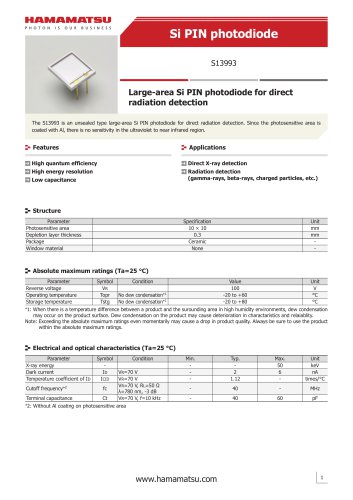
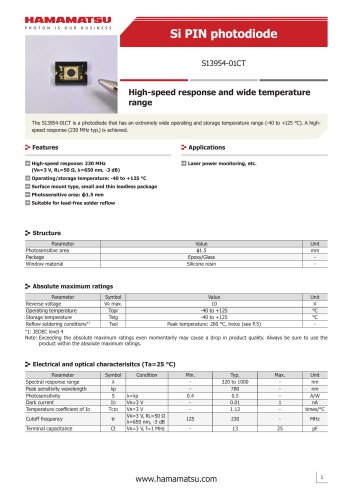
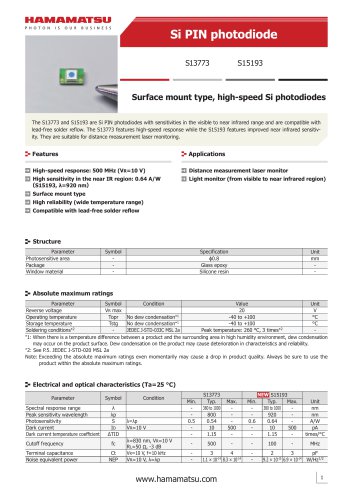
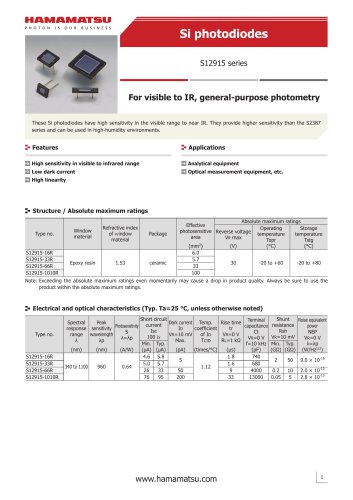
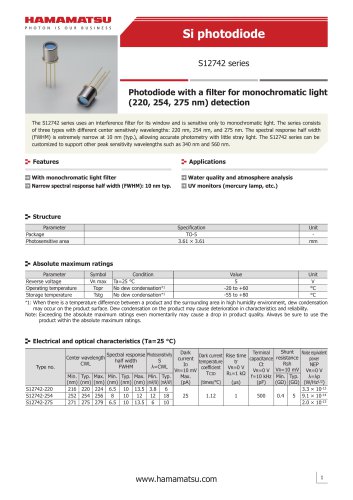
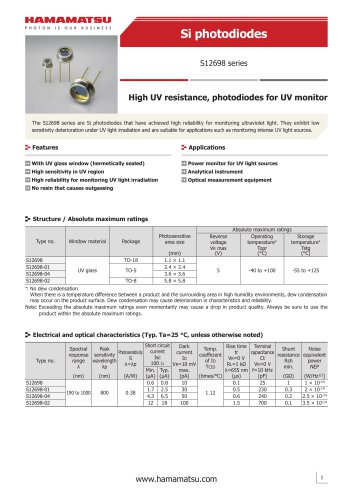
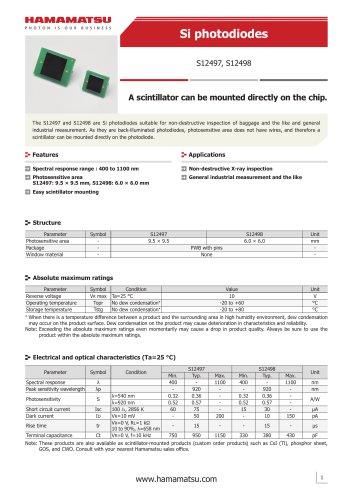
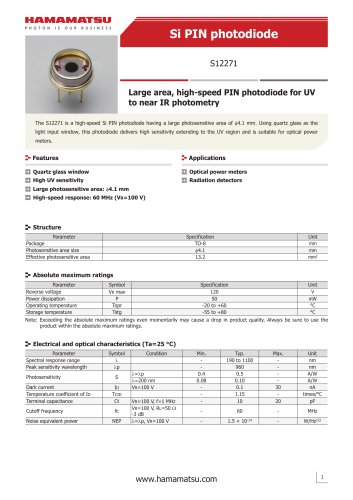
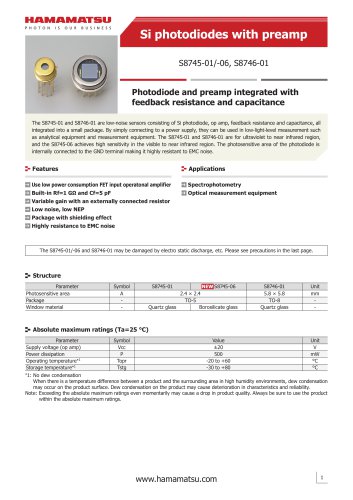
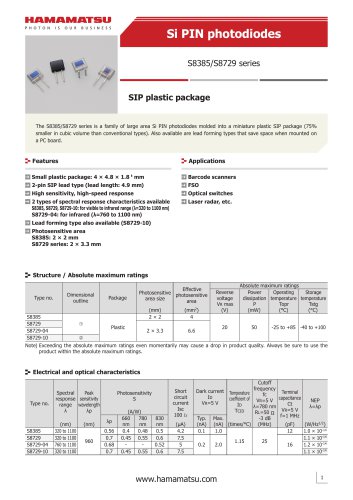
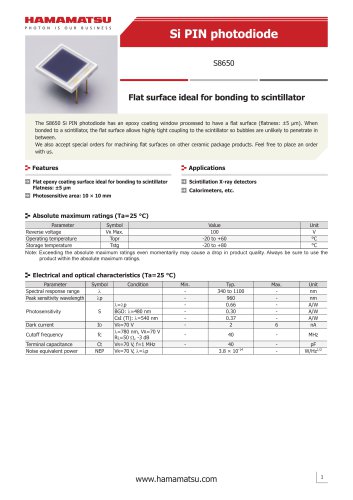
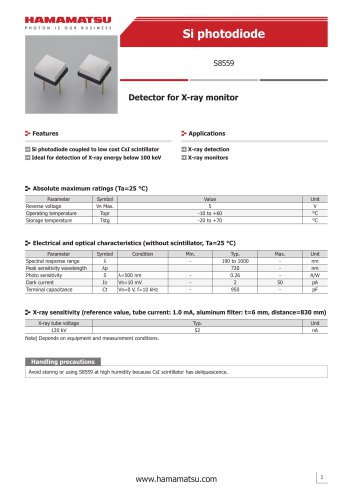
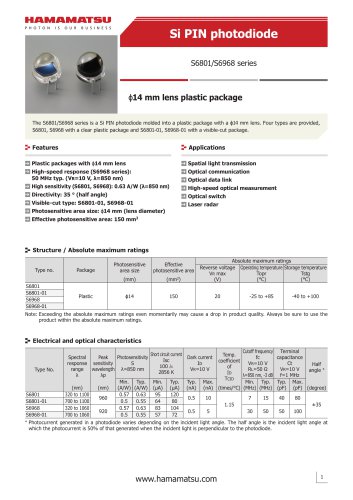
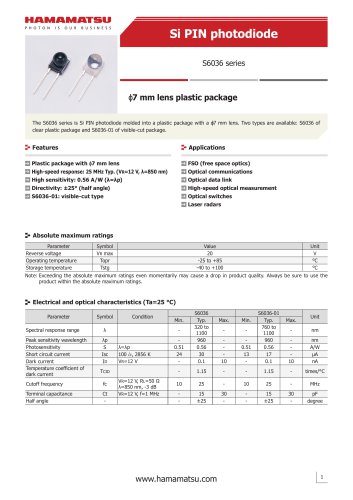
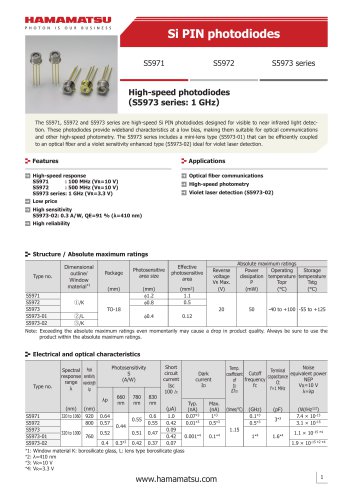
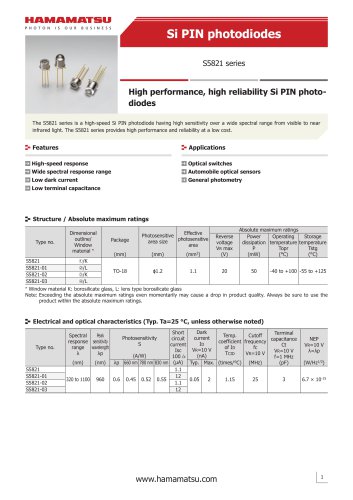
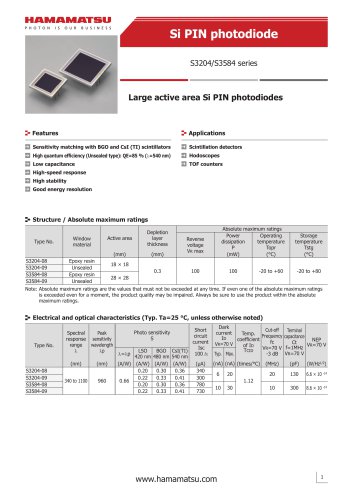
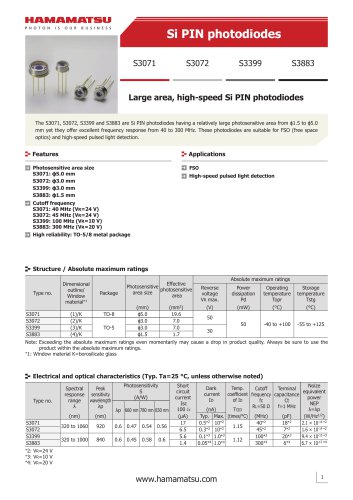
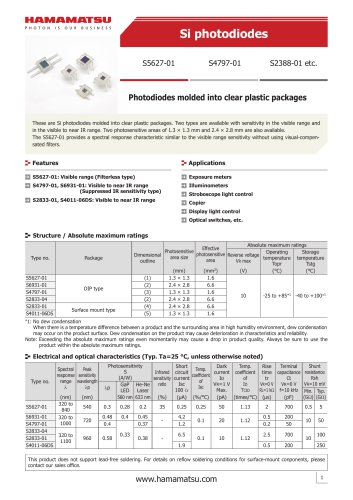
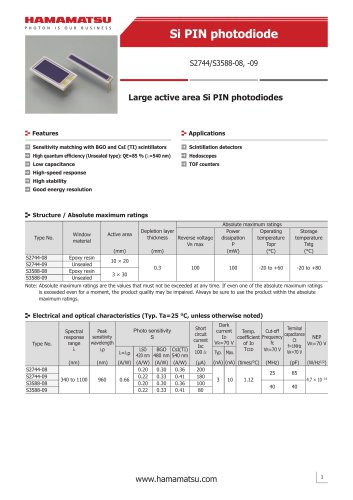
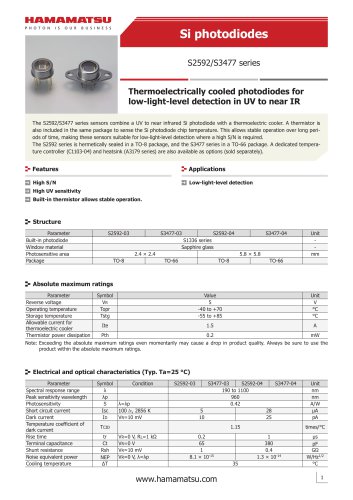
