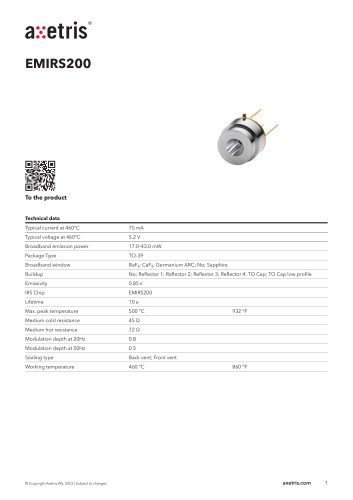
Catalog excerpts

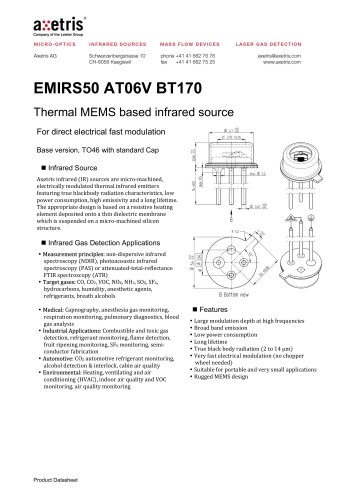
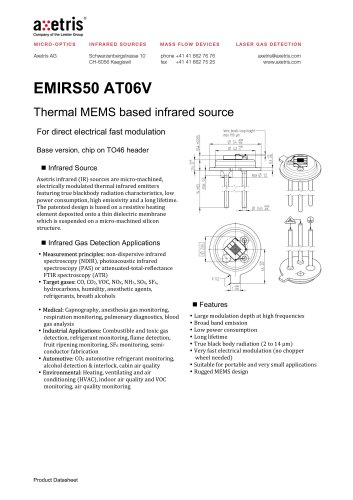
MICRO-OPTICS INFRARED SOURCES _ • ® axetris Company of the Leister Group MASS FLOW DEVICES LASER GAS DETECTION TO46 with Reflector 5 Sapphire or BaF2 window ■ Infrared Source Axetris infrared (IR) sources are micro-machined, electrically modulated thermal infrared emitters featuring true blackbody radiation characteristics, low power consumption, high emissivity and a long lifetime. The appropriate design is based on a resistive heating element deposited onto a thin dielectric membrane which is suspended on a micro-machined silicon structure. ■ Infrared Gas Detection Applications • Measurement principles: non-dispersive infrared spectroscopy (NDIR), photoacoustic infrared spectroscopy (PAS) or attenuated-total-reflectance FTIR spectroscopy (ATR) • Target gases: CO, CO2, VOC, NOx, NH3, SOx, SF6, hydrocarbons, humidity, anesthetic agents, refrigerants, breath alcohols • Medical: Capnography, anesthesia gas monitoring, respiration monitoring, pulmonary diagnostics, blood gas analysis • Industrial Applications: Combustible and toxic gas detection, refrigerant monitoring, flame detection, fruit ripening monitoring, SF6 monitoring, semiconductor fabrication • Automotive: CO2 automotive refrigerant monitoring, alcohol detection & interlock, cabin air quality • Environmental: Heating, ventilating and air conditioning (HVAC), indoor air quality and VOC monitoring, air quality monitoring ■ Features • Large modulation depth at high frequencies • Broad band emission • Low power consumption • Long lifetime • True black body radiation (2 to 14 pm) • Very fast electrical modulation (no chopper wheel needed) • Suitable for portable and very small applications • Rugged MEMS design
Open the catalog to page 1
■ Absolute Maximum Ratings (TA = 22°C) Parameter Note: Emission power in this table is defined by hemispherical radiation. Stress beyond those listed under “absolute maximum ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. Note: Diagram Rh500C — Rc22 | (Tm = 500°C) How to ensure that the maximum temperature for TM is not exceeded: 1. Determine electrical cold resistance Rc of the EMIRS device at TA=22°C 2. Ensure that anytime Rh does not exceed the representative limit as shown in this diagram with respect to these conditions: a. f > 10 Hz b. on-time (pulse duration) > 3 ms Electrical...
