Catalog excerpts

Company of the Leister Group Breath Analysis - Gastrointestinal Diseases Gas sensing modules for medical applications Axetris’ OEM gas sensing modules are able to measure both methane and carbon dioxide simultaneously, this makes them particularly suited for medical applications where the analysis of patient’s exhaled air is used to support the diagnosis of various gastrointestinal diseases, e.g. food intolerances. Brief application description The analysis of exhaled breath air is an effective non-in-vasive technique to diagnose food intolerances such as lactose intolerance, malabsorption of fructose, sucrose and sorbitol as well as diseases such as the Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO) or the infection with Helicobacter Pylori (urea breath test UBT). The breath analysis based diagnosis of above mentioned diseases is performed by measuring the concentration and ratio of specific gas components such as hydrogen (H2), methane (CH4), carbon dioxide (CO2) or ammonia (NHg). Hydrogen is produced in the intestinal lumen by bacteriological breakdown of carbohydrates and its detection helps clinicians to understand digestive problems. Methane provides important insights into the performance of the carbohydrate metabolism and significant levels of methane can suggest indigestion and are a possible indicator of fructose or lactose intolerance. Ax-etris’ gas sensing technology is capable of measuring methane with unprecedented precision and selectivity at trace levels. Carbon dioxide is considered an indicator for various infections as well as liver malfunction and excessive bacteria growth. Moreover, carbon dioxide is a quality indicator, indicating whether the patient is taking sufficiently long and deep breaths during the test phase, thus to ensure the samples used for analysis are alveolar. Low levels of carbon dioxide suggest shortness of breath. Carbon dioxide is used as a reference to derive the amount of exhaled air that has been measured by the sensor and is used as a reference to determine the correct ratio of all breath air constituents. Benefits of TDLS technology: S High selectivity and precision to target gases ■S Detection limits down to sub-ppm level •/ Optical, contact-less laser-based measurement ■/ Low cost of ownership, high reliability in the field ■S Long lifetime The before mentioned constituents in exhaled human breath air can be detected and measured with Tunable Diode Laser Spectroscopy (TDLS), where the high selectivity and the ability to measure at sub-ppm levels are well-known technology-specific strengths compared to other approaches. Our offering as OEM partner Axetris offers in-depth TDLS technology and application expertise as well as close collaboration and partnership from initial feasibilities through product design, launch and lifecycle management.
Open the catalog to page 1
Application Note LGD Breath Analysis - Gastrointestinal Diseases axetris Company of the Leister Group Size: When it comes to integrate the sensing module in a benchtop device or a portable instrument, size becomes a critical customer requirement. The small footprint design of our LGD Compact platform is well-suited to fulfill those needs. Performance: The increasingly demanding performance requirements clearly indicate the need for increased performance such as lower detection limits, higher measuring speed, multi-range and dual-gas measurement capabilities. Affordability: With the...
Open the catalog to page 2All Axetris AG catalogs and technical brochures
-
Infrared Sources
12 Pages
-
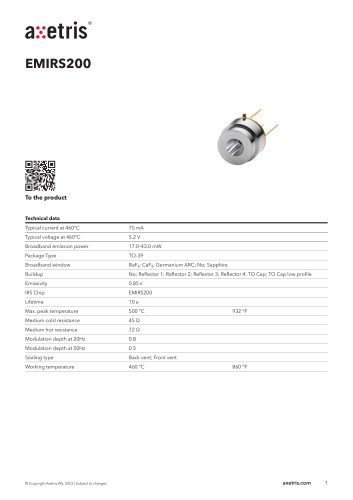
Infrared Sources EMIRS200
1 Pages
-
EMIRS200
2 Pages
-
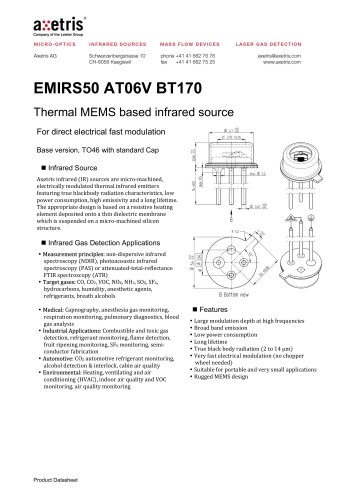
EMIRS50 AT06V BT170
8 Pages
-
EMIRS50 AT06V BR26M
8 Pages
-
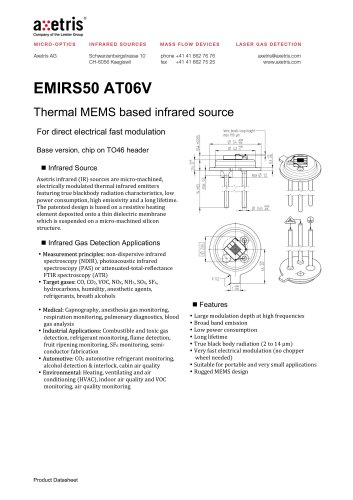
EMIRS50 AT06V
8 Pages
-
EMIRS50 AT06V BR25M
8 Pages
-
EMIRS50 AT06V BC150
8 Pages
-
MFD BaseFlo Line
2 Pages
-
EMIRS50 AT06V BC150 Series
8 Pages
-
Inductively Coupled Plasma
2 Pages
-
Gas Chromatography
2 Pages
-
MFM / MFC RS-232
24 Pages
-
Infrared Sources EMIRS50
1 Pages
-
LGDF200 A CH4
8 Pages
-
LGDF200 H HCl
9 Pages
-
FL - Infrared Source EMIRS50
2 Pages
-
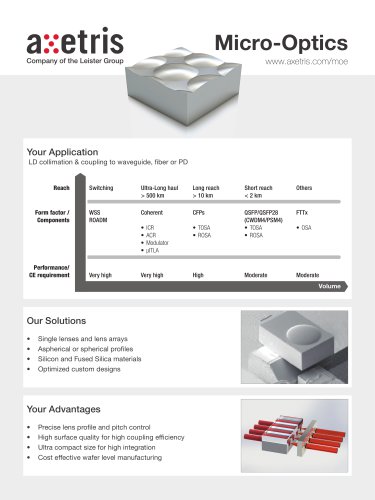
Micro-Optics
2 Pages
-
Infrared Sources EMIRS200
12 Pages
-
DS - LGDF200 H NH3
9 Pages
-
DS- LGDF200 A NH3
8 Pages
-
DS - LGDF200 A CO2
8 Pages
-
FL - Axetris MFD Plus
2 Pages
-
FL - LGD F200P2
2 Pages
-
Reflector
4 Pages
-
MEMS Services
2 Pages