
Catalog excerpts

The lens is the most basic optical component. It collects light from a source and refracts that light to form a usable image of the source. The source may produce light itself, or it may be an illuminated object. ► Effective Focal Length A lens forms animage ofthe source on a target on which it is focused at an appropriate distance away. If the source isfarfrom the lens, the lens intercepts a numberofthem so they are all brought to a common focal point. The distance along the optical axis ofthe lens from the focal point back to the effective bend point of rays near the axis (paraxial...
Open the catalog to page 2
F=Lens focal length S=Object distance S'=lmage distance ■ ForMirrors Use the lens formula and graphical techniques, butinput and output on the same sideofthe optic. Uniform illumination of a diffraction limited lens D Illumination with a laser beam with a Gaussian intensity profile for a diffraction limited lens
Open the catalog to page 3
► Plano-convex Lenses Plano-convex lenses are used to collimate diverging light or to focus collimated light. We use them as secondary focusing lenses to refocus the collimated light sources. Plano-convex lenses have low spherical aberration. Use them with the piano side facing the point source or the focus and the curved side towards the collimated beam. In a lens, the following parameters are usually used to describe it: diameter (O), center thickness (to), radius (R), edge thickness (te), focal length (f), refractive index. These parameters follow the following formulas: Plano-concave...
Open the catalog to page 4
► Double-convex Lenses These lenses are primarily used for imaging at close to 1:1, illustrating their functions. The convex surfaces usually have quite the same radius of curvature. The lenses have very low optical aberration at magnifications from 5 to 0.2. At these magnifications, coma, distortion, and chromatic aberrations are minimal. Because both convex surfaces contribute to the magnifying power, these lenses are useful for collecting and refocusing light from a small beams in applications where you should use two lenses; one to collimate the diverging beam, and the second to...
Open the catalog to page 5
We call them meniscus lenses because the two curves of the lens lieonthe same direction,just like a meniscus when viewed by its cutaway. Their parameters follow the formulas below: Specifications Material Dimension tolerance tc tolerance Clear aperture Surface quality Flatness Centration Size (O) Coating Optical grade Laser grade Normal precision High precision BK7, B270, CaF2, Silicon, Ge, Fused Silica or others 3 to 200mm or larger According to your requests Achromatic Lenses An achromat is a lens consisting oftwo cemented elements made of different materials, usually flint glass with...
Open the catalog to page 6
In addition to higher image quality, additional advantages of the cemented achromat include: simplified mounting since it becomes one unit, smaller light loss resulted from fewer surfaces, less stray light due to reduced reflections. Specifications Material Dimension tolerance tc tolerance Clear aperture Surface quality Flatness Centration Size (O) Coating Common precision High precision According to different designs +0.0, -0.2mm +0.0, -0.02mm 3.5 to 80mm or larger According to your requests Cylindrical lenses are used in applications requiring magnification in one dimension only,...
Open the catalog to page 7
Ball lenses are glass spheres commonly used in fiber optics applications ideal forfocusing light into fibers (Figure 1) as well as fiber coupling (Figure 2). The ratio for the collimated light input beam diameter to the ball lens diameter is defined as d/D (Figure 1). As the ratio increases, the back focal length increases. When coupling light from a laser into a fiber, the choice of ball is dependent on the Numerical Aperture (NA) ofthe fiber and the diameter ofthe laser beam. The NAof the ball lens must be less than or equal to NA ofthe fiber to couple all ofthe light into the fiber. The...
Open the catalog to page 8
Specifications Material Diameter tolerance Length tolerance Surface quality Size DxL (mm) ► LineGenerator Lenses Our line generator lenses can be used to display a uniform straight reference line for use in alignment, machine vision systems, construction and process control. In addition, the lenses can also be used on lower power lasers. (Note that intensity will be diminished in normal work light and distances.) On a 3.5mW laser, for example, the line would be easily visible in normal interior room light at 30 feet. Lenses are available in different fan angles. ► Cone Lenses These...
Open the catalog to page 9
Specifications Material Surface quality Size OxTxH (mm) ► Rod Lenses These components are designed for use in a variety of laser and imaging applications. The addition of this product line is part of a continued effort to support current trends toward miniaturization. Its optical performance is similar to acylinder lens. Collimated light passing through the diameter ofthe rod will be focused into a line. Quantity pricing and custom sizes, including variations in polished/groundsurfaces, are available to OEM customers upon request. Specifications Material Surface quality Size OxL (mm) ► 45°...
Open the catalog to page 10
FIFO Photonics offers many kinds of high precision prisms. The selection of the most suitable prisms is primarily dependent on the application. ► CornerCubePrisms Corner cube prisms, which have three mutually perpendicular surfaces and a hypotenuse face, are designed to reflect any ray or beam entered the prism face, regardless of the orientation of the prism, back onto itself. Amirrorwill only do that at the normal internal angle of incidence. There are three total internal reflections within the corner cube. They are called corner cubes because the three surfaces that make up the pyramid...
Open the catalog to page 13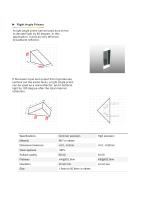
► Right Angle Prisms A right angle prism can be used as a mirror to deviate light by 90 degree. In this application, it acts as very efficient broadband reflector. Ifthe beam input and outputfrom hypotenuse surface (on the same face), a right angle prism can be used as a retroreflector, and it deflects light by 180 degree after the total internal reflection. Specifications Material Dimension tolerance Clear aperture Surface quality Flatness Deviation Size Common precision BK7 or others +0.0, -0.2mm >80% 60-40 A/4@632.8nm ±3 arc min 1.5mm to 50.8mm or others High precision
Open the catalog to page 14

