Catalog excerpts

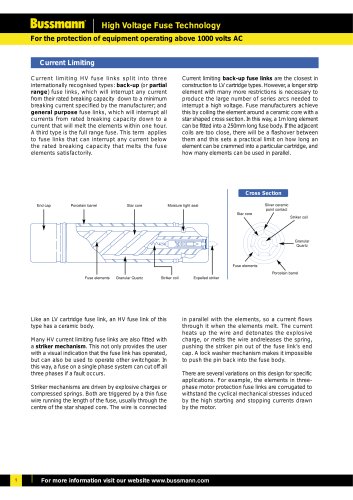
back-up fuse links are the closest inconstruction to LV cartridge types. However, a longer strip element with many more restrictions is necessary to produce the large number of series arcs needed to interrupt a high voltage. Fuse manufacturers achieve this by coiling the element around a ceramic core with a star shaped cross section. In this way, a 1m long element can be fitted into a 250mm long fuse body. If the adjacent coils are too close, there will be a flashover between them and this sets a practical limit on how long an element can be crammed into a particular cartridge, and how many elements can be used in parallel. Like an LV cartridge fuse link, an HV fuse link of thistype has a ceramic body.Many HV current limiting fuse links are also fitted witha > Current limiting HV fuse links split into threeinternationally recognised types: general purpose fuse links, which will interrupt allcurrents from rated breaking capacity down to a current that will melt the elements within one hour. A third type is the full range fuse. This term applies to fuse links that can interrupt any current below the rated breaking capacity that melts the fuse elements satisfactorily. Current limiting back-up (or partialrange ) fuse links, which will interrupt any currentfrom their rated breaking capacity down to a minimum breaking current specified by the manufacturer; and striker mechanism . This not only provides the userwith a visual indication that the fuse link has operated, but can also be used to operate other switchgear. In this way, a fuse on a single phase system can cut off all three phases if a fault occurs. Striker mechanisms are driven by explosive charges orcompressed springs. Both are triggered by a thin fuse wire running the length of the fuse, usually through the centre of the star shaped core. The wire is connected > Cross Section End capPorcelain barrel Fuse elementsGranular QuartzStriker coilExpelled striker Star coreMoisture tight seal Silver ceramicpoint contact Star coreStriker coil GranularQuartzFuse elementsPorcelain barrel in parallel with the elements, so a current flowsthrough it when the elements melt. The current heats up the wire and detonates the explosive charge, or melts the wire andreleases the spring, pushing the striker pin out of the fuse links end cap. A lock washer mechanism makes it impossible to push the pin back into the fuse body.There are several variations on this design for specificapplications. For example, the elements in three- phase motor protection fuse links are corrugated to withstand the cyclical mechanical stresses induced by the high starting and stopping currents drawn by the motor. > 1
Open the catalog to page 1
Liquid fuselinks are based on early non-currentlimiting fuse links which use liquids to quench the arc. The fuse element is anchored to the top ferrule of a glass tube filled with a quenching liquid - usually a hydrocarbon. The rest of the tube is filled with a spring that holds the element - or a strain wire in very high voltage fuse links - in tension. When the element melts, the spring pulls the two parts of the element apart, extending the arc and quenching it in the liquid. expulsion fuse links and liquid fuse links .Expulsion fuses are an effective way of protecting overhead...
Open the catalog to page 2
The time current characteristics of the Sђ range is optimised to ensure improved discrimination with upstream devices and to give fast clearance of earth faults in the secondary terminal zones. The breaking performance with low over currents is adequate to cater for all normal distribution applications, where low voltage fuse links on the secondary side take care of low overload faults, leaving the high voltage fuse links to clear major faults ahead of LV protection. The fuse links are suitable for use even where there is no secondary LV protection, provided that they are used in fuse...