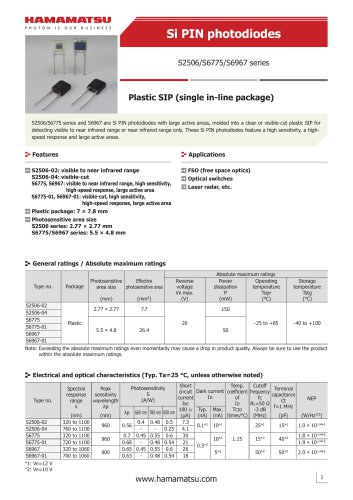
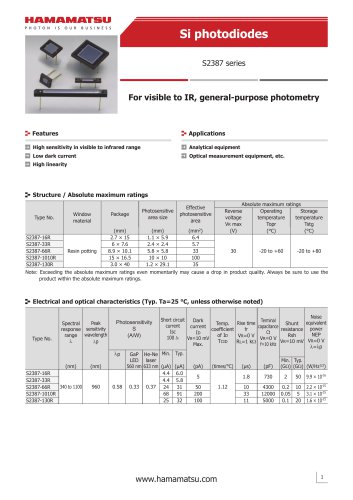
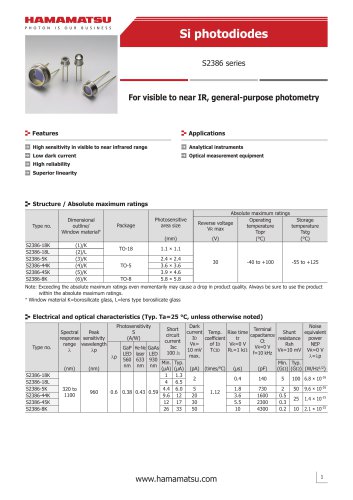
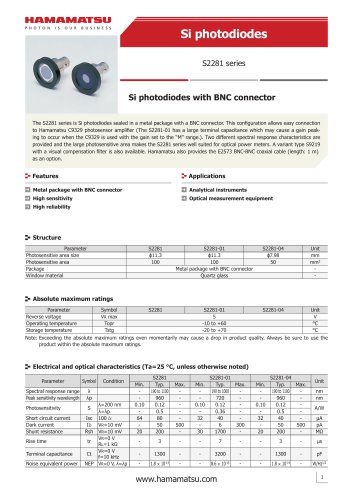
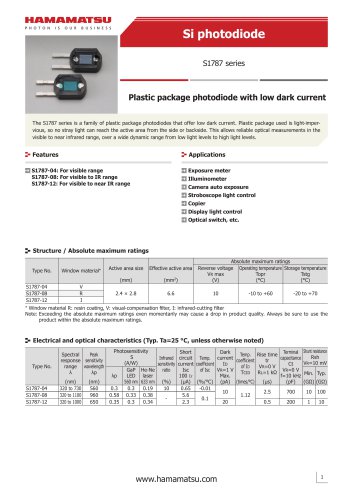
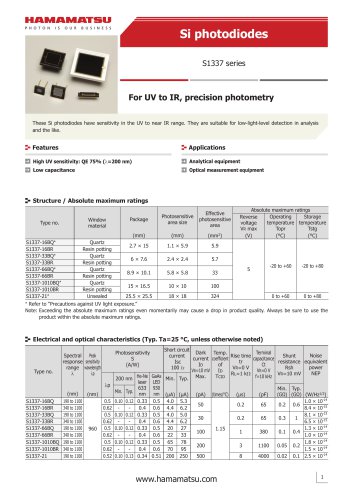
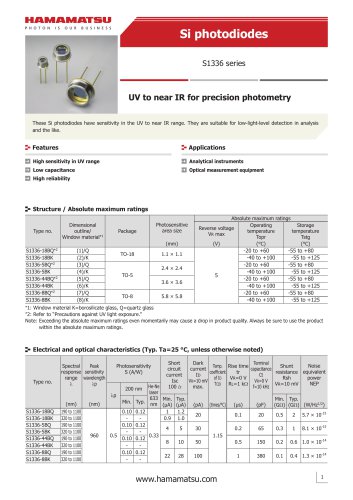
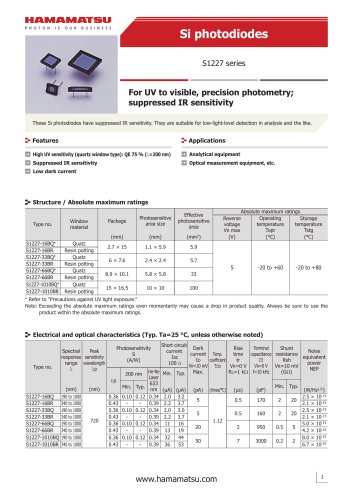
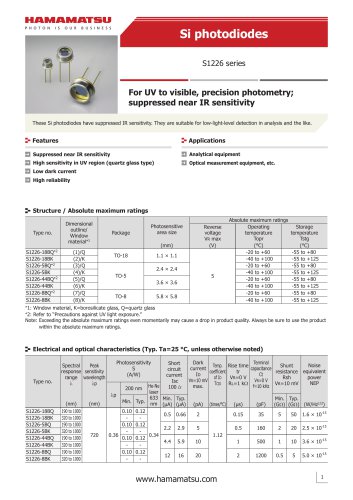
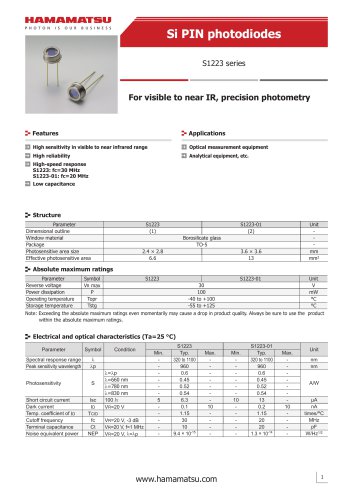
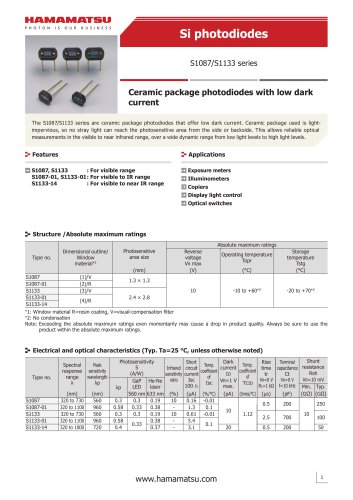
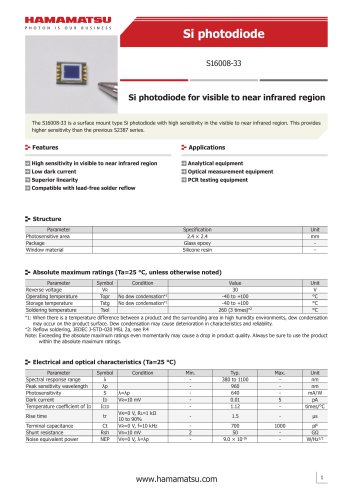
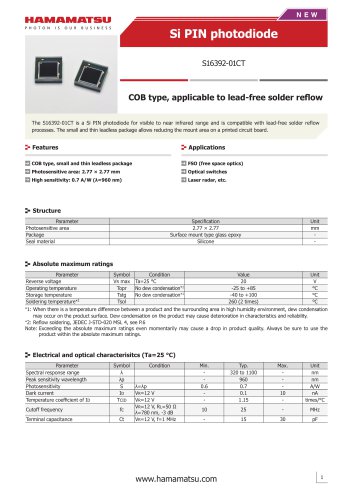
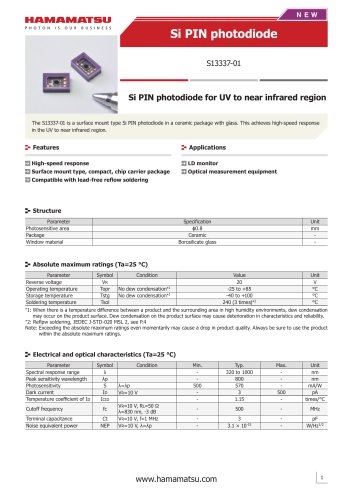
カタログの抜粋

Si photodiode MEMS mirror S13989-01H Miniature, high performance Electromagnetically driven two-dimensional laser scanning MEMS mirror The S13989-01H is an electromagnetically driven mirror that incorporates our unique MEMS (micro-electro-mechanical