
Catalog excerpts

Guide to Cell Modification & Re-Engineering Solutions Guide to Cell Modification & Re-Engineering Solutions
Open the catalog to page 1
Guide to Cell Modification & Re-Engineering Solutions
Open the catalog to page 2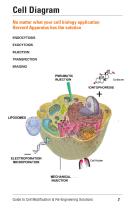
Cell Diagram No matter what your cell biology application Harvard Apparatus has the solution Guide to Cell Modification & Re-Engineering Solutions
Open the catalog to page 3
Introduction The Harvard Apparatus Advantage…Serving cell biologists with exceptional products and support. Introducing materials into cells such as, bacteria, DNA, drugs and ions, for the purpose of: - Monitoring the cells behavioral to the materials - Modifying and re-engineering the cells structure and function requires many different techniques, to get the cells to incorporate the materials into the cell to get desired effects When you choose a techniques you must ask the following questions to select the optimal technique for your applications: 1. How many cells do I need for my...
Open the catalog to page 4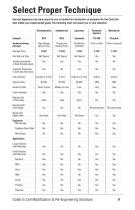
Select Proper Technique Harvard Apparatus has many ways for you to handle the introduction of samples into the Cells that best meets your experimental goals. The following chart will assist you in your selection: Electroporation Pneumatic Injectors Pico plus High Voltage Opens Pores Charge thru Existing Pores Fat Ball thru Cell Wall Transfect Hundreds of Cells Simultaneously Transfect Thousands of Cells Simultaneously Cell Container Typical yields Labor Intensive Require Lots of Technique Need to Hold Cells Rigidly Needs Cell Rigidly Held Capillary Glass Puller Large Particles and Molecules...
Open the catalog to page 5
Technique Definitions Iontophoresis is a non-invasive method of propelling high concentrations of a charged substance, normally medication or bioactive-agents, transdermally by repulsive electromotive force using a small electrical charge applied to an iontophoretic chamber containing a similarly charged active agent and its vehicle. To clarify, one or two chambers are filled with a solution containing an active ingredient and its solvent, termed the vehicle. The positively charged chamber, termed the anode will repel a positively charged chemical, whilst the negatively charged chamber,...
Open the catalog to page 6
Technique Definitions (cont.) A liposome is a spherical vesicle with a membrane composed of a phospholipid and cholesterol bilayer (see on the right). Liposomes can be composed of naturally-derived phospholipids with mixed lipid chains (like egg phosphatidylethanolamine), or of pure surfactant components like DOPE (dioleolylphosphatidylethanolamine). Liposomes. Liposomes are used for drug delivery due to their unique properties. A liposome encapsulates a region on aqueous solution inside a hydrophobic membrane; dissolved hydrophilic solutes can not readily pass through the lipids....
Open the catalog to page 7
Pneumatic Injectors PLI-100 and PLI-90 Pico-Injector Series • 5 pressures: inject, balance, clear, fill and hold • Popular applications: - Injection of mouse, frog, zebrafish and other oocytes - Extracellular brain injections - Injection of DNA, mRNA, microbeads, eurotransmitters, kinases and other proteins • Most Published Injector The PLI-100 Pico-Injector reliably delivers a wide range of volumes through micropipettes by applying a regulated pressure for a digitally set period of time. Compressed gas allows the user to deliver desired volumes from femtoliters to microliters while...
Open the catalog to page 8
Iontophoresis Neuro Phore BH-2 • Modular design; buy what you need now and add additional modules later as your protocol evolves • Accommodates 7 barrel micropipettes supports the most complex and demanding injection and recording protocols • Extremely low noise, ±105 volts compliance, allows rapid iontophoretic injection with even the smallest micropipette tips • Automatic current neutralization for minimal electrical artifacts • Digitally controlled eject and pause timing utilizes easy to read and set digital panel switches on each iontophoretic or pressure module/channel The Neuro Phore...
Open the catalog to page 9
Mechanical Injector • Infuse/ withdraw capability • Dual syringes for broad flow rate range • Easy-to-read display, the injection rate can be changed from 0.0550 pl/sec to 0.0073 ml/sec • Remote to micromanipulator injections are easy non-obstructed viewing and no heavy weight to hinder positioning • This pump has exceptional milliliter, microliter, nanoliter and picoliter smooth and accurate flow, easily set through the keyboard • The injection can be controlled by initiating the manual start button, RS232 through your computer or with the included foot pedal • Operating parameters are set...
Open the catalog to page 10
Electroporation • Specialty electrodes • Cuvettes • High throughput 96-well plates Electroporation is a techniques used to perform research on embryonic stem cells (HESC), adult stem cells, somatic cell nuclear transfer, therapeutic cloning and cancer research. Applications: • Transfection of Mammalian Cells • In Vitro, In Vivo, Ex Vivo and In Ovo Experiments • Nuclear Transfer • Plant Tissue and Protoplast Transfection • Transformation of Bacteria and Yeast Guide to Cell Modification & Re-Engineering Solutions
Open the catalog to page 11
Liposomes • Liposomes are used for studying protein-liposome interactions with compounds such as serum lipoproteins, lectins, toxins and clotting components. • Entrapment of anti-tumor agents, anti-microbial drugs, antiinflammatory and immunomodulatory agents and CNS-active drugs. The therapeutic applications are presently include cancer therapy, arthritis, metal chelation therapy, enzyme replacement therapy, hemophilia (factor VIII), myocardial infarction, and as radiopharmaceutical markers. • Liposomes are used for studying in vitro and in vivo liposomecell interactions. • They are used...
Open the catalog to page 12
Reference Reference Articles: Measurement of volume injected into individual cells by quantitative fluorescence microscopy, Lee GM., J Cell Sci. 1989 Nov;94 ( Pt 3):443-7 Information Fusing Control of the DNA Microinjection Volume Based on Stochastic Fuzzy Neural Network, Zhang Ling, Yu Yongquan, ZengBi 2006-02-21 09:22:58.0 Fluid Dynamics in Conically Tapered Microneedles, WijayaMartanto, Stephen M. Baisch, Elizabeth A. Costner, Mark R. Prausnitz, Marc K. Smith AIChEJournal, Vol.51, No.6, 1599-1607, 2005 Controlled micro release of pharmacological agents: measurementsof volume ejected in...
Open the catalog to page 13All Harvard Bioscience catalogs and technical brochures
-
Biowave 3 & Biowave 3+
2 Pages
-
Scie-Plas Product Catalogue
132 Pages
-
CMA Microdialysis Catalog
56 Pages
-
EZ READ 400 ELISA
3 Pages









































