
Catalog excerpts

LC/MS methods are rapidly becoming an important O tool for drug screening and confirmation because OO they typically don’t require a derivatization step, and are often less complicated than GC/MS methods. O You can simplify and optimize method development even further using new technologies from Agilent. O QUICK-REFERENCE METHOD GUIDE N CH 3 KeyC workflow considerations: H NH 2 H2 H NNH2 C C C C • epending on the C analytical instruments used, sample matrices – such as O CD H H Hblood, plasma, and urine – can adversely affect your system and columns. H H H Accordingly, reliable sample prep is an essential part of the workflow. O H3 • olumns and sample prep techniques should beCselected with an eye C H O NH toward return on investment – specifically, time and cost2 when compared C C to workflow performance and results. O H H • hen using an electrospray source, ion suppression caused by sample W matrices can negatively impact your MS results. O • any drugs of abuse are challenging to analyze because of factors, such as M volatility, hydrophobicity, and “stickiness” to glass and plastic.
Open the catalog to page 1
WHAT YOU’LL FIND IN THIS GUIDE Although both liquid chromatography and gas chromatography can be used for bioanalytical and forensics applications, this guide will focus on the LC/MS workflow. Depending upon the stage of testing you perform – and your ability to modify methods – the insights you find in this guide may help you improve throughput and results. Key information is organized as follows: • Outer panels: General overview, plus tips for working with analytes commonly targeted in drugs of abuse testing. • Center panels: Workflow recommendations for sample prep, separation, and...
Open the catalog to page 2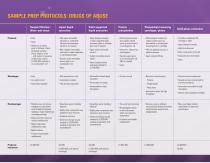
SAMPLE PREP PROTOCOLS: DRUGS OF ABUSE Sample filtration/ dilute-and-shoot Protocols Liquid-liquid extraction Solid-supported liquid extraction Protein precipitation Phospholipid removing cartridges/plates • dd water-immiscible A solvents (i.e. methylene chloride) and biological sample in a container •Apply biological sample to solid-supported liquid extraction plate or cartridge (pre-treat if needed) and organic solvent (such as acetonitrile) in a centrifugation vial • dd biological sample and A organic solvent (such as acetonitrile) to phospholipidremoving plate or cartridge • ix container...
Open the catalog to page 3
TIPS AND TOOLS: DRUGS OF ABUSE SEPARATIONS METHOD DEVELOPMENT CONSIDERATIONS Sample Prep Column Selection/Separation • an evaporate at the sample prep C extraction solvent evaporation step unless precipitated as salts by adding hydrochloric acid • Add HCl toward the end of evaporation to avoid formation of ammonium chloride salts, which cause ion suppression • oroshell 120 EC-C18, 3 x 50 mm provides excellent separation of P amphetamines and structurally similar drugs, such as ephedrine and its stereoisomer pseudoephedrine (as required by SAMHSA) • Recovery of longer-chain non-polar...
Open the catalog to page 4
TIPS AND TOOLS: DRUGS OF ABUSE SEPARATIONS continued ANALYTE METHOD DEVELOPMENT CONSIDERATIONS CHARACTERISTICS • Highly non-polar (Log P >6) Sample Prep Column Selection/Separation • ticks to glassware, LC tubing, and injector S parts • Deactivated vials/inserts and MeOH-rinsed/air-dried glassware recommended • Found in urine in a form of glucuronide conjugates • AMHSA requires converting glucuronides to THCA (most reliable conversion S method is base hydrolysis – incubation with KOH at 60 °C) • obile phase: A - 5 mM ammonium format in water; B - 100% M methanol • arboxylic acid; retained...
Open the catalog to page 5
HOW DO I CHOOSE THE RIGHT SAMPLE PREP TECHNIQUE? Select your sample prep method with your analytical goals and requirements in mind – including your lab affiliation/profile, regulatory environment, matrix, target analytes, cost considerations, and detection method. There is no standard procedure for defining a comprehensive sample preparation method, and various published procedures are often complementary, because they focus on different targeted analytes. Selecting a flexible sample preparation approach such as mixed-mode solid phase extraction (SPE) gives you a versatile tool for sample...
Open the catalog to page 6
Sample prep workflow recommendations for Bond Elut Plexa PCX Conditioning • onditioning with methanol is sufficient; equilibration with water not C needed. Sample loading • cidification (pH<6) recommended for basic and acidic analytes. A Allow samples to drip by gravity, or apply low vacuum (2-3” Hg). Wash 1 • Acidified aqueous wash for all analytes – use 2% formic acid Wash 2 • % methanol wash for most acidic and neutral analytes - test if higher 5 proportion of organic can be used without leading to analyte breakthrough • 00% methanol wash for most basic analytes (at this step,...