systems) technology. The device was made smaller by arranging the magnet beneath the mirror. High reliability was achieved by employing a hermetic seal package. Electrical current flowing in the coil surrounding the mirror produces a Lorentz force based on Fleming’s rule that drives the mirror. Hamamatsu MEMS mirrors offer a wide optical deflection angle and high mirror reflectivity. Concept drawing showing operating principle Machine vision (shape recognition) Wide optical deflection angle Industrial LiDAR Low voltage drive: suitable for installation on equipment Laser scanning microscope High reliability: hermetic seal package Various laser scan units Slow axis: linear operation possible Structure and principle In a MEMS mirror, a metallic coil is formed on a single-crystal silicon, a mirror is formed inside the coil through MEMS processing, and a magnet is arranged beneath the mirror. Within a magnetic field generated by the magnet, electrical current flowing in the coil surrounding the mirror produces a Lorentz force based on Fleming’s rule that causes the mirror to tilt. In addition, the mirror can be driven two-dimensionally with the combination of two springs formed by MEMS processing. The path of the laser light incident on the mirror surface is varied in this way to scan and project. Compared to the electrostatic or piezoelectric driven mirrors, electromagnetically driven MEMS mirrors are lower voltage driven and easier to use. Structure diagram Laser light Force Magnet Magnetic field KOTHC0058EB
カタログの1ページ目を開く
MEMS mirror Absolute maximum ratings (Ta=25 °C unless otherwise noted) Parameter Optical deflection angle*1 Drive current*2 Slow axis