
Catalog excerpts

3-Way Temperature Control Valve Model G, Version G and Accessories Typical applications For engines, turbines, gearboxes and heat exchangers: l Charge air cooling l Secondary cooling systems l Fuel and lube oil preheating l Co-generation l Engine jacket water Electric GG valve For refineries, chemical plants and oil reproduction: l Waste heat boilers l Product coolers l Product heaters Pneumatic GG valve l Product condensers Key benefits l Ease of integration - valve size matches pipe size, resulting in reduced installation time and installation costs l Flexible design - ports can be configured to suit installation l Low pressure drop - compared to other valve types G valve compared with a typical equivalent competitor’s specification. Now even more compact l Small physical size l Hand wheel allows manual adjustment of valve (optional on pneumatic valve) - simplified set up and maintenance Datasheet_GG_Temp_Control_Valve_0212_Rev7 www.amot.com
Open the catalog to page 1
3-Way Temperature Control Valve - Model G, Version G Overview AMOT G valves are 3-way control valves consisting of a heavy duty rotary valve and either a quarter turn electric or pneumatic actuator. The valves provide a high degree of accuracy and repeatability for accurate temperature control and are equally accurate in mixing or diverting service over a wide flow range. The heavy duty rotor design provides tight temperature control without high maintenance requirements. The system is available in three standard control configurations: electric; pneumatic; and electro-pneumatic, offering...
Open the catalog to page 3
3-Way Temperature Control Valve - Model G, Version G System Types Electric Valve For the electric valve, the actuator of the G valve assembly uses an electric motor which rotates in either direction in response to the ON-OFF signals received. The motor drives a gearbox connected to the rotor shaft and turns the valve rotor clockwise or counter-clockwise, a maximum of 90 degrees. At the end of travel, limit switches are incorporated to isolate the electrical supply to the motor when the valve rotor has reached either end of the rotation. A feedback potentiometer is standard and provides...
Open the catalog to page 4
3-Way Temperature Control Valve - Model G, Version G System Types continued Pneumatic Valve The pneumatic valve uses a spring return pneumatic actuator and positioner to control the rotation of the valve in response to an input signal from a pneumatic or electro-pneumatic control system. The pneumatic control system sends a pneumatic signal ranging from 0.21 to 1.03 bar (3 to 15 psi) to the actuator to correctly position the valve at the desired temperature setting. The pneumatic control system usually consists of a P+I pneumatic controller, sensor and the necessary air supply conditioning...
Open the catalog to page 5
3-Way Temperature Control Valve - Model G, Version G Overview of Valve Body Key features and benefits l Lightweight and compact l Configurable ports - allowing flexibility on installation l Low pressure drop - enables savings on either valve or pump size l High accuracy providing better temperature control Valve Body Specification Flow to: 720m3/hr Sizes: Standard flow High flow 80mm - 200mm (3” - 8”) 80mm - 200mm (3” - 8”) 3,170 US gpm For valves with higher flow rates see datasheet GEF_GPD_Temp_Control_Valve For 50 mm (2”) and for 350 mm (14”) and above see Datasheet...
Open the catalog to page 6
3-Way Temperature Control Valve - Model G, Version G Modes of Operation - Electrically Actuated The unique construction of the AMOT G valve provides total flexibility by allowing you to select the valve port positions most ideally suited to meet your application requirements. There are two main types of mode of operation: 90° rotor that allows either ports 1 or 3 to be selected as the common port; and 180° rotor that requires port 2 to be the common port. Arrow indicates valve movement with increasing temperature or mA, as viewed from above (see diagram). For electrically actuated valves,...
Open the catalog to page 7
3-Way Temperature Control Valve - Model G, Version G Modes of Operation - Pneumatically Actuated The unique construction of the AMOT G valve provides total flexibility by allowing you to select the valve port positions most ideally suited to meet your application requirements. There are two main types of mode of operation: 90° rotor that allows either ports 1 or 3 to be selected as the common port; and 180° rotor that requires port 2 to be the common port. Arrow indicates valve movement with Increasing temperature or mA, as viewed from above (see diagram). Data sh eet_G G_Tem p_Contro l_Va...
Open the catalog to page 8
3-Way Temperature Control Valve - Model G, Version G Valve Sizing (Metric units) Valve Flowrate Selection (Flowrate m3/hr) 0.40 1 – Water Valve selection curves for valves with 90o rotor. For valves with 180o rotor multiply pressure drops by 2. 2 – ISO VG32 0.35 3 – ISO VG46 4 3 2 1 4 – ISO VG68 Recommended maximum pressure drop Pressure drop bar 0.30 0.25 0.20 AMOT type G valves are designed to produce minimal pressure drop. The normal recommendation in sizing the valves is to select a pressure drop between 0.01 to 0.3 bar (0.15 and 4.5 psi). 0.15 To use the graph it is advised to use the...
Open the catalog to page 9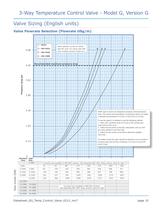
3-Way Temperature Control Valve - Model G, Version G Valve Sizing (English units) Valve Flowrate Selection (Flowrate USg/m) 1 – Water 2 – ISO VG32 5.08 3 – ISO VG46 Valve selection curves for valves with 90o rotor. For valves with 180o rotor multiply pressure drops by 2. 4 3 2 1 4 – ISO VG68 Pressure drop psi 4.35 Recommended maximum pressure drop 3.62 2.90 2.18 AMOT type G valves are designed to produce minimal pressure drop. The normal recommendation in sizing the valves is to select a pressure drop between 0.15 and 4.5 psi (0.01 to 0.3 bar). To use the graph it is advised to use the...
Open the catalog to page 10
3-Way Temperature Control Valve - Model G, Version G Valve Sizing Viscosity Correction For the selection of valves for more viscous fluids than water, the following must be calculated: Example: From the graph below: 100 cSt = correction factor of 0.68 0.68 x flow coefficient = corrected flow coefficient (Kv or Cv) Some approximate viscosities (cSt) of SAE oils at 40°C (110°F) are shown below, based on leading oil manufacturers published data. Viscosity: Find the viscosity of the fluid in which the valve is to operate. The viscosity is normally expressed in centistokes. Where ISO oil is...
Open the catalog to page 11All AMOT catalogs and technical brochures
-
IP1-Impact-Transmitter
2 Pages
-
7001 Swing Gate
4 Pages
-
4095 2-Way Vent Valve
1 Pages
-
4395 Electric Trip Switch
4 Pages
-
4103D Temperature Detector
4 Pages
-
1672 Pressure Sensing Valve
7 Pages
-
4047 Pressure Valve
5 Pages
-
4109 Vibration Sensor
7 Pages
-
Model 8402
6 Pages
-
Model 4123C
5 Pages
-
Model 4418F
9 Pages
-
Model 4420
7 Pages
-
Model 2180
6 Pages
-
XTS-W Bearing Wear Monitor (BWM)
11 Pages
-
SEDM
4 Pages
-
MPD Introduction
12 Pages
-
Control System Solutions
12 Pages
-
Chalwyn Spark Arrestors
4 Pages
-
System Selection Guide
12 Pages
-
Product Selection Guide
20 Pages
-
Intake Air Shutoff Valve
4 Pages
-
Metal Particle Detector
8 Pages
-
2 or 3-Way Pressure Valve
5 Pages




















































