
Catalog excerpts

Science & Technology CO2 Laser Cutting of Flexible Glass Substrates Xinghua Li & Sean Garner
Open the catalog to page 1
Outline • Flexible glass as an electronic substrate • CO2 laser cutting – Principles, parameters and process window • Conclusions Science & Technology
Open the catalog to page 2
Flexible Glass Enables High-Quality Electronics Substrate choice critical for device fabrication & performance • Substrate integrates designs, materials, & processes – Essential for overall optimization – Glass enables improved resolution, registration, performance & lifetime • Ultra-slim flexible glass ( 200µm thick) compatible with: – Sheet-fed & web conveyance continuous processes – High strength cutting – Reliable device assembly & packaging Flexible glass barrier Flexible glass substrate Science & Technology
Open the catalog to page 3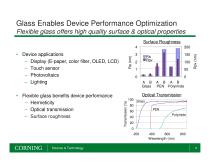
Glass Enables Device Performance Optimization Flexible glass offers high quality surface & optical properties Surface Roughness 3 Optical Transmission Transmission (%) • Flexible glass benefits device performance – Hermeticity – Optical transmission – Surface roughness • Device applications – Display (E-paper, color filter, OLED, LCD) – Touch sensor – Photovoltaics – Lighting Science & Technology
Open the catalog to page 4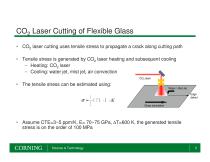
CO2 Laser Cutting of Flexible Glass • CO2 laser cutting uses tensile stress to propagate a crack along cutting path • Tensile stress is generated by CO2 laser heating and subsequent cooling – Heating: CO2 laser – Cooling: water jet, mist jet, air convection CO2 laser • The tensile stress can be estimated using: Water / Mist Jet Edge defect Glass translation • Assume CTE=3~5 ppm/K, E= 70~75 GPa, ∆T=600 K, the generated tensile stress is on the order of 100 MPa Science & Technology
Open the catalog to page 5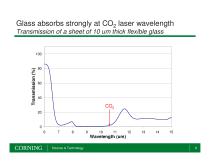
Glass absorbs strongly at CO2 laser wavelength Transmission of a sheet of 10 um thick flexible glass Wavelength (um) Science & Technology
Open the catalog to page 6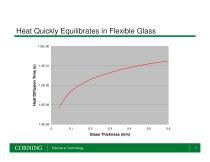
Heat Quickly Equilibrates in Flexible Glass Heat Diffusion Time (s) Science & Technology
Open the catalog to page 7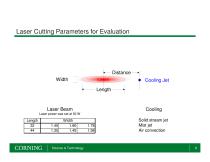
Laser Cutting Parameters for Evaluation Distance Width Laser Beam Science & Technology Solid stream jet Mist jet Air convection
Open the catalog to page 8
Laser Cutting of 100 µm Flexible Glass Laser Cutting Speed (mm/s) Laser Cutting Speed (mm/s) • Cutting speed decreased with increased distance • Cutting speed decreased slightly with increased laser beam length • Cutting speed showed little variation with respect to laser beam width 1.60 mm 1.78 mm Speed without active cooling 1.35 mm mist 1.45 mm mist 1.58 mm mist Without active cooling Distance from center (mm) 32 mm length Science & Technology Distance from center (mm)
Open the catalog to page 9
Laser Cutting of 200 µm Flexible Glass • Cutting speed decreased with increased distance • Little change in cutting speed was observed with increased laser beam length • Cutting speed showed little variation with respect to laser beam width Laser Cutting Speed (mm/s) Laser Cutting Speed (mm/s) 180 160 1.45 mm 1.60 mm 1.78 mm Without active cooling Without active cooling Distance from center (mm) 32 mm length Science & Technology Distance from center (mm)
Open the catalog to page 10
Laser Cutting of 200 µm Flexible Glass Solid water jet vs Mist Jet vs Air Convection • Cutting speed did not change with respect to cooling media (water stream, mist) • Cutting speed with air convection cooling is much slower than with forced cooling Laser Cutting Speed (mm/s) 220 200 180 160 140 1.35 mm solid 1.45 mm solid 1.58 mm solid 1.35 mm mist 1.45 mm mist 1.58 mm mist Air convection Distance from center (mm) Science & Technology
Open the catalog to page 11
Influence of Thermal Contact between Glass & Platen • Thermal contact of glass with platen affects cutting speed – Cutting speed increased by >40 mm/s for 100 µm flexible glass when a thermal barrier was used • Choice thermal barrier materials can reduce abrasion of glass with metal platen – Porous polytetrafluoroethylene film – Porous polyethylene film – Metal platen coated with polytetrafluoroethylene film • Film porosity enables vacuum holding and further reduces thermal contact Science & Technology
Open the catalog to page 12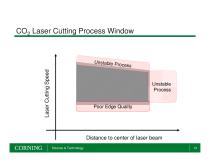
CO2 Laser Cutting Process Window Laser Cutting Speed Unstable Process Poor Edge Quality Distance to center of laser beam Science & Technology
Open the catalog to page 13
Conclusions • CO2 laser cutting enables high speed processing of flexible glass substrates • Cutting speed depends weakly on laser beam parameters • Contacts between glass and metal carrier should be minimized to avoid thermal conduction and abrasions • Process window can be clearly defined at a stable cutting condition with high edge quality Science & Technology
Open the catalog to page 14All CORNING Display Technologies catalogs and technical brochures
-
Gorilla® Glass 5
2 Pages
-
Corning Iris®
2 Pages
-
Aspheres by Corning
2 Pages
-
UltraFlat™
2 Pages
-
Tropel® FlatMaster® MSP
2 Pages
-
Optical Solutions
4 Pages
-
EAGLE XG® Slim
2 Pages
-
Scoring of AMLCD Glass
4 Pages
Archived catalogs
-
Jade® Product Information Sheet
3 Pages
-
Jade® Material Information Sheet
2 Pages

