Open the catalog to page 2
■ Ratings at Reference Operation (RO1 TA = 22°C) Parameter Note: First order on-time model using Ton: First order off-time model using Tog: Time t (ms) Relative rectangular heater voltage (Vh) pulse with a relative pulse width of 62 ms at 10 Hz (time description of reference operation RO1) Product Datasheet Recommended frequencies from 10 Hz to 100 Hz Reference Operation: combines lower cut-off frequency of 10 Hz and maximum modulation depth (max-min signal)
Open the catalog to page 3
Typical Timing Characteristics Frequency (D = 62%) Relative (to RO) max, min, max-min values of optical output power (POO) versus frequency f with fixed and compensated VH Relative (to RO) electrical drive values heater voltage VH and power PH versus frequency f for compensation Note: Diagrams a, b Relative POO, VH, PH to reference operation (RO) f=10 Hz, rect. pulse D=62% max: maximum value of POO response shape min: minimum value of POO response shape max-min: amplitude calculation of POO resp. shape Fixed VH: same voltage for all frequencies. Compensated VH: for every frequency value,...
Open the catalog to page 4
Typical Timing Characteristics Pulse Duration D1 (f = 100 Hz) Voltage pulse duration D (%) Voltage pulse duration D (%) Relative (to D=62%) max, min, max-min values of optical output power (POO) versus duty cycle D with fixed and compensated VH Relative (to RO) electrical drive values heater voltage VH and power PH versus duty cycle D for compensation Note: Diagrams a, b Relative POO, VH, PH to reference operation (RO) f=100 Hz, rect. voltage pulse max: maximum value of POO response shape min: minimum value of POO response shape max-min: amplitude calculation of POO resp. shape Fixed VH:...
Open the catalog to page 5
■ Typical electrical/thermal characteristics (RO, TA = 22°C) Parameter Cold resistance Rc22 (fi) Mean1 and upper bound of heater voltage Vh vs. cold resistance RC22 Vh(1) Relative change of membrane temperature (Tm) by changing heater voltage (Vh) Mean1and upper bound of heater power Ph vs. cold resistance RC22 Relative change membrane temperature (Tm) by changing heater power (Ph) Product Datasheet Recommended operation mode T m =4609°C, which ensures 95% confidence that the maximum temperature Tm = 500°C is not exceeded.
Open the catalog to page 6
■ Typical Optical Characteristics (RO, TA = 22°C) Wavelength X (pm) Hemispherical spectral emissive power of EMIRS50 chip surface with a typical emissivity (mean from 2 to 14 pm) of £=0.85 Rel. opt. output power Poo (1) Opt. output power Poo (mW) Relative change of optical output power (Poo) by changing heater voltage (VH) Relative change of optical output power (Poo) by changing heater power (PH) Product Datasheet
Open the catalog to page 7
■ Specified Ratings at Test Voltage VT (on-time > 20 ms, TH = TA = 22°C) Parameter Note: Other optical output specifications are possible by customer specific requirements (e.g. spectral ranges). Note: Diagram Vtsooc — Rc22 | (TM ~ 500°C) Defined test voltage Vt for specified ratings: 3 3 1. Determine electrical cold resistance Rc22 of the EMIRS device at Ta=22°C ^ 3 2 2. Drive the device with Vt for each Rc as S 3. l shown in this diagram. & 3. Ratings are only valid for Tp = Ta = 22°C 3.0 Cold resistance Rc22 (fi) Test voltage Vt versus electrical cold resistance Rc22 at Ta = 22°C Product...
Open the catalog to page 8All Axetris AG catalogs and technical brochures
-
Infrared Sources
12 Pages
-
Infrared Sources EMIRS200
1 Pages
-
EMIRS200
2 Pages
-
EMIRS50 AT06V BT170
8 Pages
-
EMIRS50 AT06V BR26M
8 Pages
-
EMIRS50 AT06V
8 Pages
-
EMIRS50 AT06V BR25M
8 Pages
-
EMIRS50 AT06V BC150
8 Pages
-
MFD BaseFlo Line
2 Pages
-
Inductively Coupled Plasma
2 Pages
-
Gas Chromatography
2 Pages
-
MFM / MFC RS-232
24 Pages
-
Infrared Sources EMIRS50
1 Pages
-
LGDF200 A CH4
8 Pages
-
LGDF200 H HCl
9 Pages
-
FL - Infrared Source EMIRS50
2 Pages
-
Micro-Optics
2 Pages
-
Infrared Sources EMIRS200
12 Pages
-
DS - LGDF200 H NH3
9 Pages
-
DS- LGDF200 A NH3
8 Pages
-
DS - LGDF200 A CO2
8 Pages
-
FL - Axetris MFD Plus
2 Pages
-
FL - LGD F200P2
2 Pages
-
Reflector
4 Pages
-
MEMS Services
2 Pages