
Catalog excerpts

GEA Wiegand GmbH GEA Evaporation Technologies Evaporation Technology using Mechanical Vapour Recompression Leading Technologies. Individual Solutions.
Open the catalog to page 1
Contents Mechanical Vapour Recompression and Evaporation 3 Principles of Mechanical Vapour Recompression 5 Mechanical Vapour Recompressors – Design and Functional Ranges 7 Operating Principles and Compressor Designs 8 Design Details of the Single-stage, Centrifugal Compressor 10 Compressor Drives 13 Monitoring and Safety Equipment 14 Compressor Controls 16 Evaporation Plants with Centrifugal Fans Thermal separation processes such as evaporation and distillation are energy intensive. In the course of their development, the aim of reducing energy costs first led to multiple-effect plants,...
Open the catalog to page 2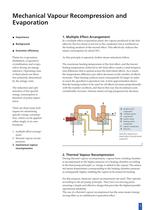
Mechanical Vapour Recompression and Evaporation Importance Background Economic efficiency Plants for evaporation, distillation, evaporative crystallisation and evaporative drying are energy intensive. Operating costs of these plants are therefore primarily determined by the energy costs. The reduction and optimisation of the specific energy consumption is therefore of prime importance. 1. Multiple Effect Arrangement In a multiple effect evaporation plant, the vapour produced in the first effect by the live steam is not lost to the condenser, but is reutilized as the heating medium of the...
Open the catalog to page 3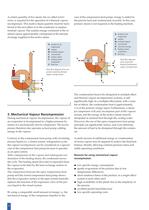
A certain quantity of live steam, the so-called motive steam, is required for the operation of a thermal vapour recompressor. This motive steam quantity must be transferred to the next effect or to the condenser as surplus residual vapour. The surplus energy contained in the residual vapour approximately corresponds to the amount of energy supplied in the motive steam. A product to be evaporated B vapour B1 residual vapour C concentrate D motive steam E heating steam condensate V heat loss case of the compression heat pump, energy is added to the process heat and continuously recycled. In...
Open the catalog to page 4
Principles of Mechanical Vapour Recompression Centrifugal compressors are volumetrically governed machines; i.e. the volumetric flow rate remains almost constant, regardless of the suction pressure. Mass flow does however change in proportion to the absolute suction pressure. specific enthalpy h (kJ/ kg) Single-stage centrifugal compressors and high pressure fans are generally used for mechanical vapour recompression systems for cost reasons. The explanations below are therefore limited to these designs. The compression cycle of the single-stage centrifugal compressor is depicted in the h,s...
Open the catalog to page 5
The specific polytropic compression work ∆ hp depends inter alia, on the polytropic exponent κ and the molar mass M of the drawn-in gas, as well as the suction temperature and the required pressure increase. For the actual coupling power of the prime mover (electric motor, gas engine, turbine etc.) a further allowance for mechanical losses is taken into account. increase in saturated steam temperature of about 12-18 K, up to a max. 30 K depending on the suction pressure. Single-stage centrifugal compressors with impellers made of standard materials are capable of achieving a water vapour...
Open the catalog to page 6
Mechanical Vapour Recompressors – Design and Functional Ranges Machines for the compression of gases operate in accordance with positive displacement or dynamic principles. With positive displacement machines, moving machine parts separate the suction chamber and the pressure chamber, and the gas pressure is increased as the volume of the operating chamber decreases. In the case of a reciprocating compressor, this is done by the movement of the piston within the cylinder. In dynamically operating machines, the gas is supplied with energy by the impeller blades rotating at high...
Open the catalog to page 7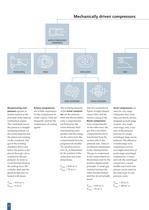
Mechanically driven compressors positive displacement compressors reciprocating rotary rotary piston axial screw compressor Reciprocating compressors operate in similar fashion to the principle of the internal combustion engine. The crankshaft moves the piston in a straight oscillating motion via the connecting rod and the piston rod running on the crosshead. The gas in the working chambers above and below the piston is displaced through valves actuated by the gas pressure. In order to avoid thermal stress at the sealing faces, the cylinder shell and the gland pocket may be heated with...
Open the catalog to page 8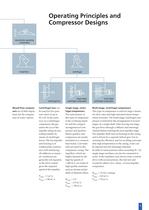
Operating Principles and Compressor Designs dynamically operating compressors mixed-flow centrifugal centrifugal fan Mixed-flow compressors are of little importance for the compression of water vapour. Centrifugal fans can be used for low pressure ratios of up to Π=1.25. In the same way as a centrifugal compressor, the gas enters the eye of the impeller along its axis, exiting radially by means of centrifugal forces. The fan impeller and housing is of welded plate construction with reinforcing rib stiffeners as required. Gearboxes are generally not required, as the drive system gives the...
Open the catalog to page 9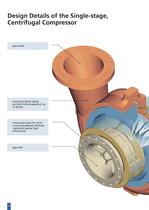
Design Details of the Single-stage, Centrifugal Compressor gas outlet one-piece spiral casing permits final pressures of up to 60 bar inlet guide vane for continuous adjustment achieves maximum partial load efficiencies gas inlet 10
Open the catalog to page 10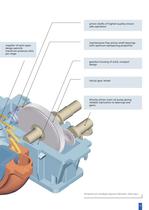
pinion shafts of highest quality ensure safe operation impeller of semi-open design permits maximum pressure ratio per stage maintenance-free pinion shaft bearings with optimum dampening properties gearbox housing of solid, compact design helical gear wheel directly-driven main oil pump giving reliable lubrication to bearings and gears 3D depiction of a centrifugal compressor (illustration: Atlas Copco) 11
Open the catalog to page 11
The impeller Gearbox The impeller is of the overhung design at the free end of the shaft (pinion shaft in the case of a compressor, main shaft in the case of a fan). The helical gears of modern compressors are integrated within the compressor. For this reason, a coupling between gear and compressor shaft is not required. Thrust collars are situated on the highspeed pinion shaft. These thrust collars transmit the residual axial thrust to the low-speed main shaft (wheel shaft). Depending on the compressor design, semi-open or closed impellers are used. The blade geometry might be radial, or...
Open the catalog to page 12All GEA Wiegand catalogs and technical brochures
-
GEA POWDEREYE® 2025
4 Pages
-
VARINLINE®
296 Pages
-
GEA LYOPLUS™
6 Pages
-
Evaporation Technology 2009
24 Pages
-
Wiegand Steam Jet Cooling Plants
16 Pages
-
Jet Vacuum Systems
8 Pages
-
Membrane Filtration
12 Pages
-
Ethanol production
2 Pages
-
perfect brewing solutions
6 Pages
-
GEA Wiegand Company Brochure
24 Pages
-
Bioethanol Technology
16 Pages
-
Distillation Technology
16 Pages
Archived catalogs
-
GEA Wiegand Services
4 Pages
-
GEA in brewing
6 Pages
-
GEA ProductGuide Brewing
24 Pages





