Optical deflection angle*1 Power consumption*3 Operating temperature*4 Storage temperature Fast axis Symbol θf_max Is_dc θs_max Pcoil Topr Tstg *1: Angle at which the torsional stress of the torsion bars becomes large and the service life is shortened *2: C current that causes damage to the wiring. Because driving the device with a DC current can shorten the service life, driving the D device with an AC current is recommended. *3: Coil power consumption. It...
カタログの2ページ目を開く
MEMS mirror Recommended operating conditions Parameter Incident angle*6 Fast axis Optical deflection angle*7 Drive frequency Incident angle*6 Optical deflection angle*7 Slow axis Drive frequency Operating temperature*9 *6: ncident angle at which a ϕ1 mm collimated laser beam is incident on the mirror positioned at an optical deflection angle of 0° I and at which the laser is within the effective area of the window material when scanning is performed at the recommended optical n of incident angle deflection angle Definition of incident angle A-A Fast axis scan direction incident angle B-B...
カタログの3ページ目を開く
MEMS mirror Electrical and optical characteristics (recommended operating conditions unless otherwise noted) Parameter Reflectance*11 Transmittance of window material*12 Resonant frequency Drive current Coil resistance Fast axis Back electromotive force Resonant frequency Slow axis Quality factor Optical deflection angle Drive current Temperature sensor Coil resistance Resistance Resistance temperature coefficient Condition λ=460 to 640 nm θin=0 to 43°*13, λ=460 to 640 nm Ta=25 °C, θf=±20°, Is=0 mA, square wave Ta=25 °C, ff=ff-r, θf=±20°, Is=0 mA, square wave Ta=25 °C, If=0.1 mA, Is=0 mA...
