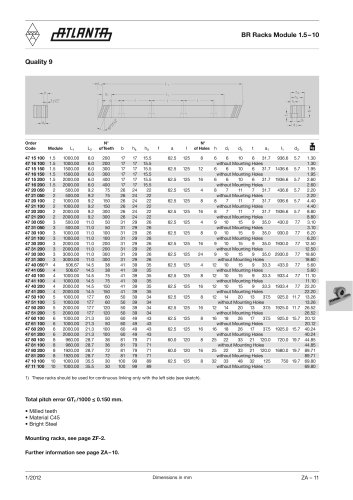
Catalog excerpts

Linear Guideway
Open the catalog to page 1
The Characteristics of PMI Linear Guideways LINEAR GUIDEWAY (1) High positioning accuracy, high repeatability The PMI linear guideway is a design of rolling motion with a low friction coeffcient, and the difference between dynamic and static friction is very small. Therefore, the stick-slip will not (2) Low frictional resistance, high precision maintained for long period The frictional resistance of a linear guideway is only 1/20th to 1/40th of that in a slide guide. With a linear guideway, a well lubrication can be easily achieved by supplying grease through the grease nipple on carriage...
Open the catalog to page 2
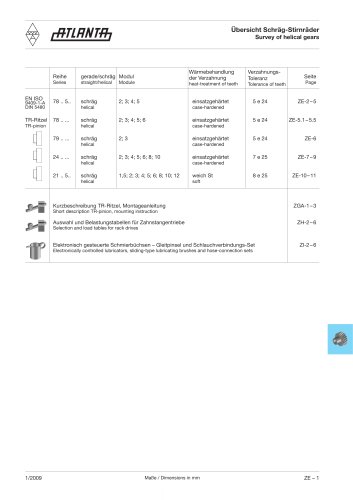
The Classification Chart of PMI Linear Guideways Type Major Application Full Ball, Heavy Load Type Full Ball, Compact Type Full Ball, Miniature Type MSA-A MSA-LA MSA-E MSB-TE MSB-E MSB-TS MSB-S • Heavy Load, High Rigidity • Self Alignment Capability • Smooth Movement • Low Noise • Interchangeability Machine Center, NC lathe, XYZ axes of heavy cutting machine tools, Grinding head feeding axis of grinding machines, Milling machine, Z axis of boring machine and machine tools, EDM, Z axis of industrial machine, Measuring equipment, Precision XY table, Welding machine, Binding machine, Auto...
Open the catalog to page 3
LINEAR GUIDEWAY Major Application MSR-E • Ultra Heavy Load • Ultra High Rigidity • Smooth Movement • Low Noise • Good lubricant Effect Machine Center, NC lathe, Grinding machine, Five axes milling machine, Jig borer, Drilling machine, Horizontal milling machine, Mold processing machine, EDM MSR-LS SME-E Ball Chain, Heavy Load Type SME-LE SME-S SME-LS SMR-E Roller Chain, Heavy Load Type SMR-LE SMR-S SMR-LS MSG-E Full Ball Wide Rail type • Heavy Load, High Rigidity • Self Alignment Capability • Ball Chain Design • Smooth Movement • Low Noise, Good Lubricant Effect • Interchangeability axis of...
Open the catalog to page 4
The Procedure of Select Linear Guideway span, No. of carriages, No. of rails change Load Rating and Service Life of Linear Guideway Parameters for calculating load on the linear guideway • Space available for installation • Size (span, No. of carriages, No. of rails) • Installation position (horizontal, vertical, tilted, or wallhung, etc.) • Magnitude, direction, and location of imposed load • Frequency of use (duty cycle) • Moving speed , acceleration • Required service life, and accuracy • Operating environment system, the load capacity and service life of the model must be taken into...
Open the catalog to page 5
4.2 Static Permissible MomentMo) When a moment is applied to a linear guideway, the rolling balls on both ends will receive the most stress among the stress distribution over the rolling elements in the system. The static permissible moment (Mo) refers to a static moment in a given direction with specific magnitude applied at the contact area under the most stress where the sum of permanent deformation develops between the raceway and rolling elements is 0.0001 times the diameter of rolling elements. Therefore, the static permissible moment sets a limit on the static moment. In linear...
Open the catalog to page 6
Hardness factor fH In order to ensure the optimum load capacity of linear guideway system, the hardness of raceway must be HRC58~64. If the hardness is lower than this range, the permissible load and nominal life will be decreased. For this reason, the basic dynamic load rating and the basic static load rating should be multiplied by hardness factor for rating calculation. See figure below. The hardness requirement of PMI linear guideway is above HRC58, thus the f=1.0. Load factor fw Although the working load of liner guideway system can be obtained by calculation, the actual load is mostly...
