 Website:
Bruker Daltonics
Website:
Bruker Daltonics
Group: Bruker
Catalog excerpts

Electron Transfer Dissociation (ETD) Look Beneath the Surface Innovation with Integrity
Open the catalog to page 1
Bruker Daltonics – Leader in ETD Technology amaZon – Featuring ETD Since its commercial introduction in 2005, Bruker has been the leader in highly efficient and sensitive electron transfer dissociation (ETD) and proton transfer reaction (PTR) technology. We are constantly developing cutting-edge solutions for in-depth characterization of proteins and top-down sequencing analysis using our ETD technology. Using smart combinations of CID and ETD our customers obtain the greatest possible depth of information. Both complementary and confirmatory identification of post-translational...
Open the catalog to page 2
ETD Applications – From PTM to Top-Down Analysis As a complementary fragmentation technique to CID, ETD is of major importance for: Localization of PTMs, such as phosphorylation, sulfonation, and nitrosylation Analysis of O- and N-glycopeptides Characterization of disulfide linkages Identification of non-tryptic peptides, such as those with multiple basic residues Determination of protein termini by top-down sequencing In vacuum RF detection Ion guide High-transmission dual ion funnel transfer line Off-axis geometry Vacuum Stage 1 AtmosphericPressure Ion Source High energy conversion...
Open the catalog to page 3
ETD and PTR on the amaZon – Technology Leadership Key technical facts ETD cleaves N-Cα bonds producing c- and z-ions Labile bonds of PTMs remain intact The most efficient reagent – Fluoranthene – is used for both ETD and PTR Highest sensitivity for low-abundance peptides on an LC timescale: Identification of 18 peptides with a Mascot score > 20 from 500 amol BSA on column The 3D advantage The “3D advantage” of the spherical ion trap is the decisive factor for the highest efficiency ETD and PTR reactions: Robust and fast trapping of cations and anions for direct ETD reaction Better cross...
Open the catalog to page 4
A Must for Protein Characterization The regulatory function of many proteins is controlled by reversible PTMs such as PTM analysis includes identification and unambiguous site localization. ETD is the method of choice for site-profiling of biologically important PTMs. In modification on the peptide backbone and therefore enables a definite assignment of the modification site. CID spectra generate significant neutral loss of sulfonation and phosphorylation abundance peptide fragments. Because it is a very labile PTM, sulfonation is especially difficult to analyze using CID. However, ETD...
Open the catalog to page 5
Complete Glycopeptide Analysis Glycopeptide analysis is of particular interest in glycomics, because detailed information about glycan, peptide and glycosylation site is needed to under- stand relationships between structure, Tools for in-depth characterization of Dramatic enhancement of glyco- peptide ionization and shift to higher charge states for highest ETD spectra quality Identification of glycan composition and structure with GlycoQuest localization of glycosylation sites Fragment triggered ETD enables targeted glycopeptide profiling. ETD is only triggered if diagnostic oxonium ions...
Open the catalog to page 6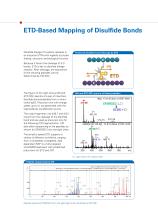
ETD-Based Mapping of Disulfide Bonds Disulfide linkage of cysteine residues is an important PTM with regards to protein folding, structure, and biological function. Because it favors the cleavage of S-S bonds, ETD is key to disulfide linkage analysis. After cleavage, the sequences Preferred disulfide bond cleavage by ETD The figure on the right shows MS and ETD MS2 spectra of a pair of interchain disulfide-bound peptides from a mono- clonal lgG2. Precursor ions with charge states up to 4+ are generated with the CaptiveSpray nanoBooster source. result from the cleavage of the disulfide bond...
Open the catalog to page 7
Top-Down Protein Characterization Sequence variant analysis of full-length hemoglobin Until now, sequence variant analysis of full-length hemo- globin has been a major after precise isolation of the multiply charged Hb chains charged) generates specific fragments that enable an unambiguous identification Typical extracted ion chromatograms sample. Several sequence- chain variants
Open the catalog to page 8
Technical Specifications Technology-driven solutions Source options Patented SmartICC™ for optimal ion storage SmartFrag™ Enhanced for reproducible high-quality MS/MS spectra generation and confident library searches Panorama fragmentation (PAN) enabling CID fragmentation without 1/3 cut-off CaptiveSpray nanoBooster: robust and reliable plug-and-play nano/cap ESI source for flow rates from 50-5000 nL/min ESI, APCI, APPI, and DIP source for direct analysis of solids and liquids Advion Triversa NanoMate Smart CE-MS coupling with grounded spray needle MS/MS modes Software solutions •...