カタログの4ページ目を開く
MEMS mirror Effect of tilting the window material The S13989-01H has a window material tilted 20° relative to the slow axis scanning direction to achieve a highly reliable sealed package. The window material tilt is set so that the laser light reflected from the front or rear surface of the window does not enter the mirror scanning projection range. Scan light Incident light Spectral transmittance of window material Reflected light from the window surface Spectral transmittance of window material (Typ. Ta=25 °C, white light source, incident angle*=8°) Incident angle: 0° Incident angle: 30°...
カタログの5ページ目を開く
MEMS mirror Optical deflection angle vs. drive current Fast axis (Typ. Ta=25 °C, θs=0°, ff=ff-r, drive current: square wave) Optical deflection angle vs. frequency (fast axis) 5 (Typ. Ta=25 °C, θf=0°, fs=60 Hz, drive current: sin wave) Optical deflection angle (°) Optical deflection angle (°) Slow axis Optical deflection angle vs. frequency (low-speed axis) -10 -15 -300 Drive current (mAamp.) Drive current (mAamp.) KOTHB0062EA M aximum optical deflection angle vs. frequency (fast axis) O ptical deflection angle vs. frequency (slow axis) (Typ. Ta=25 °C, θs=0°, If=22 mAamp., drive current:...
カタログの6ページ目を開く
MEMS mirror Dimensional outline (unit: mm) Dimensional outline (unit: mm) Mirror surface Window thickness: 1.1 ± 0.1 Connector: DF40GL-44DP-0.4V (Hirose Electric) * Window material tilt relative to the mirror (mechanical deflection angle =0°) Connection Fast axis coil (+) Fast axis coil (+) NC NC NC Slow axis coil (+) Slow axis coil (+) NC NC NC Temperature sensor (+) Temperature sensor (-) NC NC NC Slow axis coil (-) Slow axis coil (-) NC NC GND Fast axis coil (-) Fast axis coil (-) Connection Fast axis coil (+) Fast axis coil (+) NC NC NC Slow axis coil (+) Slow axis coil (+) NC NC NC...
カタログの7ページ目を開く
