
Catalog excerpts

Laser Power Control Units s-pol Laser capability to accomplish extremely precise tasks by applying high power impact within tiny spatial domain, e.g. diffraction limited spot, has lead laser power control to become an important variable that helps to optimise yield and secure successful completion of the task. There are various methods to control the power of solid state lasers which will be reviewed in this article. The simplest way to control laser output power is by controlling its gain medium pump power and in DPSS lasers it means adjustment of the current feeding laser diode. However such way of power control cannot ensure smooth and continuous laser power control because of several reasons. First of all, changing laser diode current introduces temperature shift in the diode which changes the band gap between conduction and valence bands, thus central wavelength of the pump is shifted, altering the conditions in solid state gain medium. In case of CW operation this string of related events introduce fluctuations in laser output power and it takes time to stabilize the power again. But if the laser is pulsed (e.g. passively Q-switched), not only the output power fluctuations are introduced, but also PRR and pulse duration would be altered with changing the pump power. What is more, when laser diode current is changed during the operation, additional degradation mechanisms emerge [1]. Thus this type of power control is only acceptable for the least power-sensitive applications. Extra-cavity laser power control is yet the most popular method of laser power management, for instance absorbing neutral density glass filters are useful to discretely attenuate relatively low power beams and are quite effective up to 1 J/cm² energy densities within the nanosecond regime. ND filters provide rather even attenuation over wide spectral range from UV to NIR. Quite similar are reflective neutral glass filters which are coated with metallic layer that transmits a portion of the radiation while reflecting and absorbing the rest of it. Advantage provided by metallic semi-reflecting Polarizing beam splitter cube s-pol 56° p-pol Brewster TFP Half-wave plate s-pol 72° p-pol Ultrafast TFP Glan polarizer Fig. 1. Options of polarization manipulation based attenuator. coating is the possibility to deposit thickness gradient of metallic layer allowing continuously variable density along filter cross-section. Laser sources with polarized output provide subtile attenuation option – output power control through manipulation of the polarization. Such method incorporates polarization rotator and polarizer. Polarization rotator is usually a waveplate or electrooptic (EO) modulator that rotates input polarization. Then the beam passes onto the polarizer, where orthogonal polarizations S and P are separated into two separate S and P polarized beams. Intensity ratio between the two beams is controlled by polarization
Open the catalog to page 1
rotator which can be either a waveplate or an EO modulator. The EO modulator can turn input beam polarization by 90° within tenths of picosecond [2], which makes it applicable in pulse picking/cavity dumping applications, but this comes at cost of complicated controller which must cope with voltage of several kV, thus it is used only for applications were fast open-shut rates are mandatory. If the waveplate is used as polarization rotator, it must be physically turned which slows down the polarization rotation but such scheme can be realized in both – manual and motorized control and the...
Open the catalog to page 2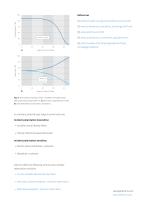
Fig. 4. Attenuation properties of two uncoated UVFS plate based attenuator operating at 1064 nm. a) attenuation dependence on AOI, b) transmitted beam polarization consistence. In summary, external laser output control units are: Incident polarization insensitive: • Variable neutral density filters • Fresnel reflections based attenuator Incident polarization sensitive: • Electro optical modulator + polarizer • Waveplate + polarizer Altechna offers the following continuously variable attenuation solutions: • Circular Variable Neutral Density Filters • Manually variable waveplate + polarizer...
Open the catalog to page 3






