
Catalog excerpts

Full Displacement Pile System Process and equipment
Open the catalog to page 1
FDP Full Displacement Pile System Soil displacement piles are bored cast in-situ concrete piles constructed by advancing a displacement boring tool into the ground with a rotary drilling rig using both torque and crowd force. The precondition for the successful deployment are modern rotary drilling rigs offering high levels of torque, downward thrust and retraction force, as well as a tall torsion-resistant drill mast. The technique is ideally suited for a wide spectrum of soil conditions ranging from sandy gravel, sand, silt and clay to soft organic soils, so long as the soil is...
Open the catalog to page 2
Advantages of the Displacement Pile System High Bearing Capacity Minimal Amount of Spoil Material Displacement of the volume of soil into the surrounding soil formation produces a highly densified body of soil. This effect results in an increase in shaft friction and base resistance (in relation to the nominal diameter). During drilling and pushing the displacement tool into the ground, the displaced volume of soil is pushed fully into the surrounding soil material by the displacement body. In the absence of soil being conveyed to the surface, this system is suited particularly well for...
Open the catalog to page 3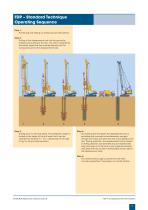
FDP – Standard Technique Operating Sequence Step 1: Positioning and setting up drilling rig over pile position. Step 2: Drilling of the displacement tool into the ground by rotating and pushing of the tool. The soil is loosened by the starter auger and then pushed laterally into the surrounding soil by the displacement body. Step 3: Drilling down to the final depth. The installation depth is limited by the height of the drill mast, but it can be extended by between 6 – 10 m, depending on the type of rig, by using a kelly extension. Step 4: On reaching the final depth the displacement tool...
Open the catalog to page 5
FDP – Standard Technique Displacement Tool Post-densification during extraction Counter-rotating flight on a conical body for densification of any loose soil areas during extraction of the tool Stabilisation Cylindrical displacement body for stabilisation of the displaced soil material Densification Conical shape of the hollow stem induces horizontal forces in the soil conveyed upwards by the flight (horizontal densification energy) Loosening The soil is loosened by the starter auger section and conveyed upwards by the flights FDP Full Displacement Pile System © BAUER Maschinen GmbH, 6/2013
Open the catalog to page 6
FDP – Standard Technique Drilling Depths and Drilling Diameter Drilling rigs of the BG-Series and universal base machines of the subsidiary company, RTG Rammtechnik (RG rigs) are ideally suited as base carriers for the FDP piling technique. Rig selection is dependent on the required drilling depth and necessary torque. The drilling depth can be increased by equipping the base machines with optional equipment (kelly extension and lattice boom extension). Ø D1 = Drilling diameter Ø D2 = Drill string diameter Ø
Open the catalog to page 7
FDP “Lost Bit” Technique As a variant, the FDP soil displacement pile system can also be deployed with a sacrificial drill bit. It differs from the standard technique by a detachable fullface drill bit, a hollow drill stem with a larger internal diameter and a concrete hopper that is mounted at the top of the hollow stem. With this set-up concrete can be placed in the pile by gravity feed alone without the application of pressure. Due to the "unpressurised" placement of the concrete, excessive consumption of concrete is kept to a minimum particularly in soft soils. It also reduces the risk...
Open the catalog to page 8
FDP – “Lost Bit” Technique Operating Sequence Step 1: Positioning and setting up drilling rig over pile position, attaching sacrificial drill bit. Step 2: Drilling of the displacement tool into the ground by rotating and pushing of the tool. The soil is loosened by the starter auger and then pushed laterally into the surrounding soil by the displacement body. Step 3: Drilling down to the final depth. The installation depth is limited by the height of the drill mast, but it can be extended by up to 6 – 10 m, depending on the type of rig, by using a kelly extension. The drilling depth can...
Open the catalog to page 9
FDP – “Lost Bit” Technique Equipment Drive assembly with concreting equipment “Lost Bit” Standard: Steel or cast iron drill bit Drill bits made of ultra high-strength concrete are in the experimental phase Concrete hopper Concrete hose pipe Camera Rotary drive Hydraulic guide FDP drill string “Lost Bit” drill string Comprising lost drill bit, starter auger, auger lead section, displacement body, drill string The auger lead section is used for loosening hard soils. It is available in different lengths. In normally displaceable soils the auger lead section is omitted. FDP Full Displacement...
Open the catalog to page 10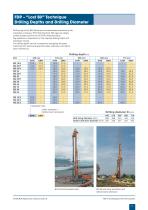
FDP – “Lost Bit” Technique Drilling Depths and Drilling Diameter Drilling rigs of the BG-Series and universal base machines of the subsidiary company, RTG Rammtechnik (RG rigs) are ideally suited as base carriers for the FDP piling technique. Rig selection is dependent on the required drilling depth and necessary torque. The drilling depth can be increased by equipping the base machines with optional equipment (kelly extension and lattice boom extension). Standard mast Kelly extension + lattice boom extension STM Drilling diameter D (mm) 440 368 Drill string diameter (mm) Hollow drill stem...
Open the catalog to page 11
FDP Displacement Pile System – Quality Assurance Control and modulation with electronic “assistants” Most of the Bauer rigs can be equipped with electronic software programmes for use with the FDP Soil Displacenment Pile System (“Drilling Assistant”), which modulate the optimal rate of penetration and crowd force during the drilling process for an optimal speed of rotation of the displacement tool. The desired initial parameters can be input by the rig operator with the help of simple onscreen menues. By using a programmable “extraction assistant”, the speed of extraction and volume of...
Open the catalog to page 12All BAUER Maschinen GmbH catalogs and technical brochures
-
brochure BAUER
20 Pages
-
BAUER Dynamic Compaction
4 Pages
-
Ground Improvement
16 Pages
-
SMW Soil Mixing Wall – System
12 Pages
-
CSM- Cutter Soil Mixing
16 Pages
-
SMW Soil Mixing Wall ? System
12 Pages
-
VDW Double Head Drilling System
12 Pages
-
MC 64 Foundation crane
14 Pages
-
MC 96 Foundation crane
14 Pages
-
MC 128 Foundation crane
10 Pages
-
BD 50 Decanter
8 Pages
-
Well Drilling Unit
4 Pages
-
Ground Improvement
16 Pages
-
TBA 300 Deep Drilling Unit
8 Pages
-
TBA 200 Deep Drilling Unit
8 Pages
-
Exploration and Mining Equipment
12 Pages
-
MC Foundation Cranes
12 Pages
-
TR Depth Vibrators
4 Pages
-
BC 32 Trench Cutter
6 Pages
-
BG 36 H Rotary Drilling Rig
12 Pages
-
BG 20 H Rotary Drilling Rig
12 Pages
-
BG 12 H Rotary Drilling Rig
12 Pages

