Open the catalog to page 7
WHICH LC COLUMN IS BEST FOR MY APPLICATION? You are likely under pressure to process more samples, faster – without compromising accuracy; therefore, you need to consider several factors during LC column selection. For example, poor column robustness can reduce column lifetime and lead to costly rework. In addition, samples with high analyte concentrations may require a column with higher capacity. A robust first choice for drugs of abuse: Poroshell 120 columns F ast Guards for UHPLC are also available to further extend column lifetime without reducing Fast LC performance. • ast separations...
Open the catalog to page 8
Choosing the right mobile phase • Mobile Phase B: 0.1% formic acid in methanol Part Number Includes one each of Poroshell 120 EC-C18, Phenyl-Hexyl and Bonus-RP • Mobile Phase A: 0.1% formic acid in water A good general mobile phase for basic drugs of abuse applications is: Includes one each of Poroshell 120 SB-Aq, Phenyl-Hexyl and Bonus-RP For THCA, use 5 mM ammonium formate in water for A, and 100% methanol for B. Optimizing column temperature For maximum column lifetime, you should generally run your analyses below 40 °C. More kits are available for other Agilent columns; see...
Open the catalog to page 9All Agilent Technologies - Life Sciences and Chemical catalogs and technical brochures
-
Agilent 280 Series AA Systems
12 Pages
-
Inorganic Standards
40 Pages
-
InfinityLab LC Supplies
148 Pages
-
General Chromatography
164 Pages
-
Sample Preparation (2018/2019)
144 Pages
-
MS500
12 Pages
-
FLAME ATOMIC ABSORPTION SPECTROSCOPY
104 Pages
-
Agilent training
27 Pages
-
AGILENT VACUUM PRODUCTS CATALOG
536 Pages
-
Vacuum Measurement Catalog
44 Pages
-
AGILENT ION Pumps
53 Pages
-
AGILENT DIFFUSION PUMPS
35 Pages
-
AGILENT Rotary Vane Pumps
29 Pages
-
Agilent InfinityLab LC Series
16 Pages
-
3100 fractionator
8 Pages
-
4200 MP-AES
12 Pages
-
Agilent GPC/SEC Solutions
12 Pages
-
Agilent?s biomass solutions
12 Pages
-
X-ray Crystallography
12 Pages
-
Agilent ProPulse NMR System
5 Pages
-
An autosampler like no other
4 Pages
-
Agilent U1450A/U1460A
19 Pages
-
Agilent B1507A
22 Pages
-
Agilent M9703A
16 Pages
-
W1905 Radar Model Library
16 Pages
-
M8048A ISI Channels
7 Pages
-
Agilent J-BERT M8020A
27 Pages
-
Agilent N8900 Series
10 Pages
-
I/O Hardware
16 Pages
-
Advanced Design System
16 Pages
-
RF & Microwave Attenuators
4 Pages
-
E4980AL Precision LCR Meter
8 Pages
-
FieldFox Handheld Analyzers
8 Pages
-
AFM/SPM Accessories
20 Pages
-
VEE 9.32
24 Pages
-
89600 VSA Software
9 Pages
-
Command Expert
2 Pages
-
E5061B Network Analyzer
8 Pages
-
E5071C ENA Network Analyzers
18 Pages
-
N9038A MXE EMI Receiver
2 Pages
-
N9322C Basic Spectrum Analyzer
10 Pages
-
Digital Multimeters
25 Pages
-
M9361A PXI Downconverter
2 Pages
-
Power Meters and Power Sensors
34 Pages
-
E7515A UXM Wireless Test Set
2 Pages
-
Agilent Power Products
31 Pages
-
E5063A Network Analyzer
8 Pages
-
Leak Detection Catalog
41 Pages
-
Agilent 7820A GC brochure
8 Pages
-
Agilent GC-MSD and QTOF
96 Pages
-
Agilent GC-MSD 5977
39 Pages
-
Agilent Intro BERLIN
24 Pages
-
1290 Infinity Quaternary LC
24 Pages
-
1260 Infinity Bio-inert
26 Pages
Archived catalogs
-
Diffusion Pumps Catalog
37 Pages






















































































































