Open the catalog to page 9
Further Reading Bruker brochures CaptiveSpray nanoBooster The revolution in Proteomics Ionization Glyco Analysis Solutions Expanding the frontier in Glycobiology amaZon speed Ion Trap Performance Beyond Imagination Bruker Application Notes App-Note LCMS-57 In-depth Characterization of Neutral and Acidic Glycopeptides by ZIC-HILIC Enrichment and Mass Spectrometry Jessica Wohlgemuth, Sven Andrecht, Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany; Andrea Schneider, Anja Resemann, Arndt Asperger, Bruker Daltonik GmbH, Bremen, Germany (2010) App-Note LCMS-66 Straightforward N-glycopeptide analysis combining fast...
Open the catalog to page 10All Bruker Daltonics catalogs and technical brochures
-
Maritime Detection Systems
7 Pages
-
SVGps
4 Pages
-
RAPIDplus
7 Pages
-
TIMON
13 Pages
-
RoadRunner
5 Pages
-
MATRIX-MG Series
7 Pages
-
MALDI Biotyper® CA System
12 Pages
-
RAID-XP
5 Pages
-
RAID-M Series
7 Pages
-
HDX Solution
2 Pages
-
EVOQ GC-TQ
8 Pages
-
timsTOF PRO
8 Pages
-
Agri Solutions brochure
8 Pages
-
PesticideScreener
8 Pages
-
Elute LC series
8 Pages
-
nanoElute®
6 Pages
-
timsTOF™
8 Pages
-
rapifleX™
8 Pages
-
amaZon SL
6 Pages
-
compact
8 Pages
-
MALDI Biotyper
56 Pages
-
rapifleX™ MALDI Tissuetyper™
8 Pages
-
MALDI PharmaPulse™
4 Pages
-
Toxtyper
6 Pages
-
impact II
12 Pages
-
maxis II
12 Pages
-
amaZon speed
10 Pages
-
Albira Brochure
12 Pages
-
prime
12 Pages
-
solarix
10 Pages
-
Metabolomics
12 Pages
-
aurora M90
10 Pages
-
Clean Room Pack
4 Pages
-
MATRIX-F FT-NIR Spectrometer
2 Pages
-
TANGO
12 Pages
-
The new autoflex? series
10 Pages
-
MM 2
6 Pages
-
µRAID
4 Pages
-
Radiation Backpack Sentry
4 Pages
-
Posterbook Metabolomics ebook
14 Pages
-
CaptiveSpray nanoBooster
8 Pages
-
Scion SQ Series GC-MS
8 Pages
-
solariX XR
12 Pages
-
aurora Elite
6 Pages
-
nano-Advance UHPLC
8 Pages
-
EVOQ
12 Pages
-
CaptiveSpray
4 Pages
-
ImagePrep
4 Pages
-
micrOTOF-Q II
12 Pages
-
PROTEINEER fc II
4 Pages
-
Ultraflextreme
16 Pages
-
Autoflix speed
10 Pages
-
microflex
6 Pages
-
SCION 436-GC
4 Pages
-
SCION 456-GC
4 Pages
-
GC CARE
8 Pages
-
Brochure BioTools 2.2
10 Pages
-
Brochure micrOTOF II
8 Pages
-
Brochure EASY-nLC
6 Pages
Archived catalogs
-
impact HD
12 Pages
-
RAID-M 100
6 Pages
-
compact?
6 Pages
-
micrOTOF-Q III
6 Pages
-
Toxtyper
8 Pages
-
MALDI Biotyper
12 Pages
-
Brochure MetaboliteTools 1.1
8 Pages
-
Brochure ProfileAnalysis
4 Pages















































































