Pages
-
CAMSIZER X2 Brochure
12 Pages
-
CAMSIZER P4 Brochure
12 Pages
-
Brochure-TPNA-500
6 Pages
-
AP-370 Series Brochure
12 Pages
-
OMNI TERS Probes
2 Pages
-
NanoRaman Brochure
7 Pages
-
51 series Brochure
6 Pages
-
VULCAN Evo
4 Pages
-
MEDAS
8 Pages
-
OBS-ONE GS
6 Pages
-
MEXA-ONE Brochure
26 Pages
-
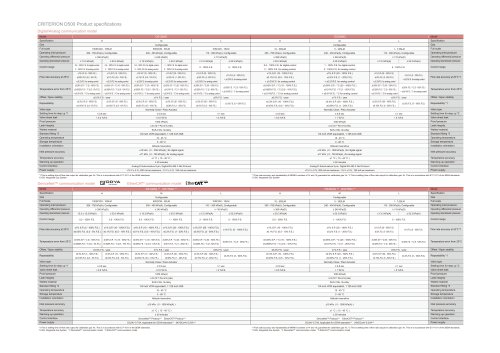
CRITERION D507 Series
3 Pages
-
Mass flow Controller & Meter
2 Pages
-
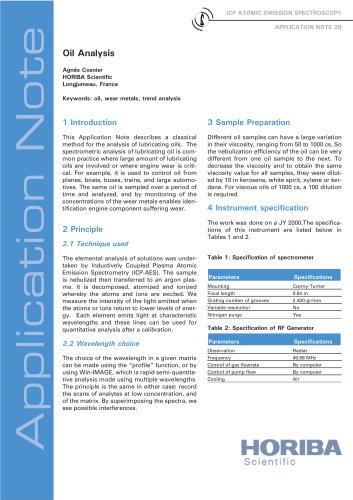
Oil analysis
3 Pages
-
Back number of CSR Reports
13 Pages
-
HORIBA Report
86 Pages
-
Soap Film Flow Meter
1 Pages
-
Analog pressure regulator
1 Pages
-
MI/MV
1 Pages
-
LV-F series
1 Pages
-
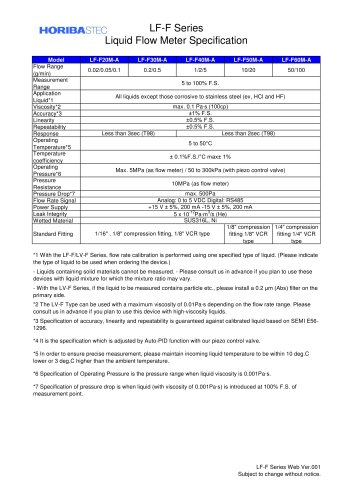
LF-F series
1 Pages
-
Criterion, D200 series
16 Pages
-
Pressure Controller
8 Pages
-
SEC-Z500MGX
16 Pages
-
Fluid Controle Equipment
4 Pages
-
Rasidual Gas Analizer
6 Pages
-
Vaporizers
8 Pages