
Catalog excerpts

Experimental Validation of Autodesk® 3ds Max® Design 2009 and Daysim 3.0 NRC Project # B3241 Submitted to: Autodesk Canada Co. Media & Entertainment Submitted by: Christoph Reinhart1,2 1) National Research Council Canada - Institute for Research in Construction (NRC-IRC) Ottawa, ON K1A 0R6, Canada (2001-2008) 2) Harvard University, Graduate School of Design Cambridge, MA 02138, USA (2008 - )
Open the catalog to page 1
Experimental Validation of Autodesk® 3ds Max® Design 2009 and Daysim 3.0 Abstract This report compares daylight simulation results generated with two simulation programs, Autodesk® 3ds Max® Design 2009 software (3ds Max Design) and Daysim 3.0 (Daysim), to real indoor illuminance measurements in a sidelit space. The sidelit space was in a single location, but was configured with five fenestration and glazing options, and operated under a variety of sky conditions. The measurements form a set of five ‘daylighting test cases’ to evaluate the simulation capabilities and limitations of different...
Open the catalog to page 3
Radiance simulation predictions approached physical measurements under thousands of sky conditions in full-scale spaces with either a clear glazing and a lightshelf (Mardaljevic 1995; Jarvis and Donn 1997), venetian blinds (Reinhart and Walkenhorst 2001), or a translucent glazing (Reinhart and Andersen 2006). For a detailed discussion of these validation studies the reader is referred to the Reinhart/Andersen study. If validation studies based on measured data carry such weight among design practitioners interested in physically based simulation, it initially seems surprising that that...
Open the catalog to page 4
glazing and a diffuse lightshelf2. A larger objective of this work is to promote the use of validation studies among software developers and with the NRC having its own data set will allow the NRC to further distribute it to other parties. An acknowledged limitation of the new data set is that direct and diffuse irradiances were collected instead of sky luminance distribution. The absence of measured sky luminances limits the evaluator’s capability of differentiating between modeling errors introduced by the sky model versus the global illumination engine. On the other hand this combined...
Open the catalog to page 5
Figure 2(b) shows that there is a roughly 1.9 m high hedge in close vicinity to the two test rooms. The hedge was planted to visually separate the test rooms from the surrounding building, giving someone working in the test rooms an enhanced feeling of privacy. This measure was required since the test room is also used for human subject research. For the duration of the test case measurements the hedge was covered with a black cloth to reduce simulation errors due to inaccurate reflectances of the hedge. Interior illuminance measurements were taken with fifteen Licor illuminance sensors for...
Open the catalog to page 6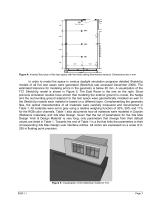
Figure 4: Inverted floor plan of the test space with the three ceiling illuminance sensors. Dimensions are in mm. In order to model the space in various daylight simulation programs detailed SketchUp models of all five test cases were generated (SketchUp last accessed December 2008). The estimated tolerance for modeling errors in the geometry is below 20 mm. A visualization of the TC1 SketchUp model is shown in Figure 5. The East Room is the one on the right. Since previous simulation studies have shown that modeling the exterior ground is crucial, the hedge and the surrounding ground...
Open the catalog to page 7
Table 1: Optical properties of all materials in the NRC Daylighting Laboratory. Layer Name Measurement Description Material modifier in Daysim/Radiance void plastic InteriorBackWall 00 5 0.77 0.77 0.77 0.004 0 Arch & Design Material * Parameters in 3ds Max Design #diff_color (color 197 197 197) #refl_weight 0.004 #refl_func_low 1.0 #refl_func_high 1.0 Back wall Three Minolta CM2500d spectrophotometer measurements of different wall sections. Results: 77% diffuse reflectance, 0.4% specular reflectance. Six Minolta CM2500d spectrophotometer measurements of different parts of the ceiling....
Open the catalog to page 8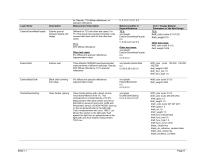
Layer Name Exterior ground between façade and hedge lot. Results: 11% diffuse reflectance, no specular reflectance Measurement Description Different for TC3 and other test cases. For TC.3 the gravel was exposed whereas it was covered with black cloth for the other test cases. TC.3: 22% diffuse reflectance. Other test cases: 0% diffuse and specular reflectance (approximated value) Arch 7 Design Material Parameters in 3ds Max Design TC.3: #diff_color (color 51 51 51) #refl_weight 0.0 Other test cases: #diff_color (color 0 0 0) #refl_weight 0.006 Exterior wall Three Minolta CM2500d...
