
Catalog excerpts

Stud Welding What is stud welding and how does it work? The 12 most important questions and answers … Time and cost savings New design potentials Unsurpassed economy
Open the catalog to page 1
Stud welding processes Stud Welding Advantages ... In many areas stud welding is the most economic fastening method for components. If using thin plates, stud welding is often the only technical solution. With this HBS information brochure we want to show you the advantages of our technology. After answering the 12 most important questions about stud welding, we provide you with an overview on different stud welding processes as well as the innovative MARC-technology (pad welding with rotating ARC).
Open the catalog to page 2
Stud welding processes Tremendous time and cost savings No: drilling – punching – threading – gluing riveting – screwing – finishing New design potentials Very low distortion by extremely short welding time. No leaking caused by drilled holes. High strength. One-sided accessibility of the component is sufficient. Weldable even onto very thin plates. Joining of different materials is possible. Unsurpassed economy Can be automated to a very high degree. Very short welding time (1 msec to 1.5 sec), fast weld rates. Fast and easy handling leads to high productivity. No marks on backside of...
Open the catalog to page 3
Advantages Questions + Answers Stud welding processes Pad welding process stud welding? Welding elements like threaded studs, pins, tapped pads etc. are welded by an arc without additional stud welding work? 3 An arc is ignited between the face of the stud and the surface of work piece; once both parts are melted, the stud is smoothly pressed against the work piece and then joined together.
Open the catalog to page 4
Stud welding processes 3. What kind of processes are available? Capacitor discharge stud welding with tip ignition (TS) according to DIN 1). Especially suited for welding on thin plates from about 0.5 mm. Minimum plate thickness: 1/10 of stud diameter. Welding range: M3-M8 (M10). Drawn arc stud welding (DS) according to DIN 1), process variations: drawn arc stud welding with ceramic ferrule or shielding gas; short cycle drawn arc stud welding; capacitor discharge drawn arc stud welding. Especially suited for welding on thicker plates of 2 mm and above. Minimum plate thickness: 1/8 of stud...
Open the catalog to page 5
Stud welding processes 5. How strong is the joint? Because the stud is joined with the work piece over the whole surface of the stud, the strength of the joint is even higher than the base material or the stud. 6. Which materials are weldable? Generally materials of the same kind should be welded*. Capacitor discharge stud welding according to DIN steel (mild and alloyed steel), aluminum, brass. Drawn arc stud welding according to DIN steel (mild and alloyed steel), aluminum. * Other materials/combinations on request. 1)
Open the catalog to page 6
Stud welding processes 7. Which stud diameter and stud length can be welded? Capacitor discharge stud welding according to DIN 2) : M3 to M8 (M10), dia. 2 to 10 mm Drawn arc stud welding according to DIN 2) : dia. 2 to 25 mm (M24) Lengths: Ask for the HBS-brochure “Product survey – Stud Welding Fasteners“. 8. Which stud shapes are available? Capacitor discharge stud welding according to DIN 2) : threaded studs, pins, studs with internal thread, christmas tree studs, paint clearing studs, grounding clips, cupped head pins, insulation pins. Drawn arc stud welding according to DIN 2) :...
Open the catalog to page 7
Advantages Questions + Answers Stud welding processes Pad welding process welding process last? 3 Capacitor discharge stud welding: 1 to 3 msec 3 Drawn arc stud welding: 5 msec to 1.5 sec plate Surface is required? 3 The surface of the plate must be electrically conductive. 3 Varnish, aluminum layers, scale, rust and plastic surfaces are to be removed. Check galvanized and oily plates for their 3 Manual stud feeding: 5 to 6 studs per minute* (average). 3 Automatic stud feeding: 40 studs per minute* (average). " Production rate depends on application and type of HBS studwelders.
Open the catalog to page 8
Stud welding processes 12. How to automate stud welding? HBS delivers a wide product range: Starting with a hand held welding gun with automatic stud feeding, semi-automatic systems, up to fully automated stud welding units and robotic applications. Single source – by HBS. Ask for our HBS-brochure "Product survey – Automatic Stud Welding". Very suitable to weld various welding elements onto work pieces of different component heights.
Open the catalog to page 9
Stud welding processes The stud welding processes ... CD Capacitor discharge stud welding with tip ignition with contact The capacitor battery will be charged according to chosen charging voltage. The stud (with ignition tip) is placed onto the work piece and pressed by a spring in the welding gun onto the work piece (contact). The current circuit is closed. After triggering the welding process, the rapidly increasing current evaporates the ignition tip and ignites the arc. Stud and work piece are melted. The stud is moved forward to the plate. The arc is cut as soon as the stud touches the...
Open the catalog to page 10
Advantages Questions + Answers Stud welding processes Pad welding process 3 Gap welding is different from the procedure described above: Before welding starts, the stud is positioned in a defined and adjustable distance above the work piece (gap). 3 After triggering the welding process, the stud is accelerated by a spring to the plate surface. 3 If there is contact between the ignition tip on the work piece, the process continues as described above. 3 Welding time is approx. 1 msec; thus e.g. welding of aluminum becomes feasible without using a shielding gas 3 Recommended plate thickness...
Open the catalog to page 11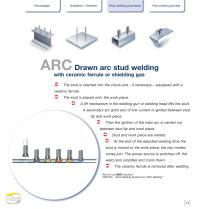
Stud welding processes ARC Drawn arc stud welding with ceramic ferrule or shielding gas The stud is inserted into the chuck and – if necessary – equipped with a ceramic ferrule. The stud is placed onto the work piece. A lift mechanism in the welding gun or welding head lifts the stud. A secondary arc (pilot arc) of low current is ignited between stud tip and work piece. Then the ignition of the main arc is carried out between stud tip and work piece. Stud and work piece are melted. At the end of the adjusted welding time the stud is moved to the work piece, the two molten zones join. The...
Open the catalog to page 12All HBS Bolzenschweiß-Systeme catalogs and technical brochures
-
Systems for drawn arc
1 Pages
-
HBS Catalogue Welding Elements
65 Pages
-
HBS Catalogue Accessories
144 Pages
-
PEGASAR 500 ACCU
3 Pages