Open the catalog to page 3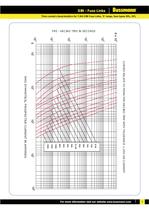
CURVES RELATE TO MEAN PRE-ARCING TIME WITH TOLERANCE + RMS SYMMETICAL PROSPECTIVE CURRENT IN AMPERES 6.3A10A16A 20A 25A31.5A40A50A63A 80A 100A125A160A 10% ON CURRENT 5 >
Open the catalog to page 6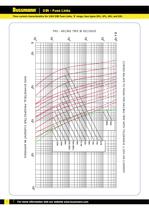
CURVES RELATE TO MEAN PRE-ARCING TIME WITH TOLERANCE + RMS SYMMETICAL PROSPECTIVE CURRENT IN AMPERES 160A 200A 6.3A10A16A 20A25A31.5A40A50A (SDL) 63A (SDL)80A100A 125A 10% ON CURRENT 5 >
Open the catalog to page 7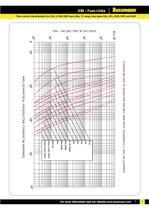
CURVES RELATE TO MEAN PRE-ARCING TIME WITH TOLERANCE + RMS SYMMETICAL PROSPECTIVE CURRENT IN AMPERES 6.3A10A16A20A25A31.5A (SDM)40A (SDM)50A (SFM)63A80A/75A100A (15.5kV ONLY) 125A (15.5kV ONLY) 10% ON CURRENT 5 >
Open the catalog to page 8
CURVES RELATE TO MEAN PRE-ARCING TIME WITH TOLERANCE + RMS SYMMETICAL PROSPECTIVE CURRENT IN AMPERES 80A100A125A160A 6.3A10A 16A20A 25A31.5A40A (SDM)50A63A71A 10% ON CURRENT 5 >
Open the catalog to page 9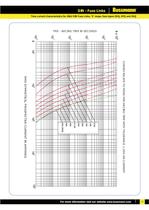
CURVES RELATE TO MEAN PRE-ARCING TIME WITH TOLERANCE + RMS SYMMETICAL PROSPECTIVE CURRENT IN AMPERES 6.3A10A16A20A25A31.5A40A50A63A (SXQ) 10% ON CURRENT 5 >
Open the catalog to page 10
CURVES RELATE TO MEAN PRE-ARCING TIME WITH TOLERANCE + RMS SYMMETICAL PROSPECTIVE CURRENT IN AMPERES 100A80A 63A50A40A 31.5A 25A20A16A 10A 6.3A 10% ON CURRENT 5 >
Open the catalog to page 11
4 3 CURVES RELATE TO MEAN PRE-ARCING TIME WITH TOLERANCE + RMS SYMMETICAL PROSPECTIVE CURRENT IN AMPERES 40A31.5A25A20A16A10A6.3A 45A 10% ON CURRENT 5 >
Open the catalog to page 12
The Bussmann range of motor fuse links are designed to meet the specific requirements necessary for motor protection. During the starting cycle of direct on-line motors, the fuse elements will reach a considerably higher temperature than during normal operation; (this is due to the the high amount of current the motor will draw as it starts, typically, 6 times its normal load current value). This results in expansion and contraction of the fuse elements and could cause premature operation of the fuse.Bussmann motor fuse links encompass an advanced design to minimise this effect. This...
Open the catalog to page 17
Fuse Links provide short circuit protection in motor circuits to both the motor starter and cables from the starter to the motor.Overload protection is provided by the motor starter, generally by an overload relay and contactor. Combination striker trippingmay also form part of associated equipment which houses the fuse links and motor starters. > For any motor the fuse current rating is determined by magnitude and duration of starting current, except in a few situations where the starting currents are very light. The fuse current rating should therefore be selected as follows: > In the...
Open the catalog to page 18All COOPER Bussmann catalogs and technical brochures
-
Micro Blade Fuses
2 Pages
-
FMG Fuse Holder
1 Pages
-
Battery Isolators
2 Pages
-
True Sine Wave Inverter
2 Pages
-
Converters / Equalizers
2 Pages
-
Multi-Battery Isolators
4 Pages
-
High Speed Fuses
2 Pages
-
HC7 Series
2 Pages
Archived catalogs
-
Product Guide
6 Pages
-
Full Line catalog
240 Pages