Open the catalog to page 7
Friction Coefficient Calculation of Working Load A linear guideway manipulates linear motion by rolling elements between the rail and the carriage. In which type of motion, the frictional resistance of linear guideway can be reduced to 1/20th to 1/40th of that in a slide guide. This is especially true in static friction which is much smaller than that in other systems. Moreover, the difference between static and dynamic friction is very little, so that the stick-slip situation does not occur. As such low friction, the submicron feeding can be carried out. The frictional resistance of a...
Open the catalog to page 8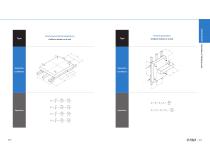
Type Operation Conditions Overhung horizontal application: Uniform motion or at rest Type Vertical application: Uniform motion or at rest Operation Conditions
Open the catalog to page 9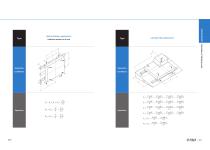
Type Operation Conditions Equations Wall installation application: Uniform motion or at rest Type Laterally tilted application z 5 73 C\ C o Equations FcosQ F cosQ l3 FcosQ14 FsinQhj FcosQ F cosQ l3 FcosQ l4 FsinQhj F cosQ F-cosQ l3 F cosQ 14 FsinQ-hj FcosQ FcosQ l3 FcosQ l4 _ Fsind hj
Open the catalog to page 10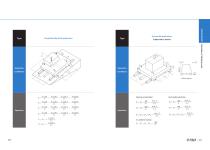
Type Operation Conditions Equations Longitudinally tilted application Type Horizontal application: Subjected to inertia z 5 73 cn c o F cosQ F cosQ l3 F cosQ -14 F-cosQ FcosQlj FsinQhj 2li FsinQhj FsinQhj 2-Ti FsinQh, 2-l} Equations During acceleration _ mg ma,l3 During deceleration
Open the catalog to page 11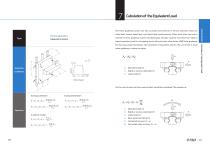
Operation Conditions Equations Vertical application: Subjected to inertia an= Velocity diagram During deceleration mg l, 21, Calculation of the Equivalent Load The linear guideway system can take up loads and moments in all four directions those are radial load, reverse-radial load, and lateral load simultaneously. When more than one load is exerted on linear guideway system simultaneously, all loads could be converted into radial or lateral equivalent load for calculating service life and static safety factor. PMI linear guideway has four-way equal load design. The calculation of...
Open the catalog to page 12
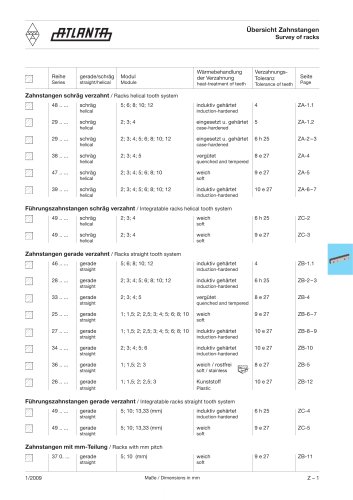
The Calculation of the Mean Load Types of Varying Load in consideration of varying loads of the host-system operation conditions. The mean load (Pm) is the load that the service life is equivalent to the system which under the varying load Calculation of Mean Load Loads that change monotonously conditions. The equation of mean load is: Total running distance (mm) Running distance under load Pn (mm) Exponent (Ball type:3, Roller type:10/3) Mean load (N) Minimum load (N) Examples for calculating mean load The Calculation of the Mean Load LINEAR GUIDEWAY When a linear guideway system receives...
Open the catalog to page 13All Atlanta Drive Systems catalogs and technical brochures
-
Linear Rail Systems
63 Pages
-
UHPR StrongLine DIN 5 Racks
1 Pages
-
Right-Angle Bevel Gearboxes
18 Pages
-
ATLANTA Product Overview
12 Pages
-
ATLANTA BG Servo-Bevel Reducers
13 Pages
-
ATLANTA B Servo-Worm Reducers
16 Pages
-
ATLANTA E Servo-Worm Reducers
18 Pages
-
ATLANTA HP Servo-Worm Reducers
17 Pages
-
ATLANTA HT Servo-Worm Reducers
15 Pages
-
ATLANTA Pinion Range
40 Pages
-
ATLANTA Rack Range
39 Pages