Catalog excerpts

SPIETH Hydrodynamic Radial-Slide-Bearings Series GLM Works Standard SN 03.01
Open the catalog to page 1
1.1. SPIETH Hydrodynamic Radial-Slide-Bearing 4 2. Adjustable SPIETH Radial-Slide-Bearing 5 2.5. Mounting and adjustment of play 8 3. Table of dimensions for Radial-Slide-Bearing Series GLM 10 4.1. Ascertainment of load capacity 11 4.2. Ascertainment of heating of the bearing 11 4.3. Viscosity of standard lubricants 13 4.4. Standard values for bearing play 13
Open the catalog to page 3
1. General In modern and powerful machines the importance of the spindle bearing is increasing. Solutions for these tasks are offered by roller bearings as well as by slide bearings. Increasing demands for long tool life as well as for surface performance, shape accuracy, and fabrication tolerances of the work pieces has been shown in the last years, that especially at hydrodynamic sectionalised surface slide bearings – with its caused by the lubricating film high damping properties and concentric accuracy – the smoothness as well as the insusceptibility to shock together with its high...
Open the catalog to page 4
The external lubrication by a pump is the most secure and efficient lubrication system. Especially for high sliding speeds which need a high quantity of oil for cooling the external lubrication supply by a pump is absolutely necessary. For this lubrication system any spindle position can be allowed. There is only the need for sufficient pump pressure to negotiate circuit and duct resistance to ensure an adequate quantity of oil for the temperature equation. As said before, the carrying liquid thrust will be created by itself after the rotation of the spindle has started. 1.5. Sealing Slide...
Open the catalog to page 5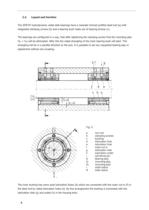
2.2. Layout and function The SPIETH hydrodynamic radial slide bearings have a meander formed profiled steel hull (a) with integrated clamping screws (b) and a bearing bush made out of bearing bronze (c). The bearings are configured in a way, that after tightening the clamping screws first the mounting play (S1 + S2) will be eliminated. After this the radial strangling of the inner bearing bush will start. This strangling will be in a parallel direction to the axis. It is possible to set any requested bearing play or adjustment without any scraping. Fig. 3: a b c d e f g h i S S1 S2 r R iron...
Open the catalog to page 6
The lubrication flutes are dividing the bushing bore in a few sliding surfaces. During the adjustment of bearing play, these sliding surfaces are changing their original radius in the way, that there will arise a wedge crack between sliding surface and spindle. The tightest point of this wedge crack will be in the middle of the sliding surface and will expand in both directions to the lubrication flutes. SPIETH hydrodynamic radial slide bearings are independent of the rotation direction of the spindle as the lubricant can flow under the developed pressure in the squeezed wedge crack and can...
Open the catalog to page 7
2.4.2. Spindle For an accurate concentricity the spindle contact surface has to be done cylindrically according to tolerance g5. Recommended quality of the spindle is a surface roughness of 0,4 – 0,63 µm best realized by smooth grinding. The material of the spindle is dependent of the requirements. For high operational demands the spindle should be case hardened (≈ HRC 64) or nitrogen hardened (≈ HV 8500 N/mm2). Regarding to the for bearing play adjustment necessary control of contact pattern we recommend following for using two bearings with the same size: The diameter of the first to...
Open the catalog to page 8
2.5.5. As the bearing play is now 0,01 mm bigger than the wanted movement play, remove the spindle and apply a coating of inking paste. To assess the contact pattern by the left ink impression, the coating of the inking paste has to be kept real thin. 2.5.6. Reinsert the spindle into the radial-plain-bearing and generate a contact pattern by radial and axial movements of the spindle. Remove the spindle and assess the ink impressions left. 2.5.7. If the contact pattern in the radial-plain-bearing is equally at all sliding sections, the final movement play can be set by tightening the...
Open the catalog to page 9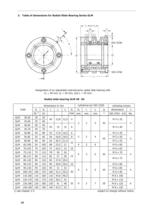
3. Table of dimensions for Radial-Slide-Bearing Series GLM Designation of an adjustable hydrodynamic radial slide bearing with Radial slide bearing GLM 40 ' 65 1) see chapter 2.3. subject to change without notice.
Open the catalog to page 10
4. Calculation of Bearing With the here presented method the designer is given the possibility to collect the for bearing definition needed but unknown values by graphic method. This method is easy and sufficient enough. 4.1. Ascertainment of load capacity (Nomogram I) The SPIETH hydrodynamic radial slide bearing Type GLM has nearly wedge shaped retain fields in defined geometric dimensions. Therefore the load bearing capacity is according to technical literature: F = C⋅η⋅u⋅b ⋅ l2 ho 2 The smallest operational lubrication gap is according to technical literature about the size of h o ≈ 2µm...
Open the catalog to page 11
and the friction loss P= 1 ⋅F⋅u 200 In the diagram of Nomogram II are two overlapping cases displayed: Case 1: heat emission at the bearing surface. At an exothermic surface A ≈ 10 ⋅ d 2 and the heat transmission number W α = 20 K ⋅ m 2 the dissipation of friction loss at the bearing surface P = α ⋅ A ⋅ ∆Tair As a result of this, the high temperature of the bearing is ∆Tair ≈ K air ⋅ P d2 ; K ⋅ m 2 whereby K air = 0,005 W In this case the high temperature will be ascertained with the diameter scale in the Nomogram II. Case 2: heat emission to the coolant At a supposed specific heat Nm c =...
Open the catalog to page 12
4.3. Viscosity of standard lubricants In the Nomogram III the dynamic viscosity η of some standard lubricants in dependency of the working temperature can be ascertained. 4.4. Standard values for bearing play The bearing play is the resulting difference of the adjusted diameter of the bearing sliding surfaces and the diameter of the shaft. In the Nomogram IV there are standard values for the bearing play, graded in dependence of the bearing size and the allowed high temperature. 4.5. Calculation examples N'gr. IV N'gr. III Nomogram I and II Reading bearing code dimensions case 1 heat...
Open the catalog to page 13All SPIETH-MASCHINENELEMENTE GmbH & Co KG catalogs and technical brochures
-
catalogue
98 Pages
-
Clamping Nuts
8 Pages
-
Radial Plain Bearings
6 Pages
-
Guide Gibs
8 Pages
-
Guide Bushings
16 Pages
-
Clamping Sets
22 Pages
-
Locknut
22 Pages
-
Introduction
11 Pages
Archived catalogs
-
Product Range
8 Pages
-
Tension Nut Type AM
8 Pages
-
Precision Locknut heavy MSW
12 Pages
-
Precision Locknut MSR/MSA
12 Pages




