MEMS mirror Mechanical deflection direction of mirror due to drive current The direction of the mirror’s mechanical deflection varies depending on the direction of the drive current flowing through the coil as follows. No drive current Negative current applied to the slow axis coil Positive current applied to the fast axis coil Positive current applied to the slow axis coil Negative current applied to the fast axis coil Fast axis Slow axis Note: s the drive frequency of the MEMS mirror increases, the phase lag of the optical deflection angle with respect to the drive A current increases. ∙...
カタログの8ページ目を開くHAMAMATSUのすべてのカタログと技術パンフレット
-
PHOTON COUTING HEAD
4 ページ
-
FLAT PANEL TYPE
4 ページ
-
SPAD MODULES
5 ページ
-
LIGHTNINGCURE
29 ページ
-
Xenon Flash Lamps
19 ページ
-
ORCA-FUSION C14440-20UP
12 ページ
-
NanoZommer series
8 ページ
-
C13410 series
4 ページ
-
C13410-06A
4 ページ
-
PMA-12
8 ページ
-
L12542
4 ページ
-
FLAT EXCIMER
16 ページ
-
Optical Gauge series
23 ページ
-
L15208-01
3 ページ
-
L15856-01
3 ページ
-
L14001-01
2 ページ
-
L11854-336-05
2 ページ
-
L14351-02
4 ページ
-
GC-113A
2 ページ
-
IMAGEMX2 series
8 ページ
-
ORCA-Fusion BT
9 ページ
-
DIUTHAME
12 ページ
-
J12853
2 ページ
-
J12432-01
2 ページ
-
J10919 SERIES
2 ページ
-
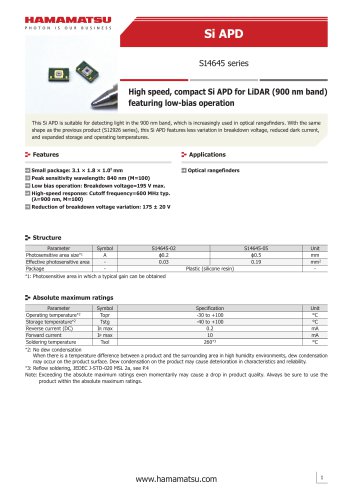
Si APD S14644 series
6 ページ
-
C15780-401
4 ページ
-
H15460-40
4 ページ
-
R14755U-100
2 ページ
-
Photo IC for rangefinder
14 ページ
-
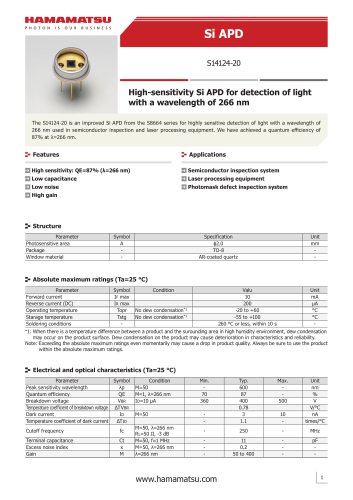
Si APD S14124-20
3 ページ
-
Si photodiode S10043
3 ページ
-
Si photodiode S9674
5 ページ
-
Si photodiode S8559
3 ページ
-
Si photodiode 8193
3 ページ
-
Si photodiode S7686
4 ページ
-
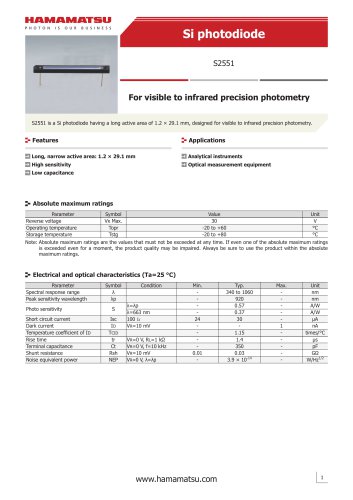
Si photodiode S2551
4 ページ
-
C13398 series
5 ページ
-
InGaAs Image sensors
17 ページ
-
Si APD S14645 series
6 ページ
-
Si APD S14643-02
6 ページ
-
MEMS mirror S13124-01
10 ページ
-
LIGHT SOURCES
23 ページ
-
PHOTOTUBES
8 ページ
-
FLAME SENSOR UVTRON
4 ページ
-
PSD
8 ページ
-
InGaAs Photodiodes
20 ページ
-
Infrared Detectors
36 ページ
-
Photo IC
8 ページ
-
Image Sensors
48 ページ
-
Si Photodiodes
48 ページ
-
Si APD
16 ページ
-
MPPC®, MPPC modules
34 ページ
-
Photonic Devices
44 ページ
-
IMAGE INTENSIFIERS
20 ページ
-
FLOW CELLS
4 ページ
-
COMPACT HIGH VOLTAGE
2 ページ
-
SCANBLOCK C10516
4 ページ
-
UV TRONR DRIVING
2 ページ
-
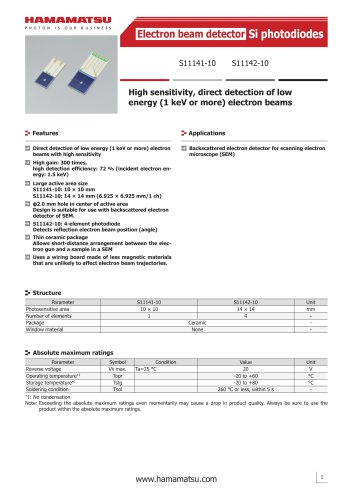
High sensitivity
2 ページ
-
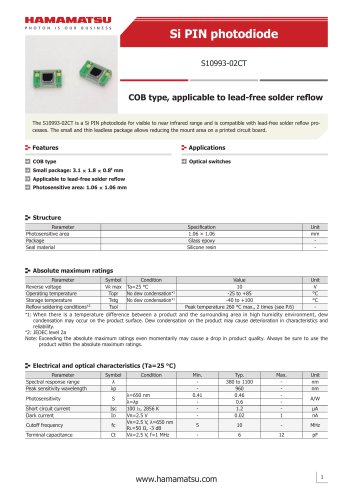
Si photodiodes
41 ページ
カタログアーカイブ
-
Opto-semiconductor Catalog
38 ページ