Open the catalog to page 9
Layer Name Measurement Description Light shelf Three Minolta CM2500d spectrophotometer measurements of different parts of the light shelf. Results: 83% diffuse reflectance, 0.2% specular reflectance External window sill Six Minolta CM2500d spectrophotometer measurements of different mullion parts. Results: 60% diffuse reflectance, 15% specular reflectance Internal venetian blinds Four Minolta CM2500d spectrophotometer measurements of different parts of the venetian slats (top and bottom). Results:74% diffuse reflectance, 2% specular reflectance External venetian blinds Four Minolta CM2500d...
Open the catalog to page 10
Translucent panel Based on goniophotometer and integrating sphere measurements (Reinhart and Andersen 2006). Result: Translucent panel with a direct diffuse-diffuse transmittance of 16%’ #diff_weight 0.0 #refr_color (color 255 255 255) #refr_trans_on true #refr_transc (color 41.3355 41.3355 41.3355) #refr_transw 1.0 #opts_1sided true Translucent central glazing Based on integrating sphere measurements (Reinhart and Andersen 2006). Result: Tinted double glazing with a direct normal visible transmittance of 31%. This corresponds to a transmissivity of 34%. #diff_color (color 0 0 0)...
Open the catalog to page 11
For all test cases measurements were taken under a variety of sunny and cloudy sky conditions (Table 2). While the original measurement interval was 30 seconds the data was averaged down to 15 minute time step intervals. Table 2 reports the number of sky conditions collected for each test case when the outside vertical façade illuminance was over 1000 lux. Table 2: Overview of the number of sky conditions (15 minute averages) that were considered for each test case. # of sunny skies * # of cloudy skies total # of sky conditions TC 1 No Shading 1678 636 2314 TC 2 Lightshelf 1488 779 2267 TC...
Open the catalog to page 12All AUTODESK catalogs and technical brochures
-
Autodesk ® Flame®
2576 Pages
-
Autodesk® In Games
7 Pages
-
Autodesk® DirectConnect
80 Pages
-
AUTODESK ® 3DS MAX
1358 Pages
-
CEIT-KE
2 Pages
-
Novax DMA
2 Pages
-
autocad_civil3d
6 Pages
-
building_design_suite_2013
4 Pages
-
autocad_design_suite_2013
2 Pages
-
autocad_mep_brochure
4 Pages
-
acade_jic_overview_broch_us
4 Pages
-
alias_2013_
10 Pages
-
Autodesk Utility Design
2 Pages
-
Autodesk Toxik
4 Pages
-
Autodesk Subcontractor
4 Pages
-
Autodesk Smoke
2 Pages
-
Autodesk Mudbox
4 Pages
-
Autodesk MotionBuilder
4 Pages
-
Autodesk Moldflow Adviser
4 Pages
-
Autodesk Maya
4 Pages
-
Autodesk Lustre
6 Pages
-
Autodesk LandXplorer
4 Pages
-
Autodesk Inferno
1 Pages
-
Autodesk Flare
1 Pages
-
Autodesk Flint
1 Pages
-
Autodesk Cleaner XL
2 Pages
-
Autodesk Cleaner
2 Pages
-
Autodesk Buzzsaw
4 Pages
-
Autodesk Backdraft Conform
6 Pages
-
AutoCAD P&ID
4 Pages
-
AutoCAD Inventor Suites
32 Pages
-
AutoCAD Electrical
4 Pages
-
AutoCAD Revit MEP Suite
4 Pages
-
Autodesk Quantity Takeoff
4 Pages
-
Autodesk Revit Structure
8 Pages
-
AutoCAD Civil
6 Pages
Archived catalogs
-
BIM and Visualization
11 Pages
-
map3D_2013
2 Pages
-
3DS
8 Pages
-
autocad_lt_2013
2 Pages
-
acade_jic
4 Pages
-
factory_design_suite_2013
4 Pages
-
Autodesk Topobase
2 Pages
-
Autodesk Revit Structure
8 Pages
-
Autodesk Ecotect Analysis
4 Pages
-
Autodesk Alias Surface
4 Pages
-
Autodesk Alias Design
4 Pages
-
AutoCAD Structural Detailing
6 Pages
-
AutoCAD MEP
6 Pages
-
AutoCAD Mechanical
4 Pages
-
AutoCAD LT
2 Pages
-
AutoCAD Map 3D
4 Pages
-
Autodesk MapGuide Enterprise
4 Pages
-
AutoCAD Raster Design
2 Pages
-
Autodesk Navisworks Review
4 Pages
-
AutoCAD Civil 3D
2 Pages
-
Autodesk 3ds Max Design
4 Pages
-
AutoCAD Architecture
4 Pages
















































































